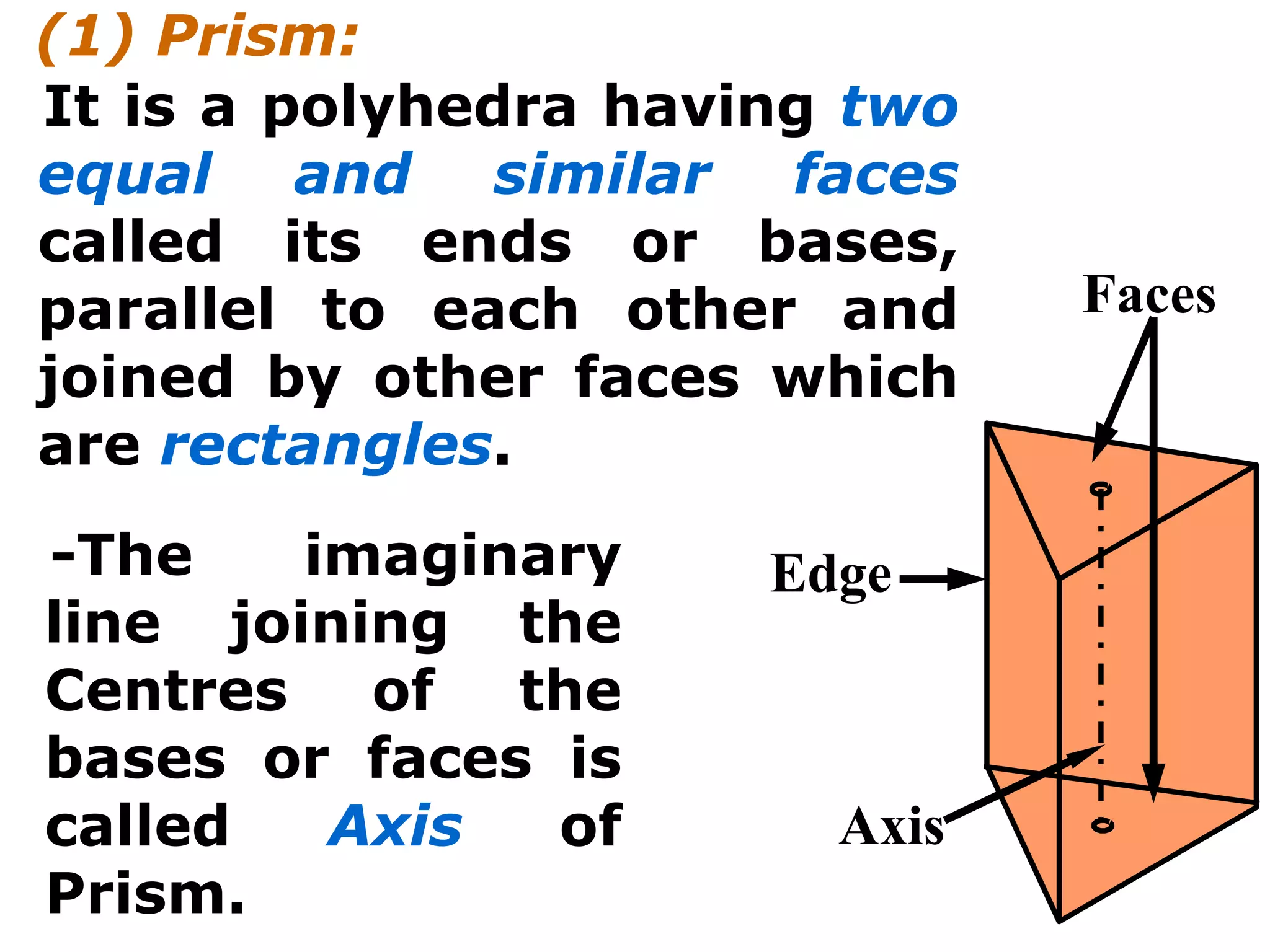
