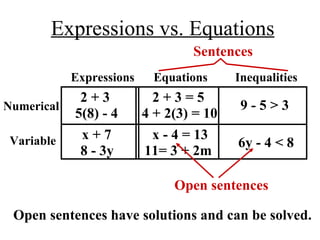
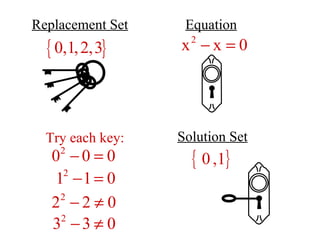
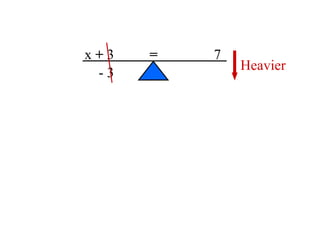
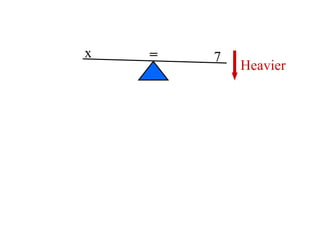
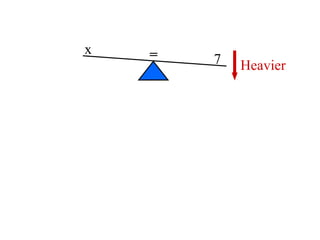
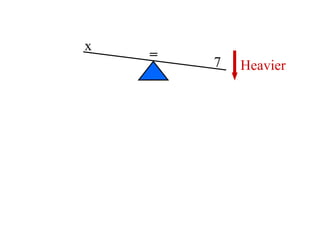
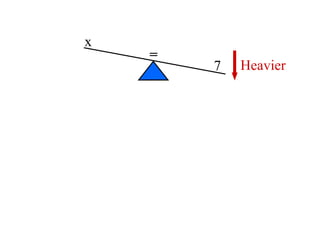
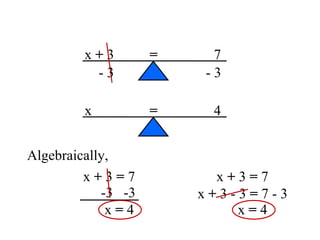
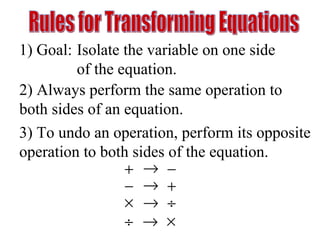
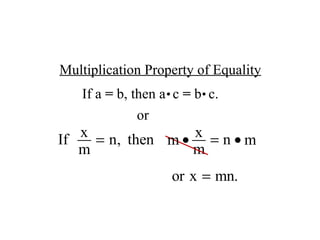The document discusses solving equations over replacement sets. It provides definitions of key terms like expressions, equations, inequalities, and open sentences. It then gives examples of identifying expressions, equations, inequalities, and whether sentences are true, false, or open. The document also covers properties of equality and strategies for solving equations, like isolating the variable.