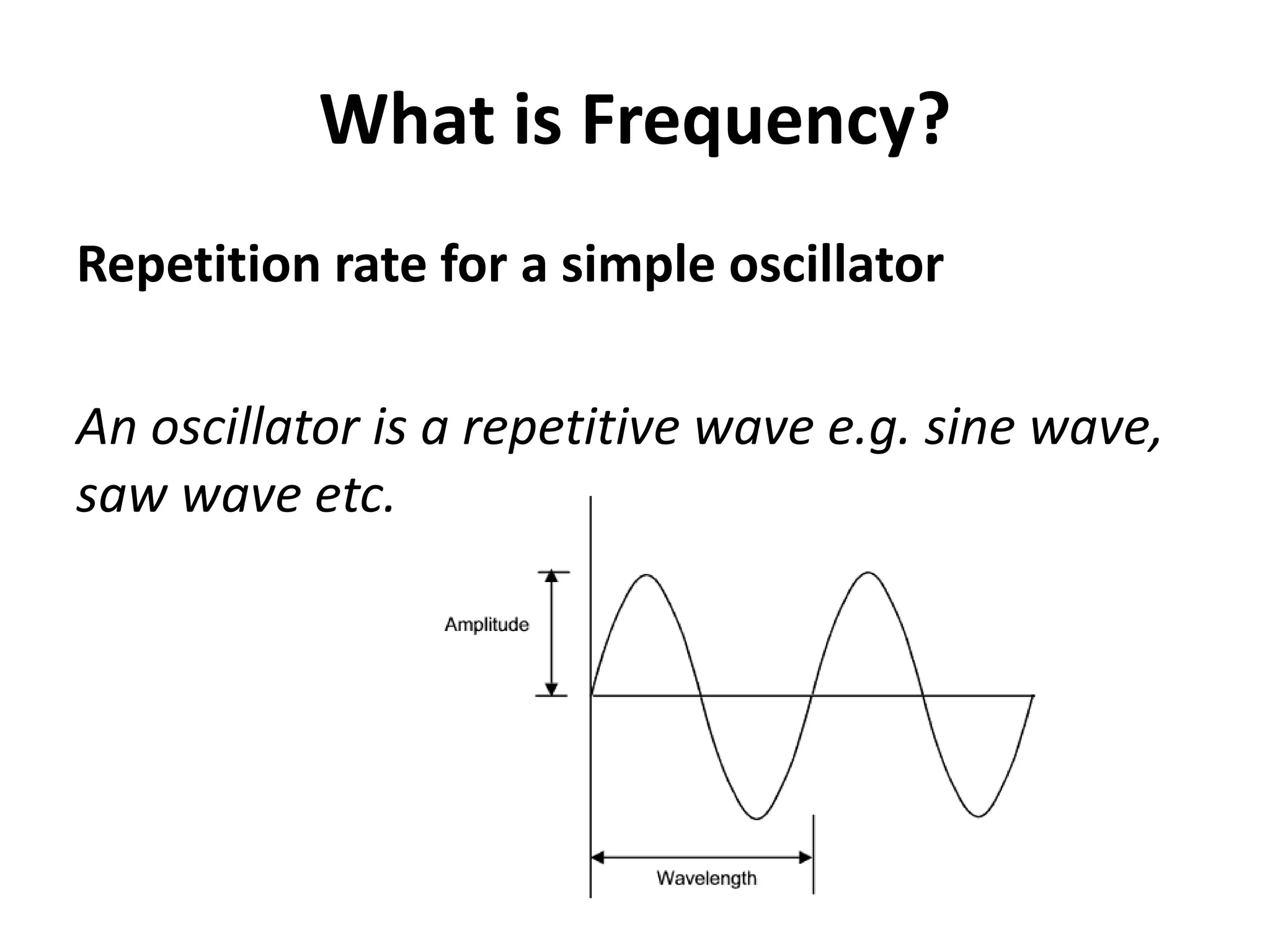
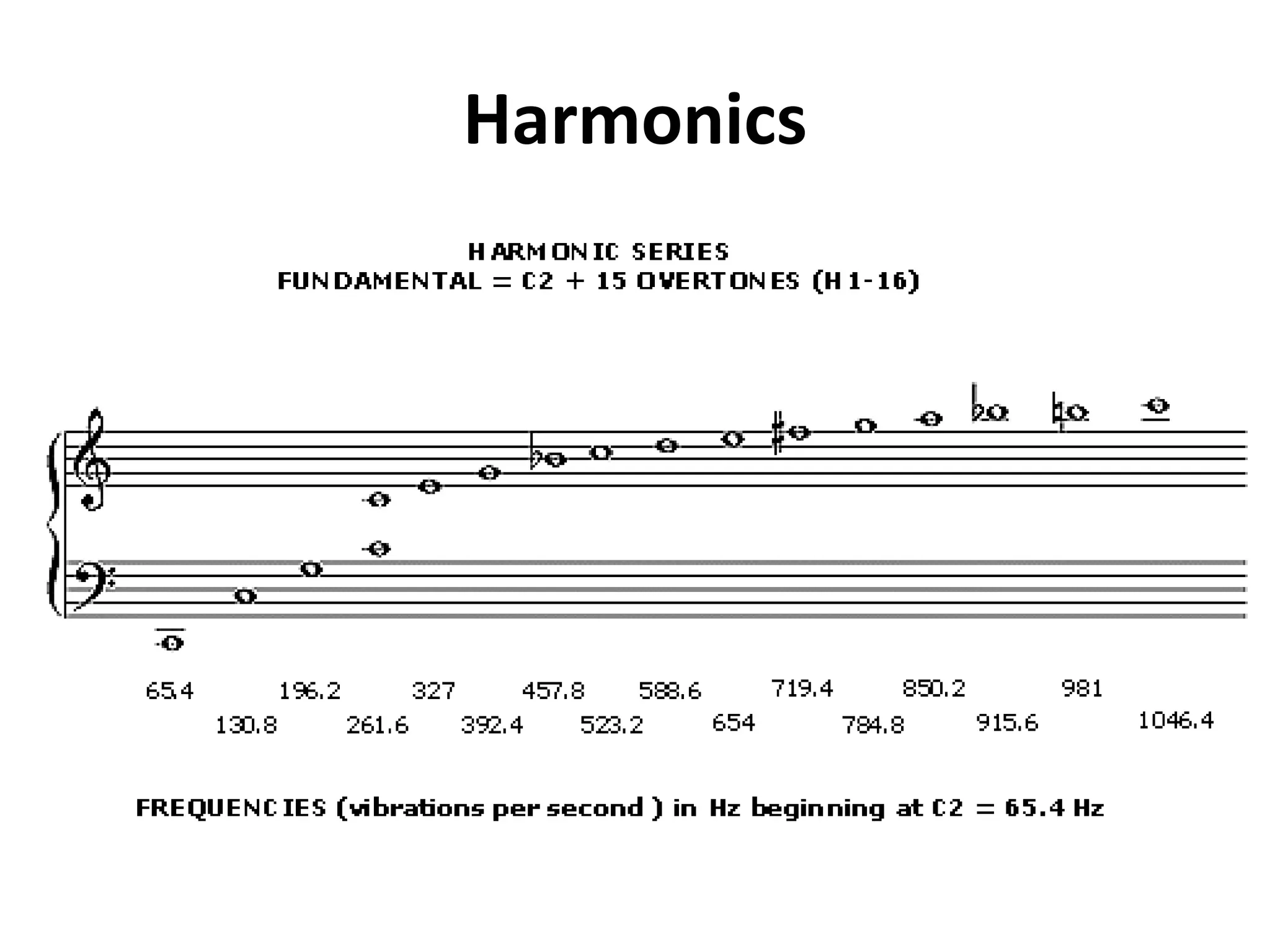
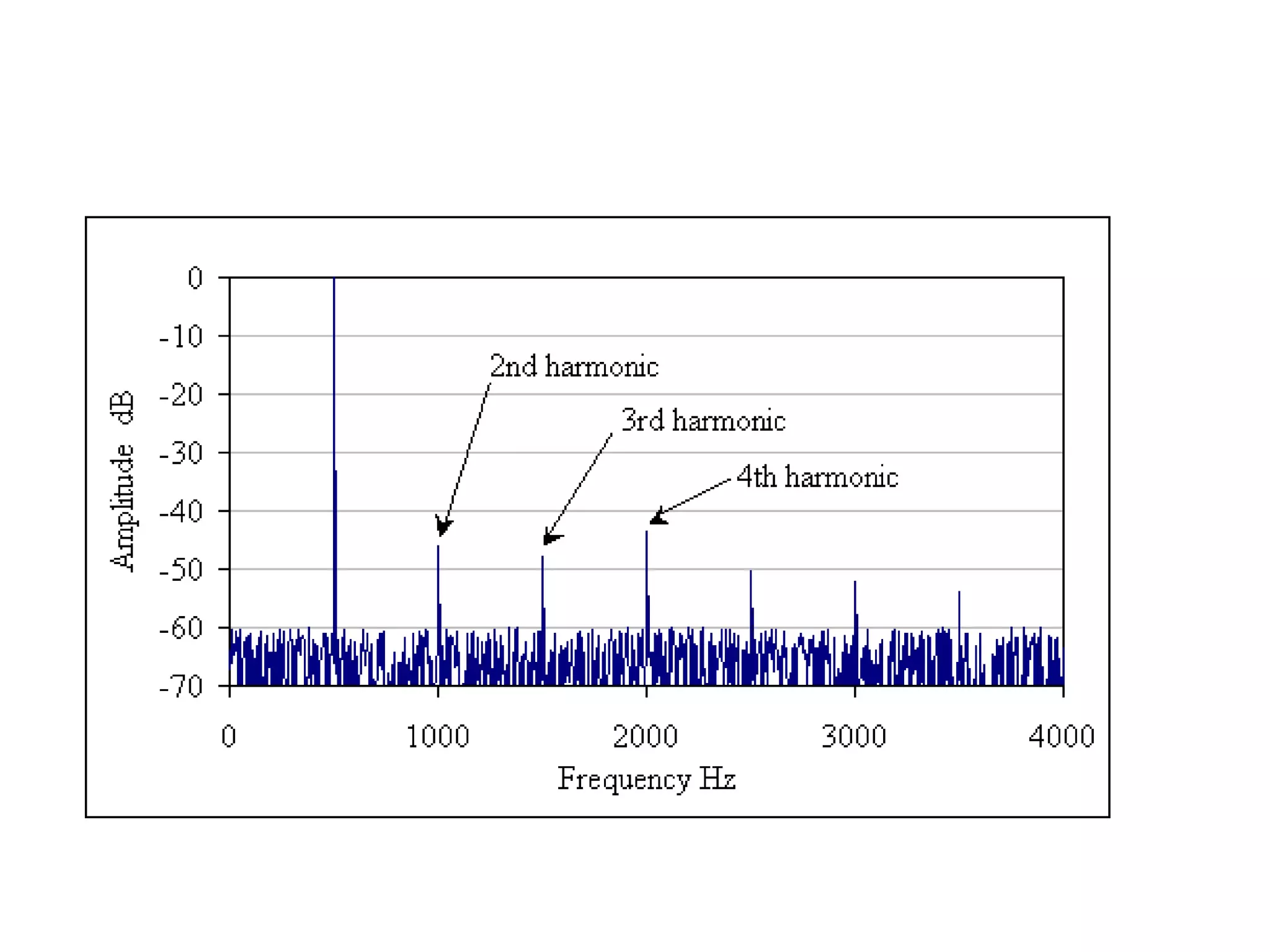