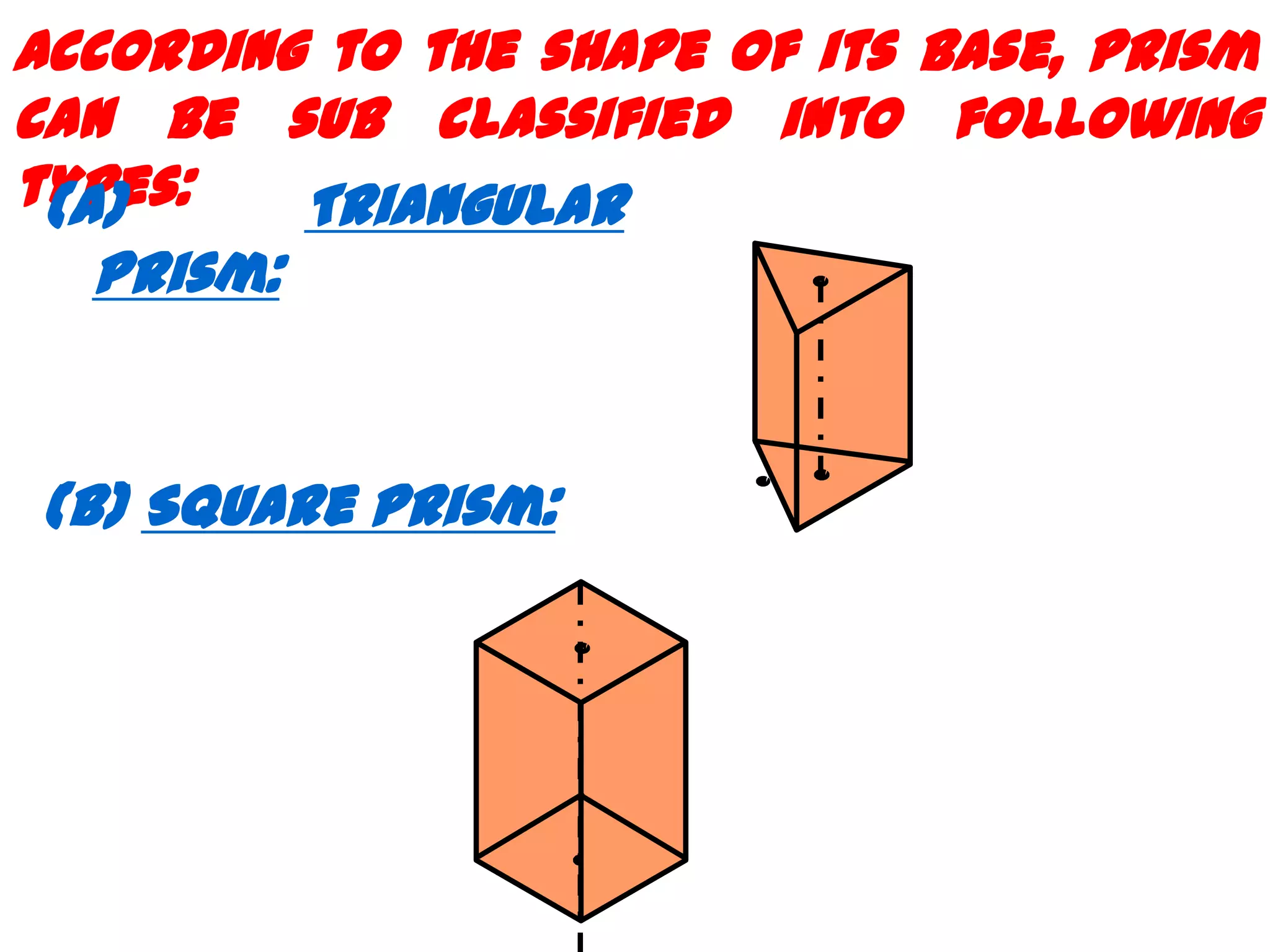
