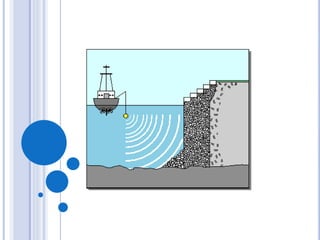
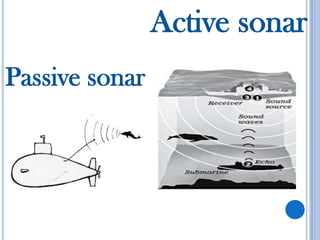
SONAR is used to determine ocean depth and locate underwater objects. There are two main types of SONAR - active and passive. Active SONAR emits sound pulses and measures their reflection to determine distance and direction. Passive SONAR listens without transmitting. SONAR is used to detect submarines, map underwater features, calculate depth, and locate sunken ships and fish. To determine ocean depth using SONAR, high frequency sound vibrations called ultrasonic vibrations are transmitted into the water. The time for the vibrations to return is used to calculate the distance of the reflecting surface below.