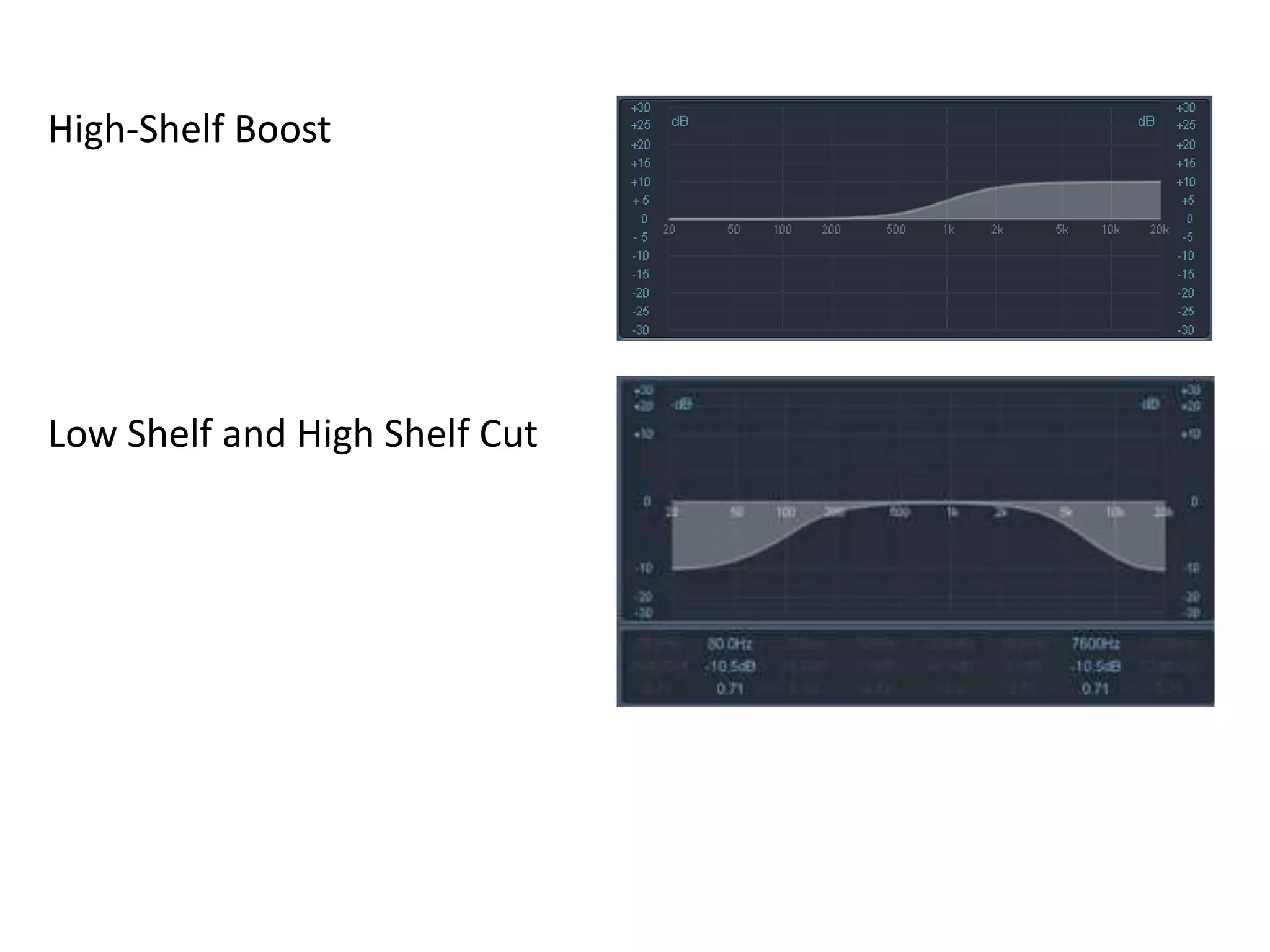
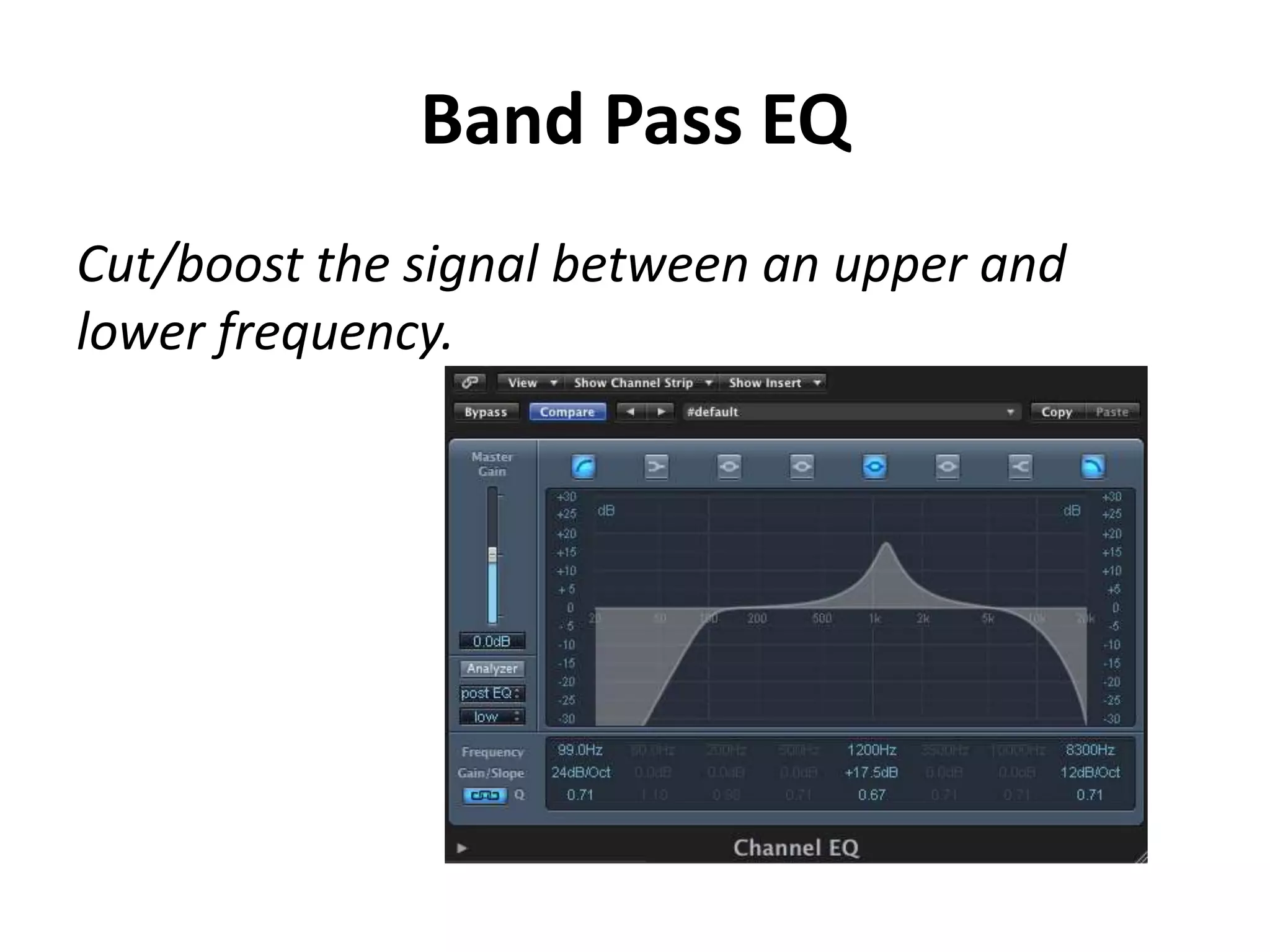
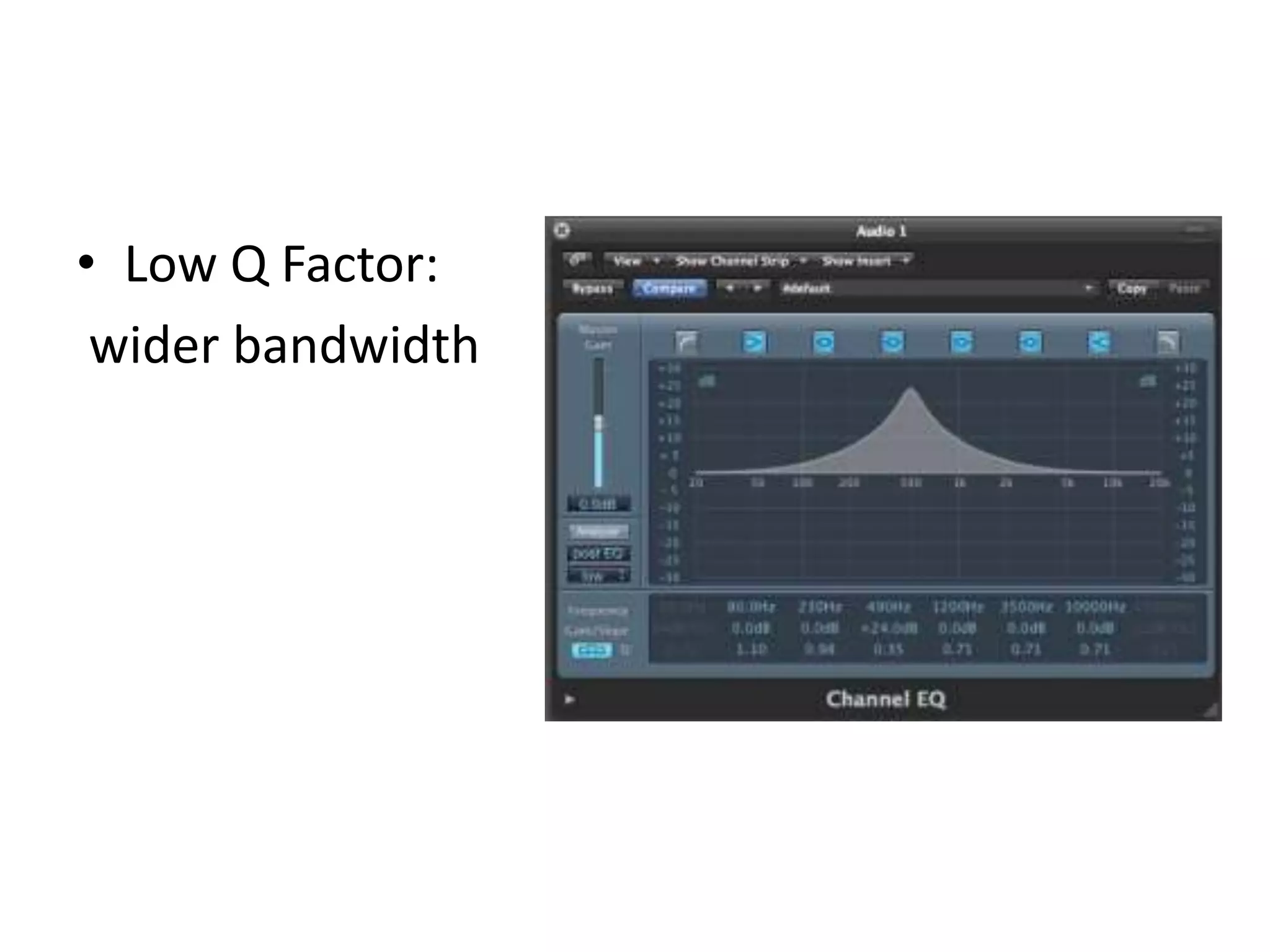
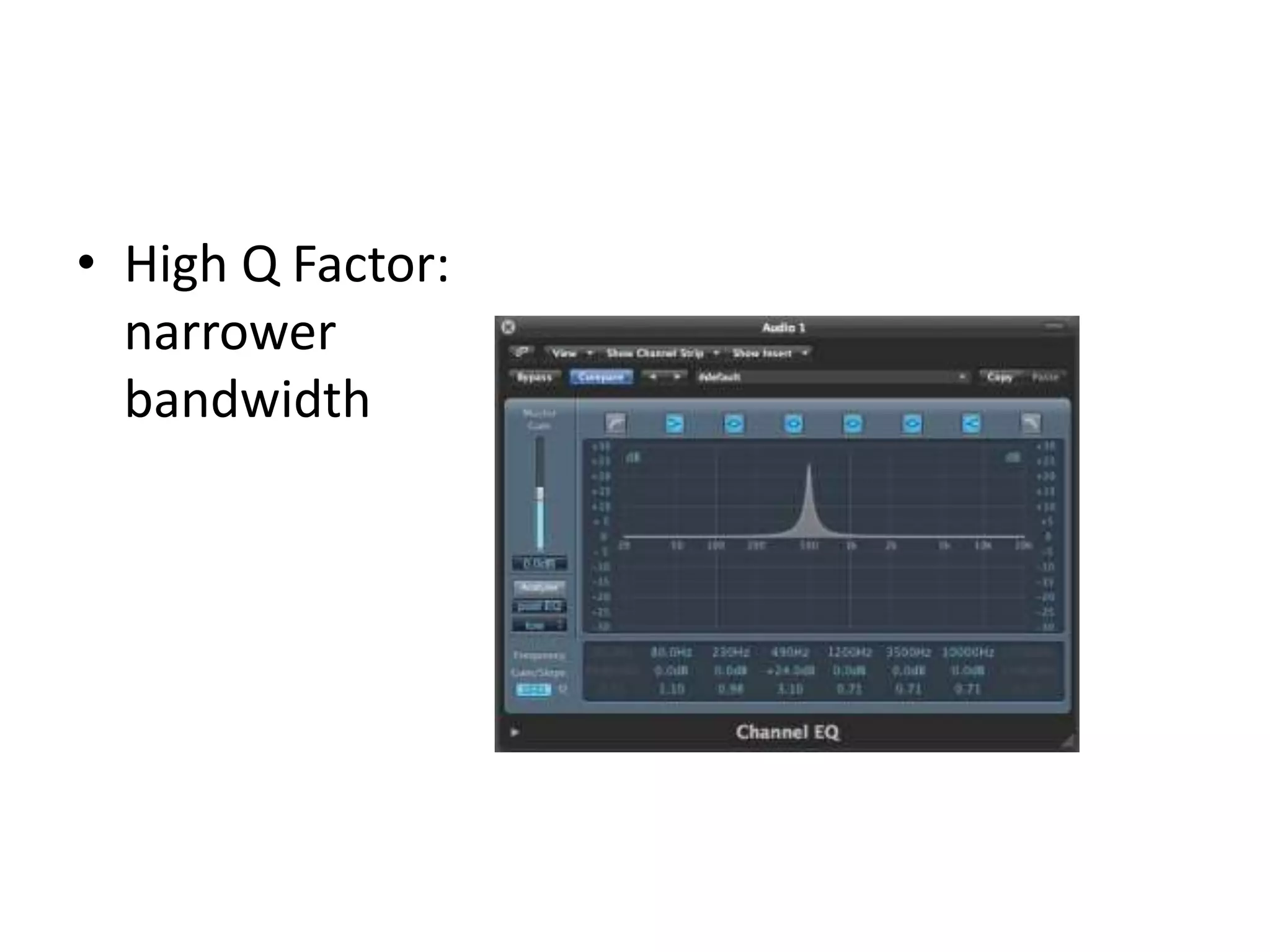