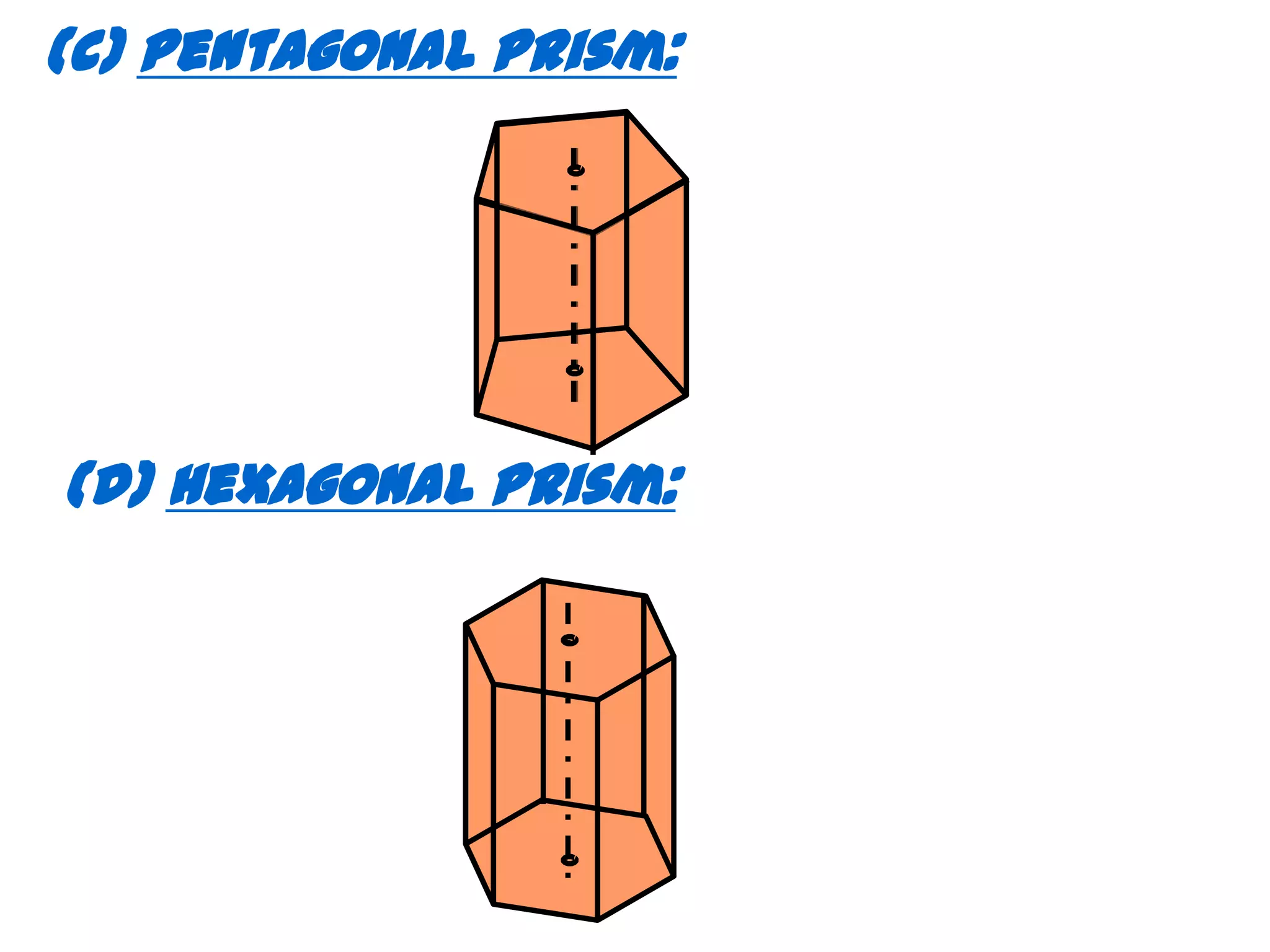
