The document defines and describes various three-dimensional geometric shapes:
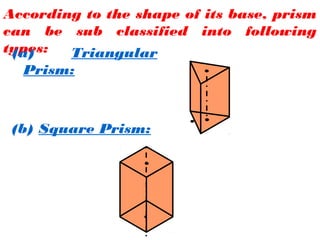
- Prisms and pyramids are defined as polyhedra having two bases joined by rectangles or triangles. They can be classified by the shape of their base.
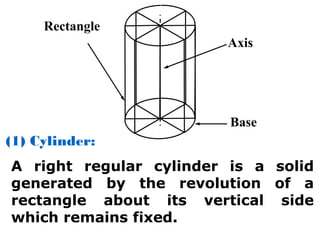
- Solids of revolution are generated by revolving a two-dimensional shape around a fixed line, and include cylinders, cones, spheres and other shapes.
- Key terms used for projections of solids are also defined, such as axis, apex, generator, frustum and truncated solids.
- Examples are given of different solids with specifications and step-by-step workings to draw their projections in different orientations.