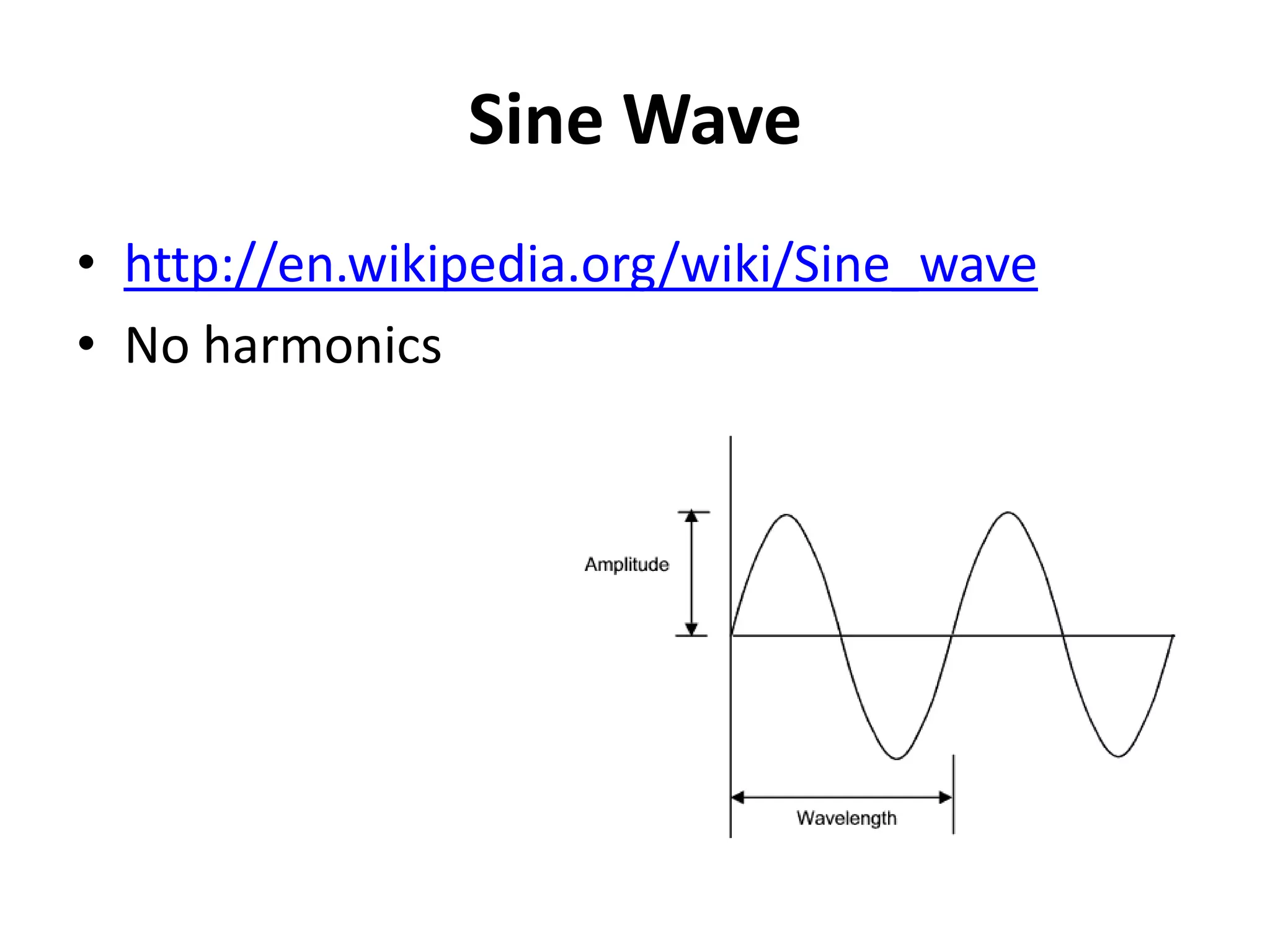
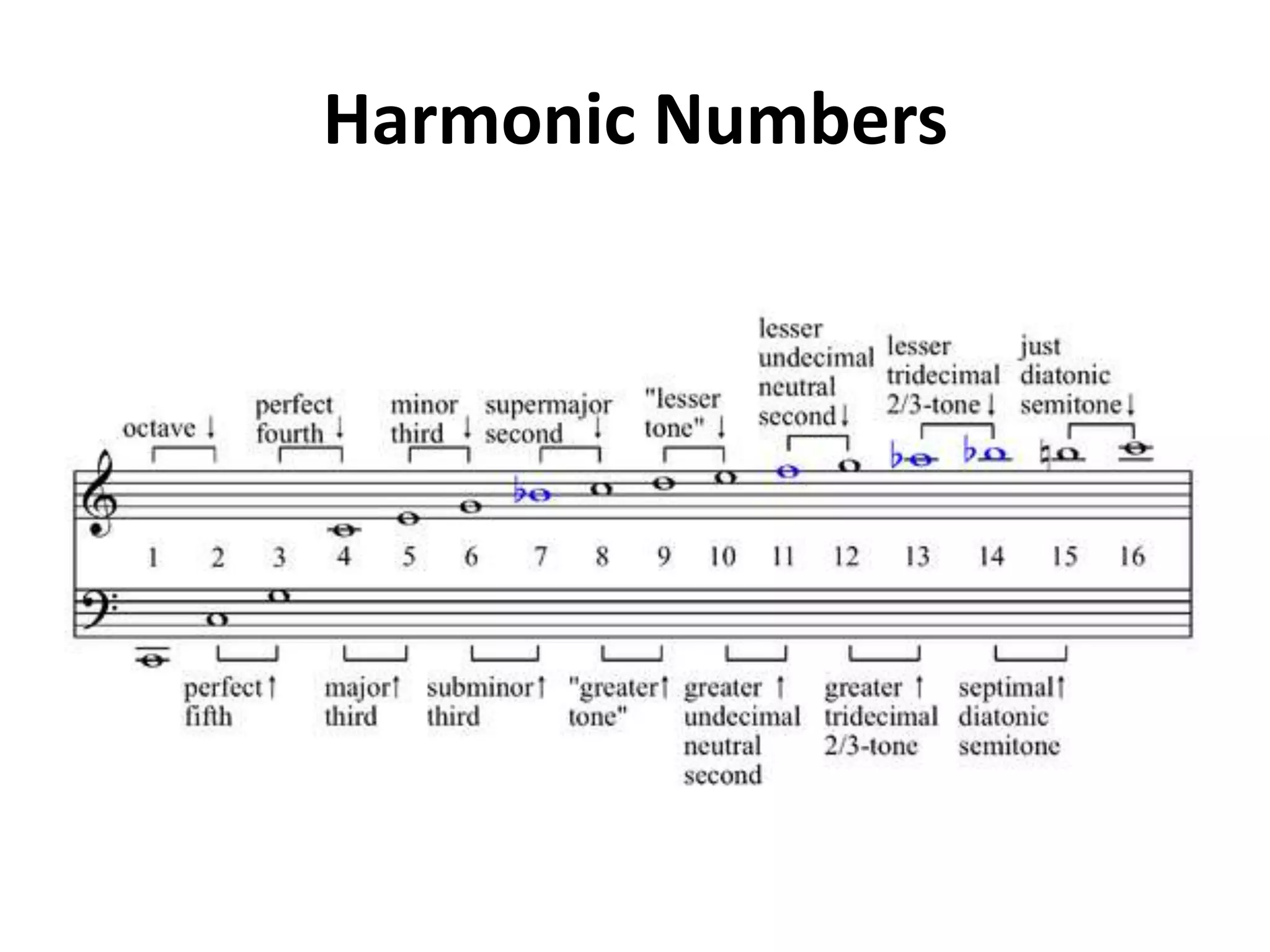
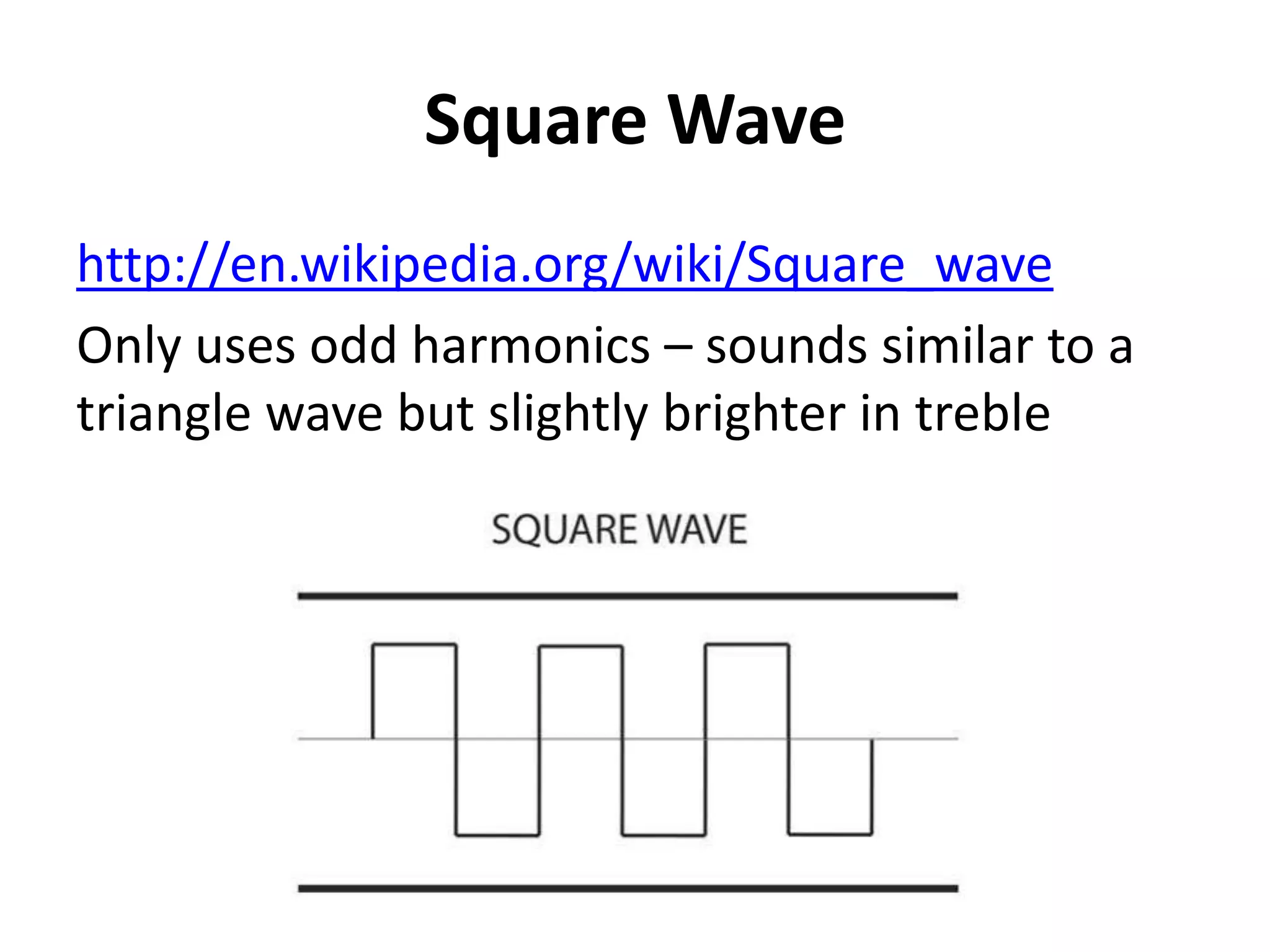