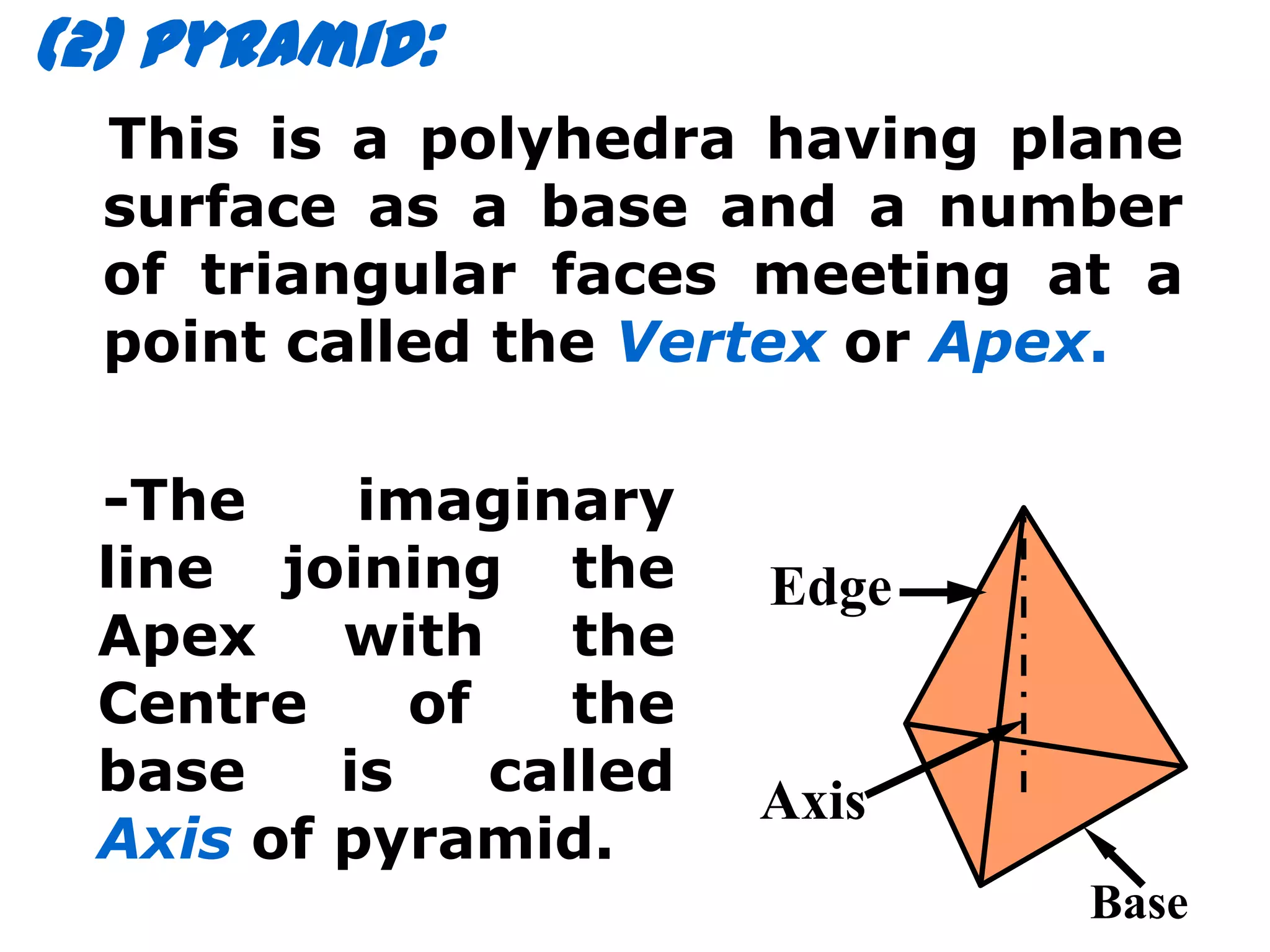
