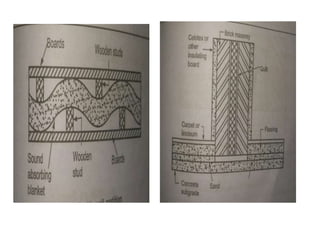
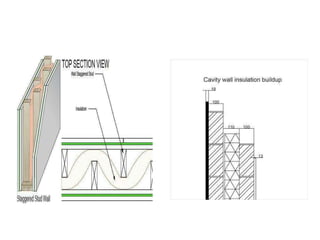
This document discusses sound insulation in buildings. It defines noise and sound insulation, and explains that sound insulation materials work to reduce transmission of sound through walls, floors, and partitions, while sound absorbers reduce reflection. General considerations for sound insulation include locating buildings away from noise sources, planning room layouts, using resilient flooring, and installing expansion joints. Common sound insulating materials are rigid materials like masonry, porous materials, and flexible porous materials like felt and mineral wool. Vertical barriers like walls and partitions can be insulated using techniques like cavity wall construction, double walls, and porous partition walls. Noise control in residential buildings involves siting away from noise, using landscaping, limiting hard surfaces, false ceilings, isol