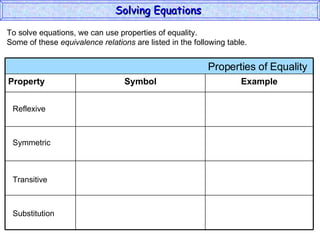
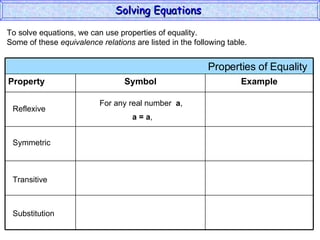
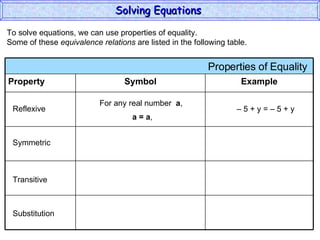
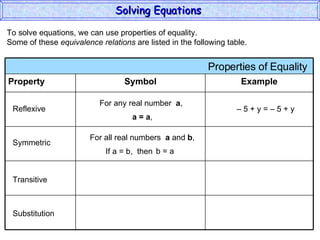
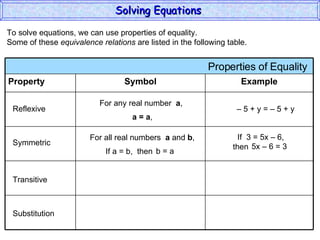
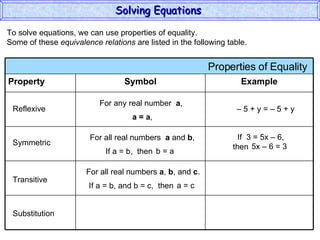
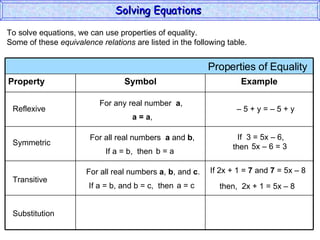
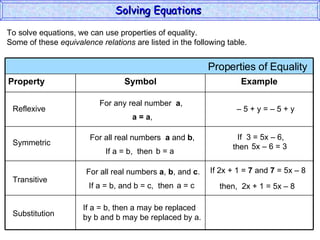
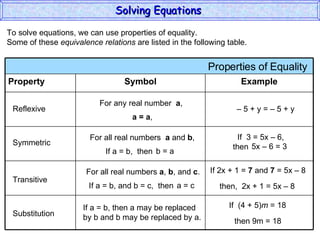
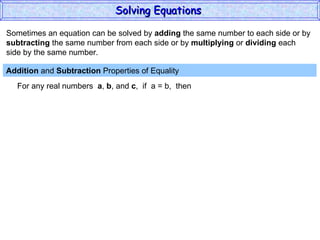
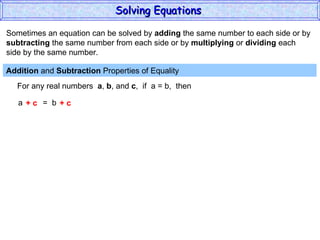
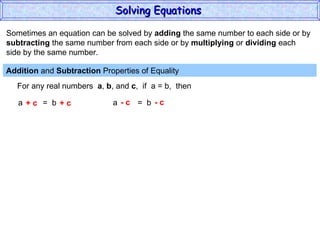
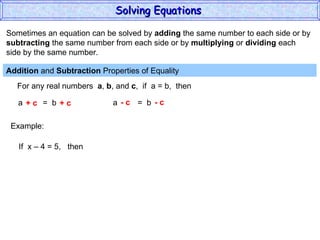
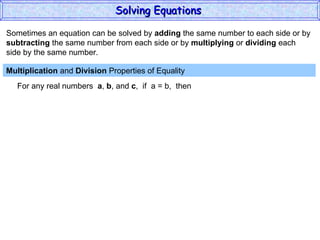
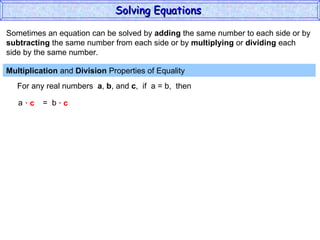
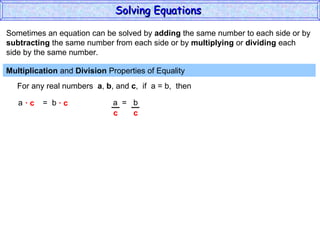
The document discusses solving equations. It defines key terms like open sentence and equation. It explains that an open sentence with variables is neither true nor false until the variables are replaced with numbers, with each valid replacement called a solution. It outlines properties of equality like reflexive, symmetric, and transitive properties that can be used to solve equations, such as adding or subtracting the same number to both sides.