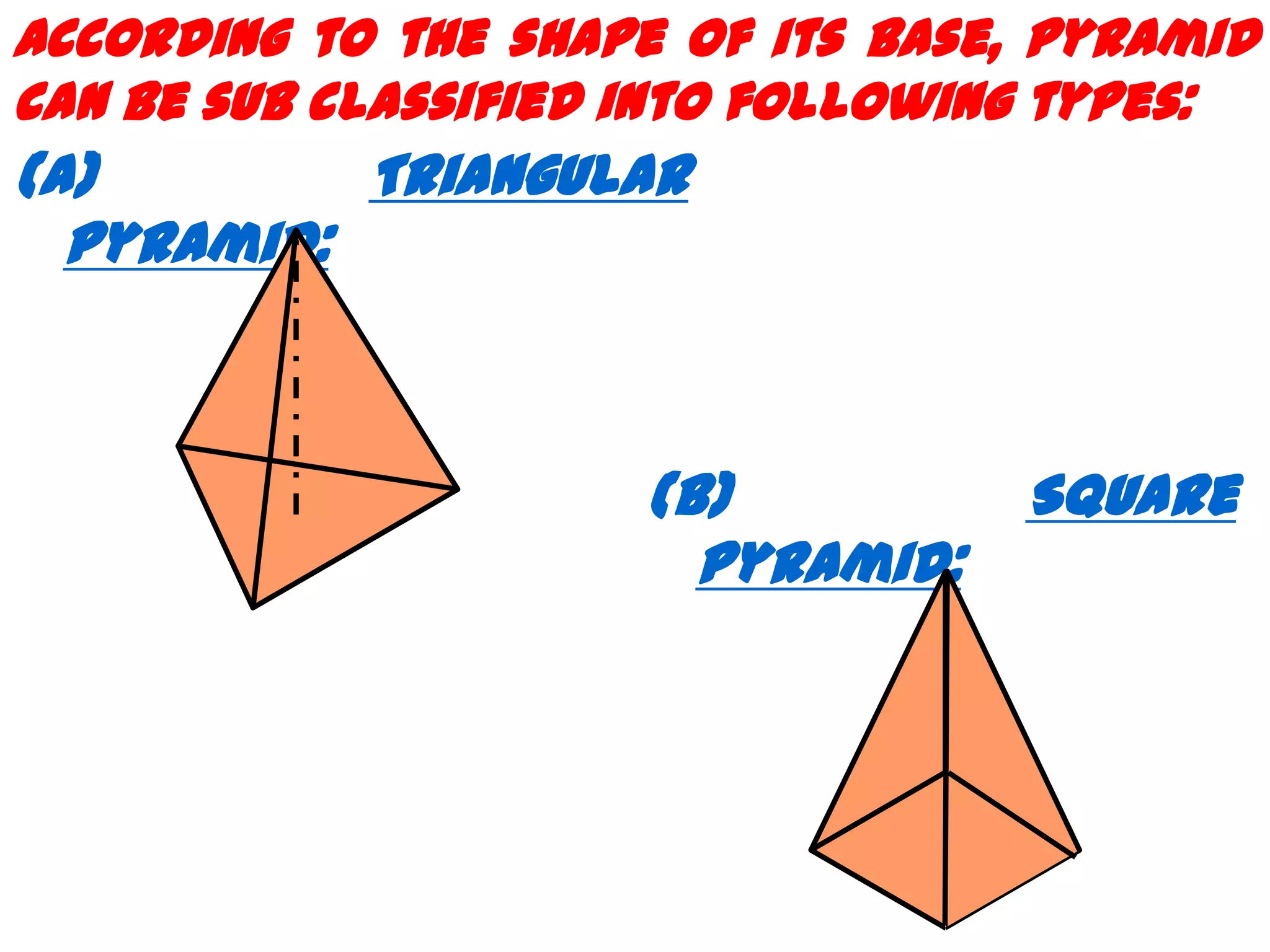
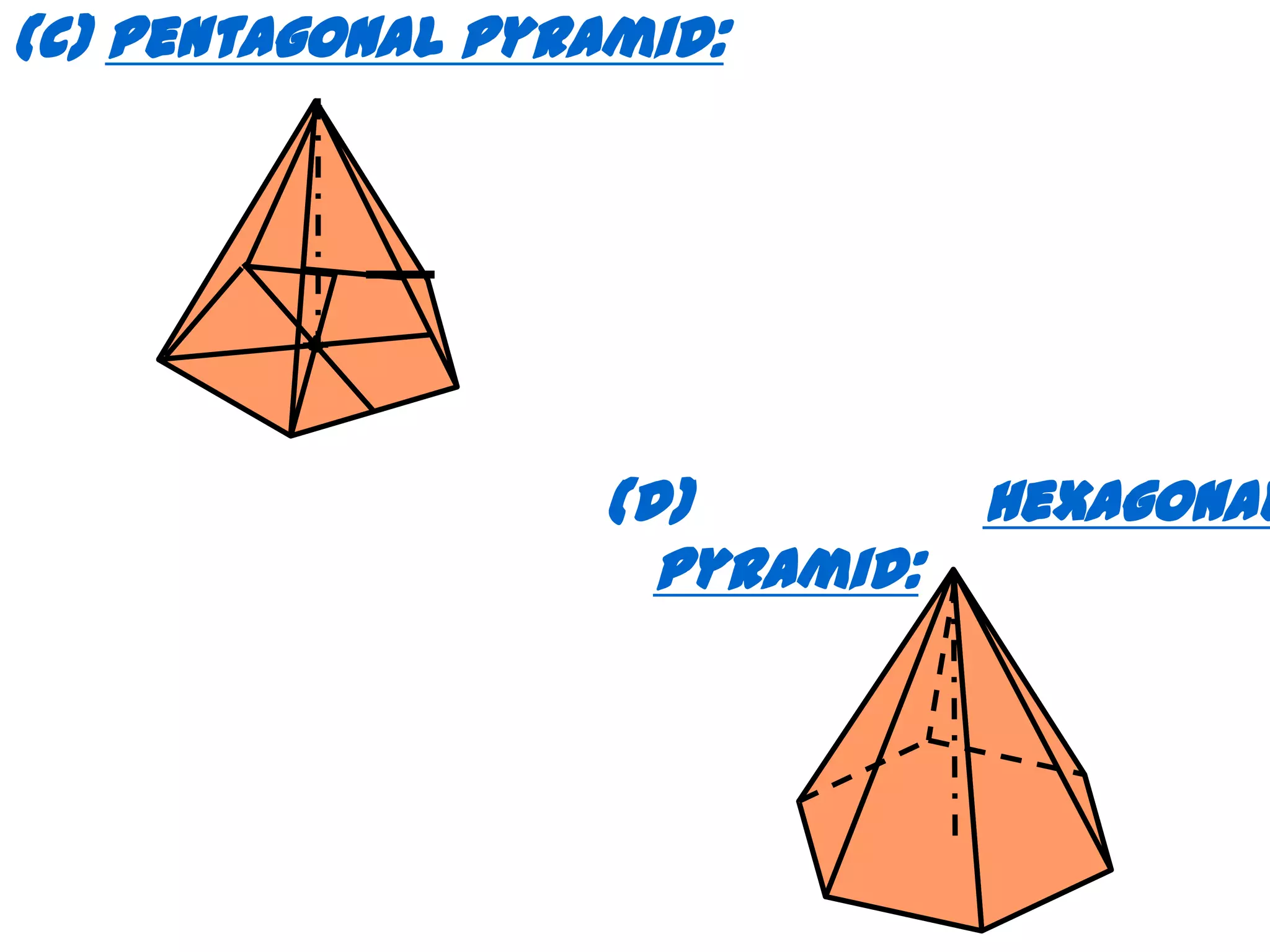
