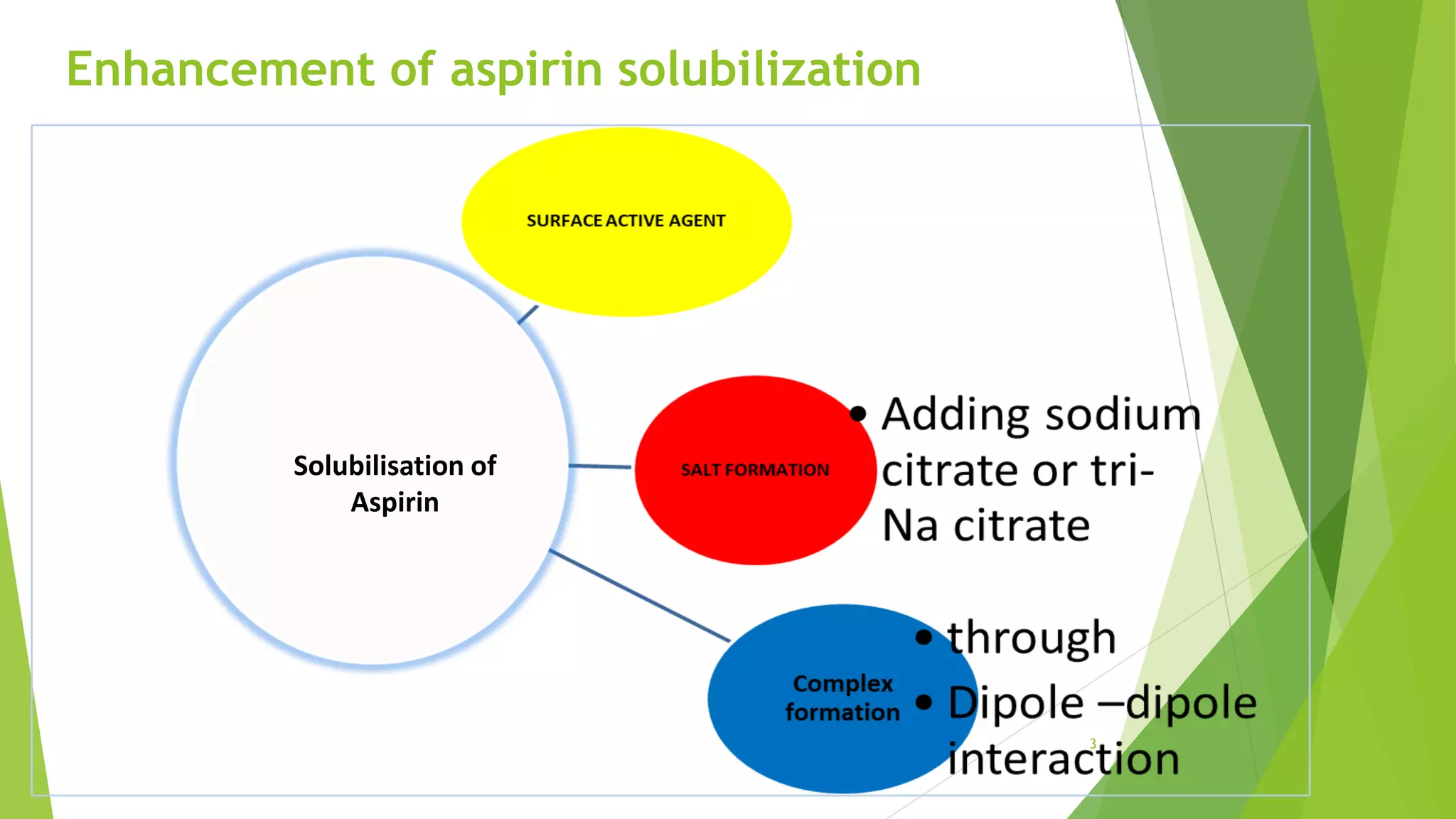
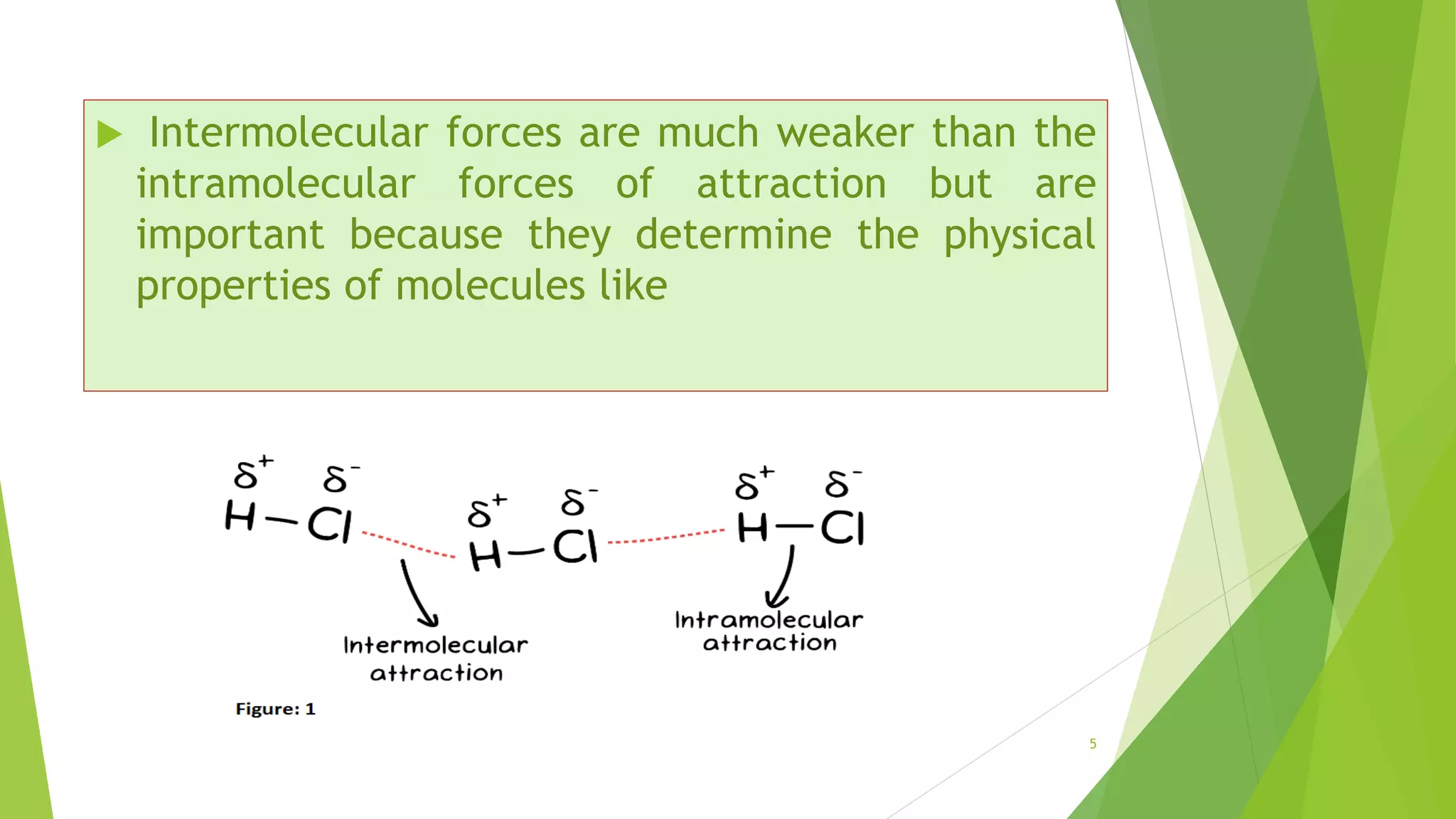
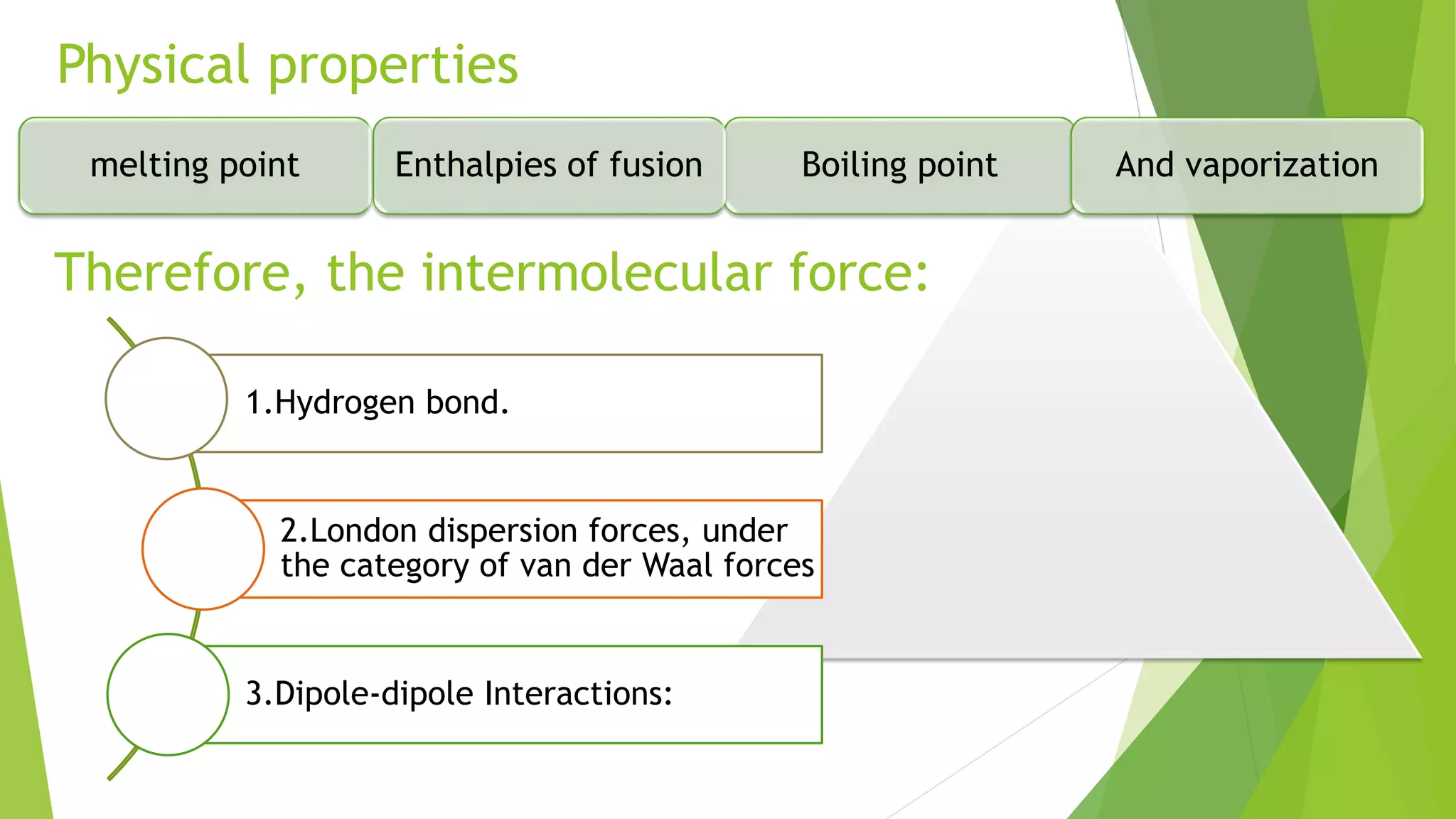
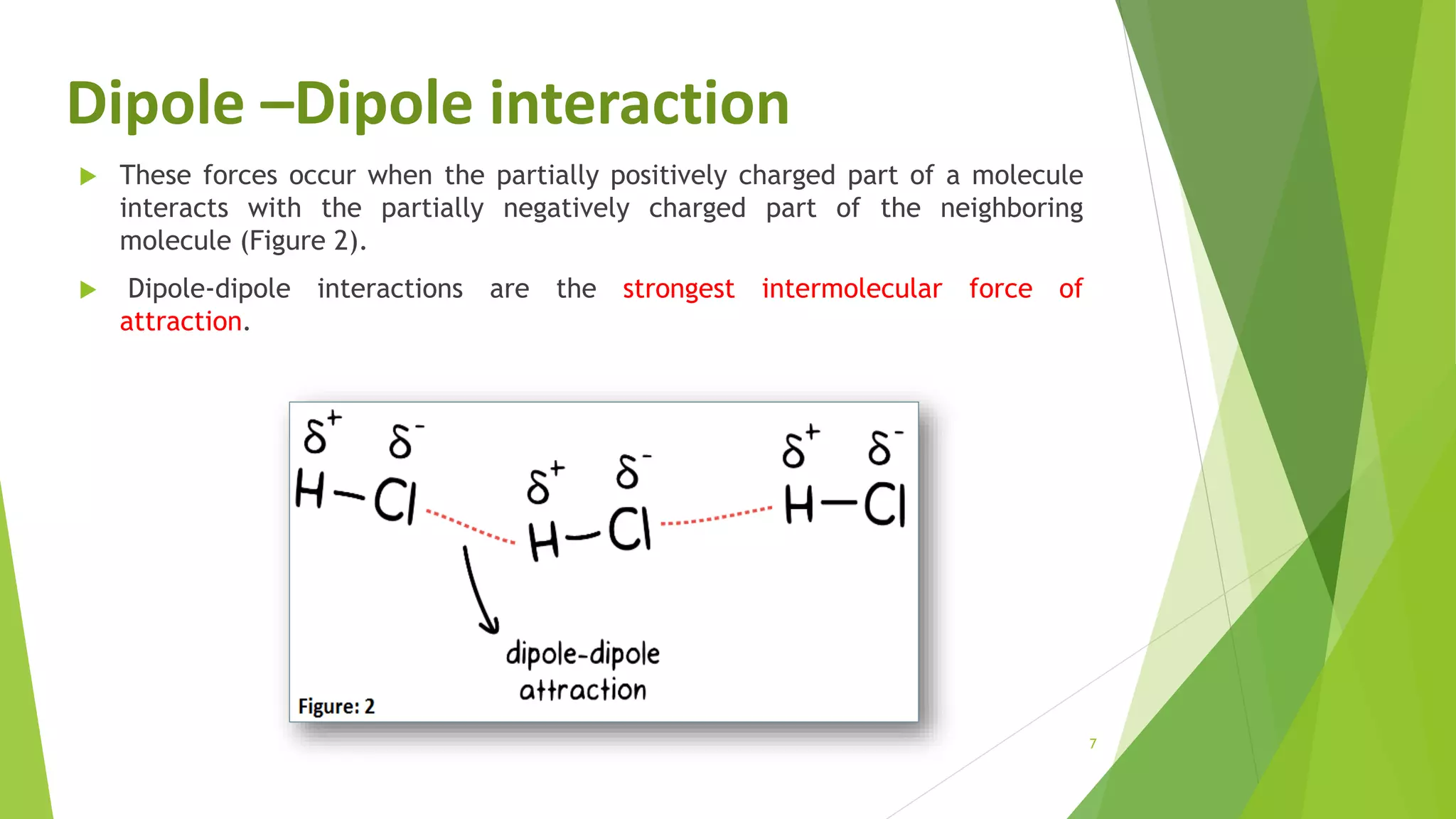
The document discusses the solubilization of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) and methods to enhance its solubility, such as using effervescent formulations with sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. It details an experimental method involving the addition of aspirin to distilled water, followed by filtration and titration with NaOH to determine the percent dissolved. Additionally, it explains intermolecular forces, particularly dipole-dipole interactions, which influence the physical properties of aspirin solutions.