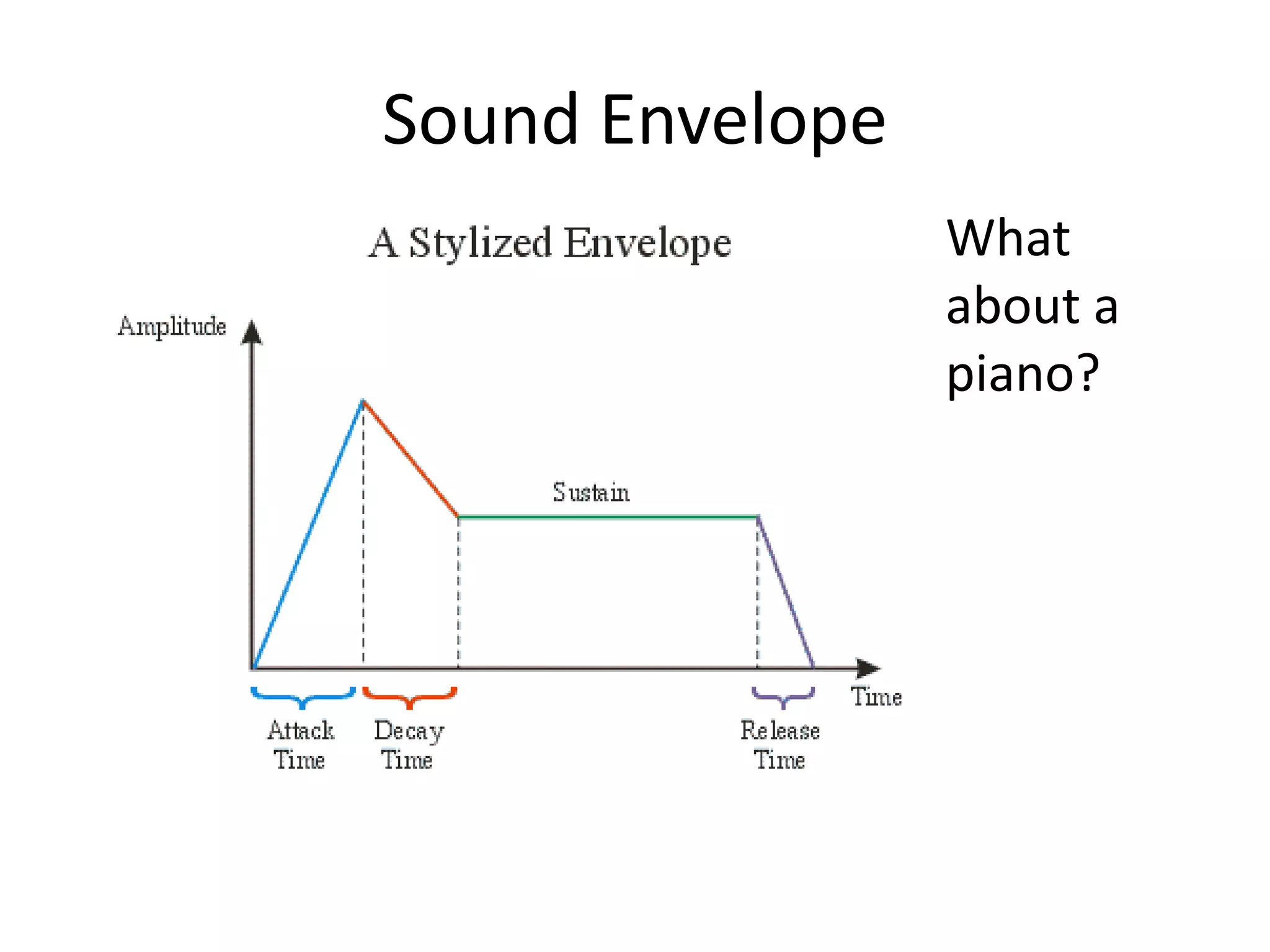
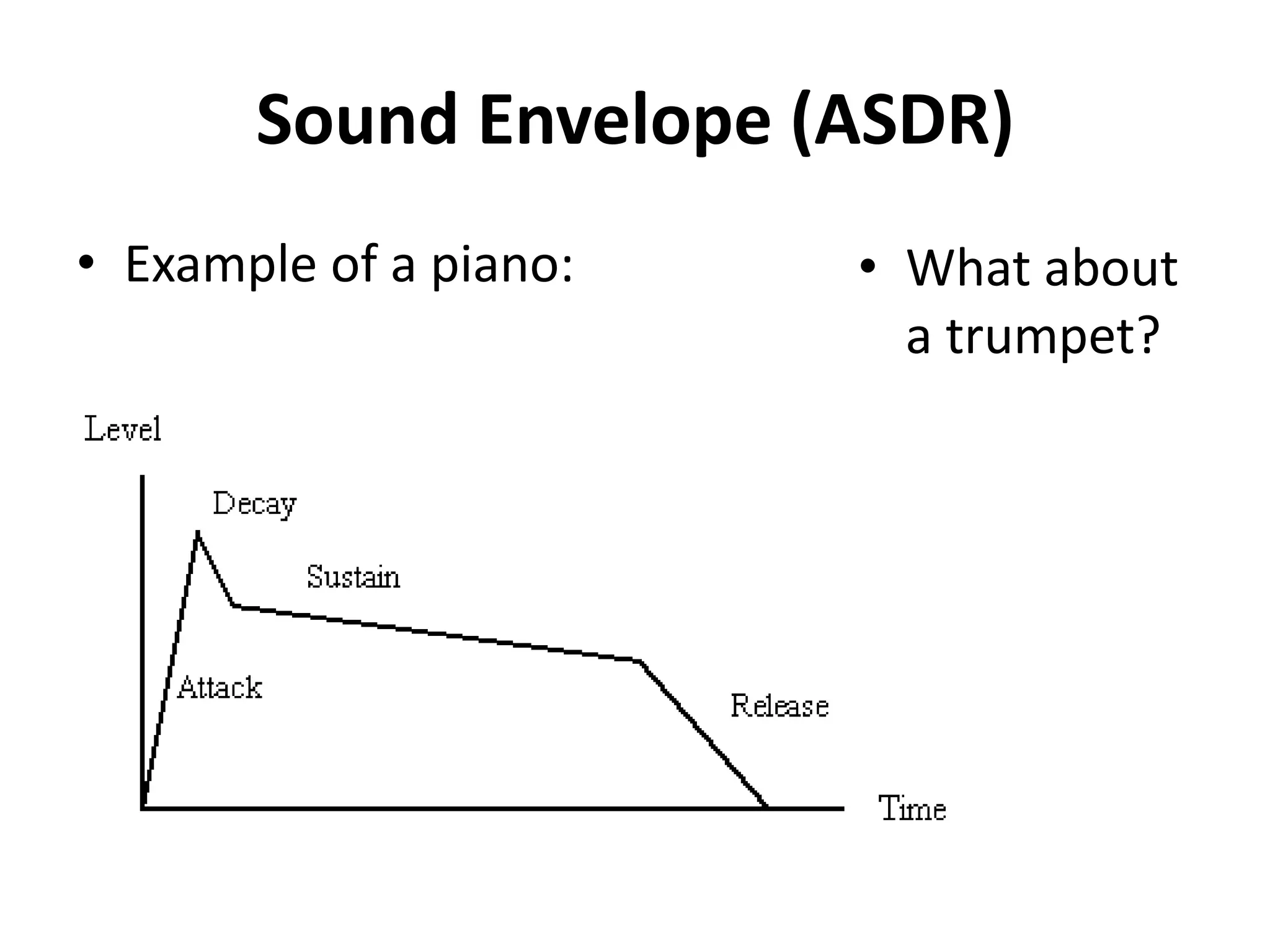
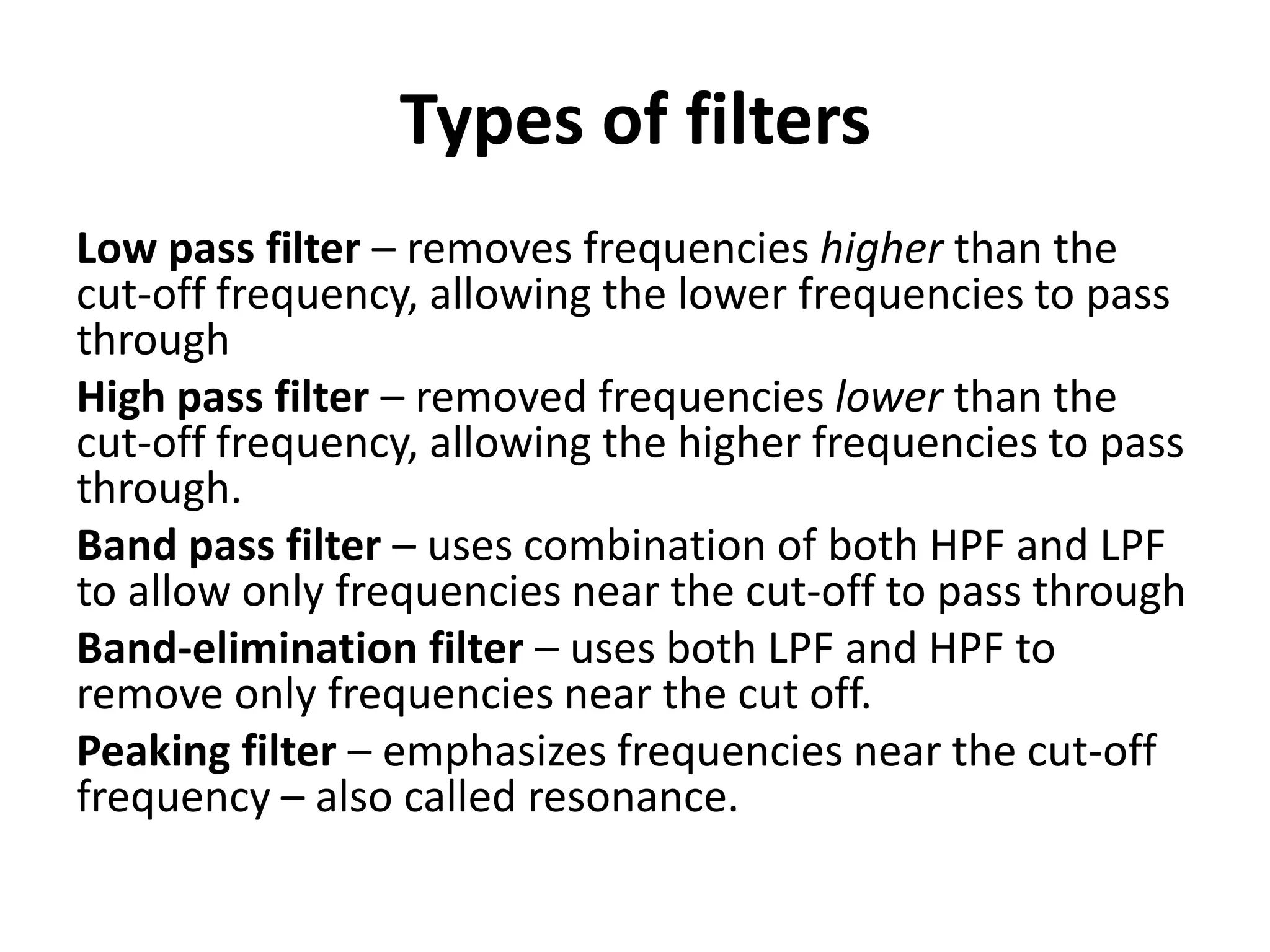
This document discusses concepts related to music technology including sound, pitch, frequency, harmonics, equalization (EQ), synthesis, oscillators, sound envelopes, and filters. It explains that sound is pressure disturbances propagating through a medium, usually air, while pitch is the repetition rate of a sound determined by its fundamental frequency. It describes how EQ is used to boost or cut certain frequencies to alter tonal qualities. Synthesis and sound design are also covered, noting how oscillators, envelopes, and filters can be used to manipulate raw waveforms and create customized sounds.