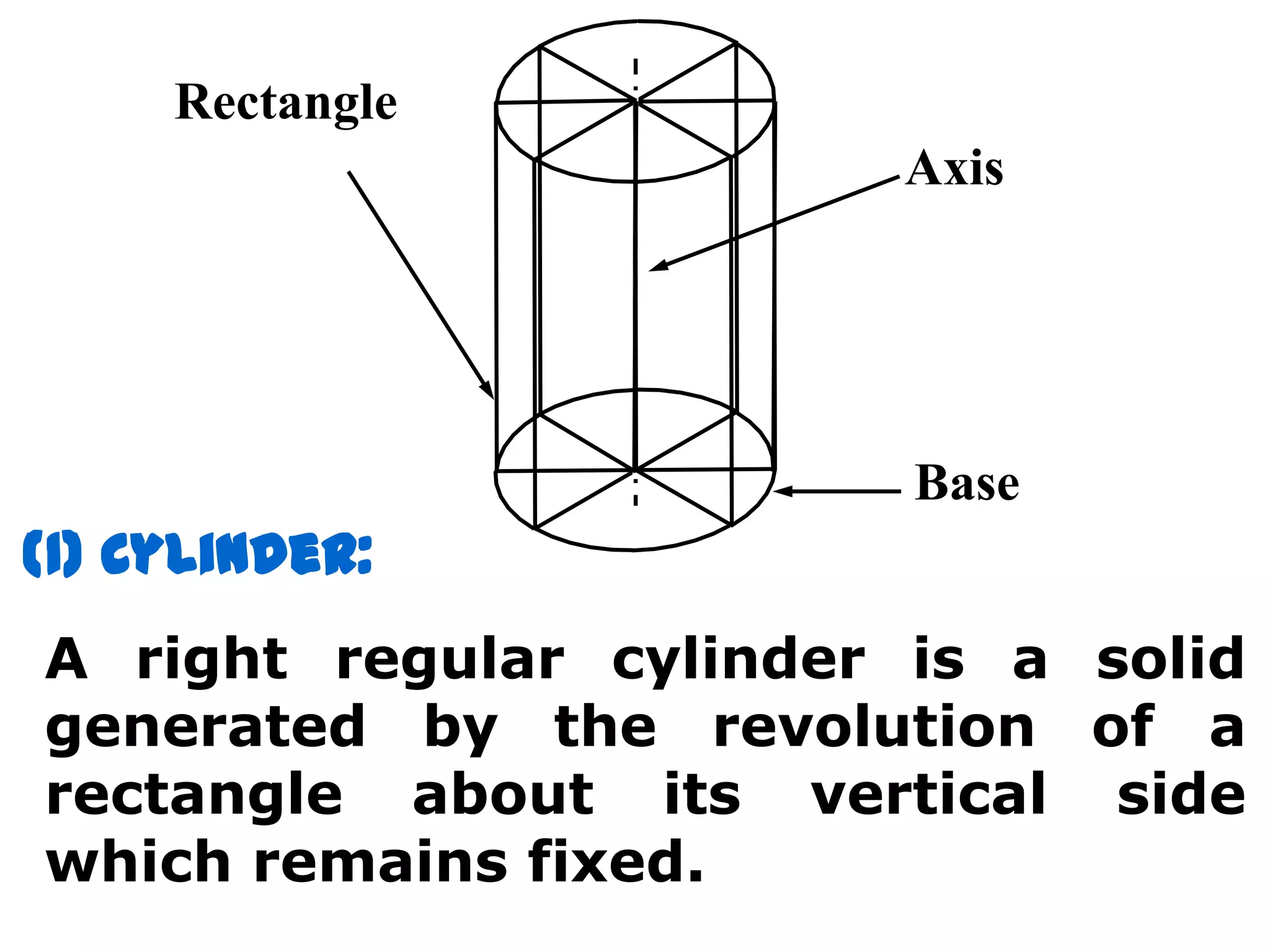
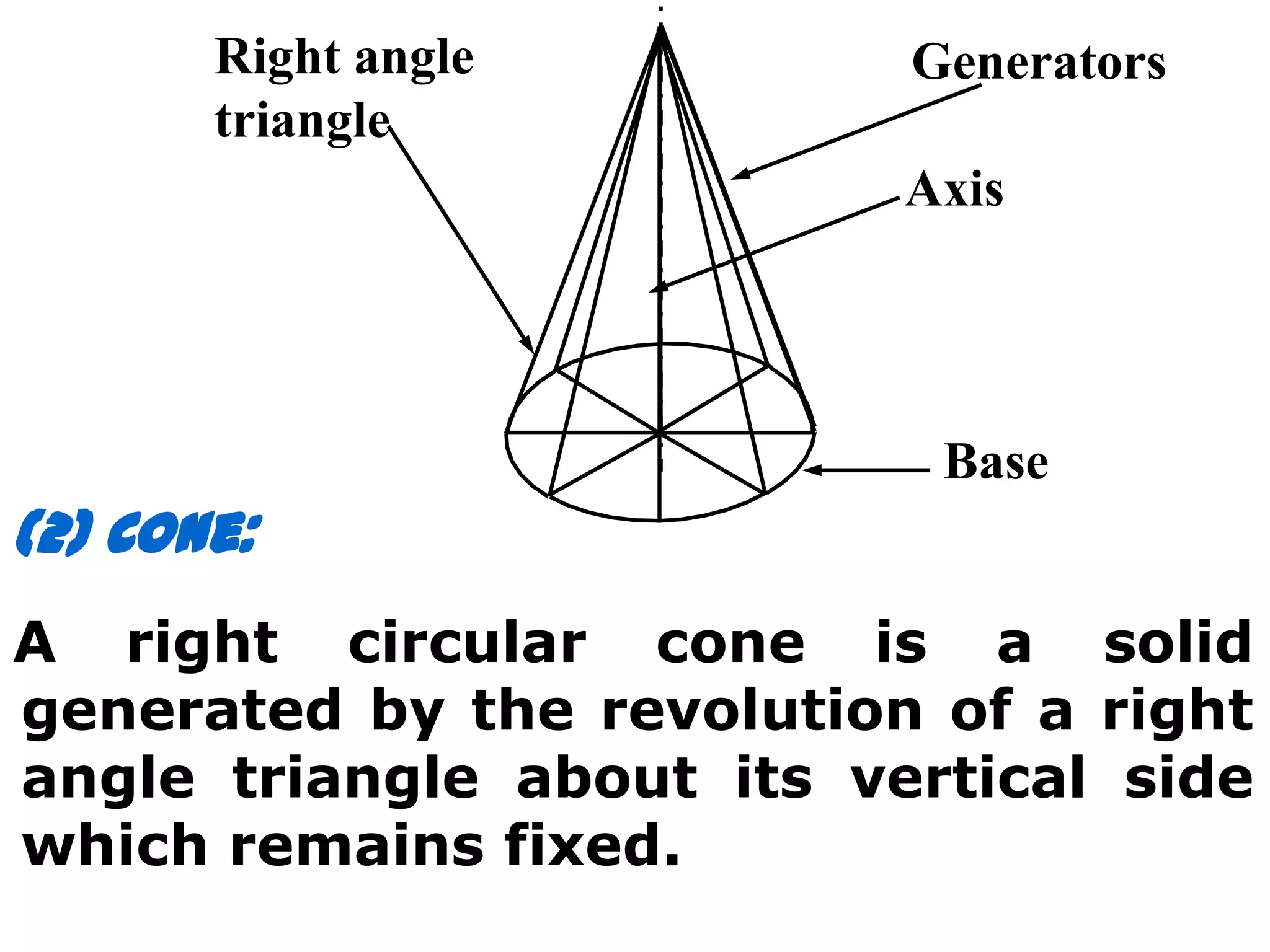
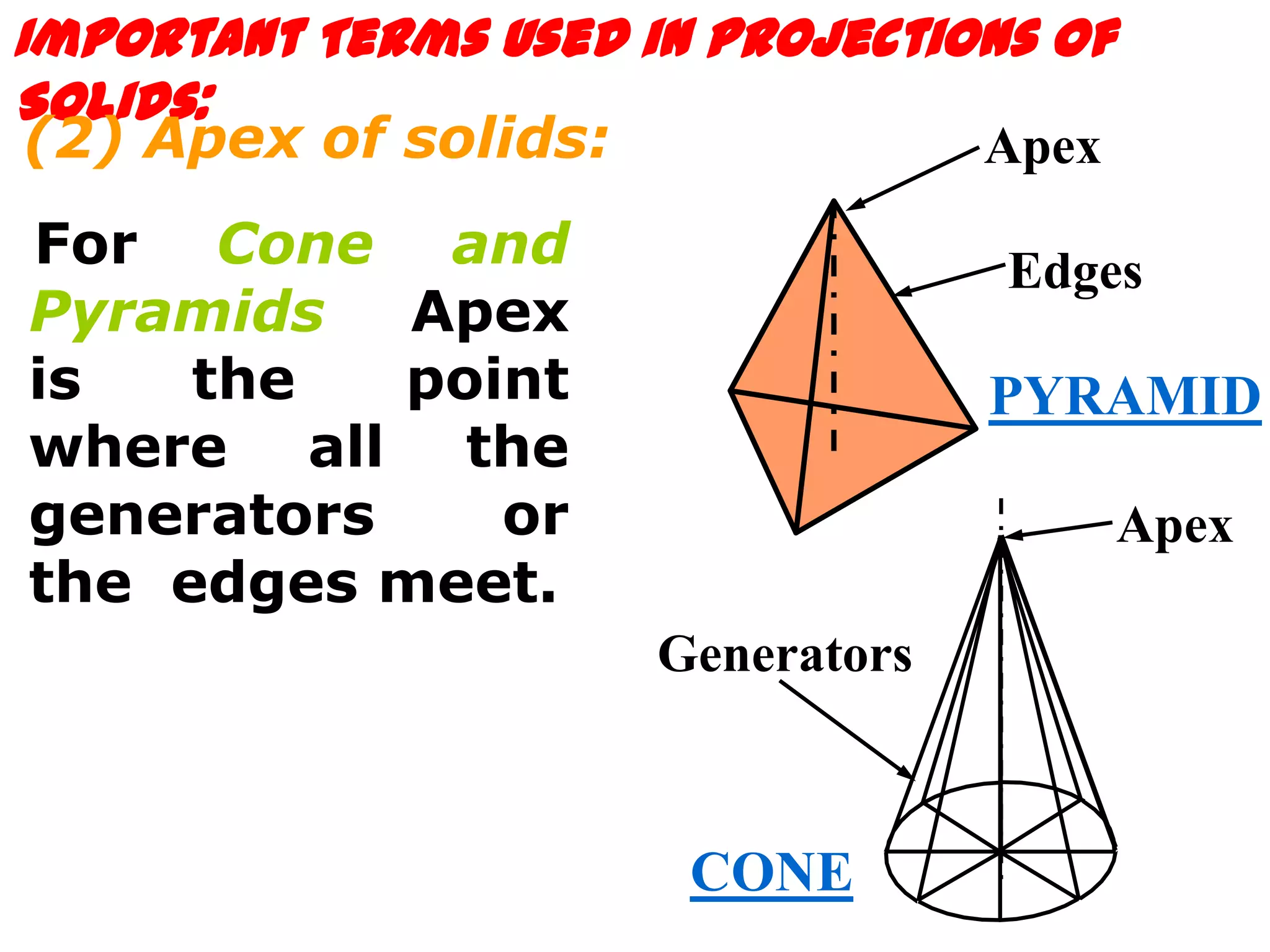
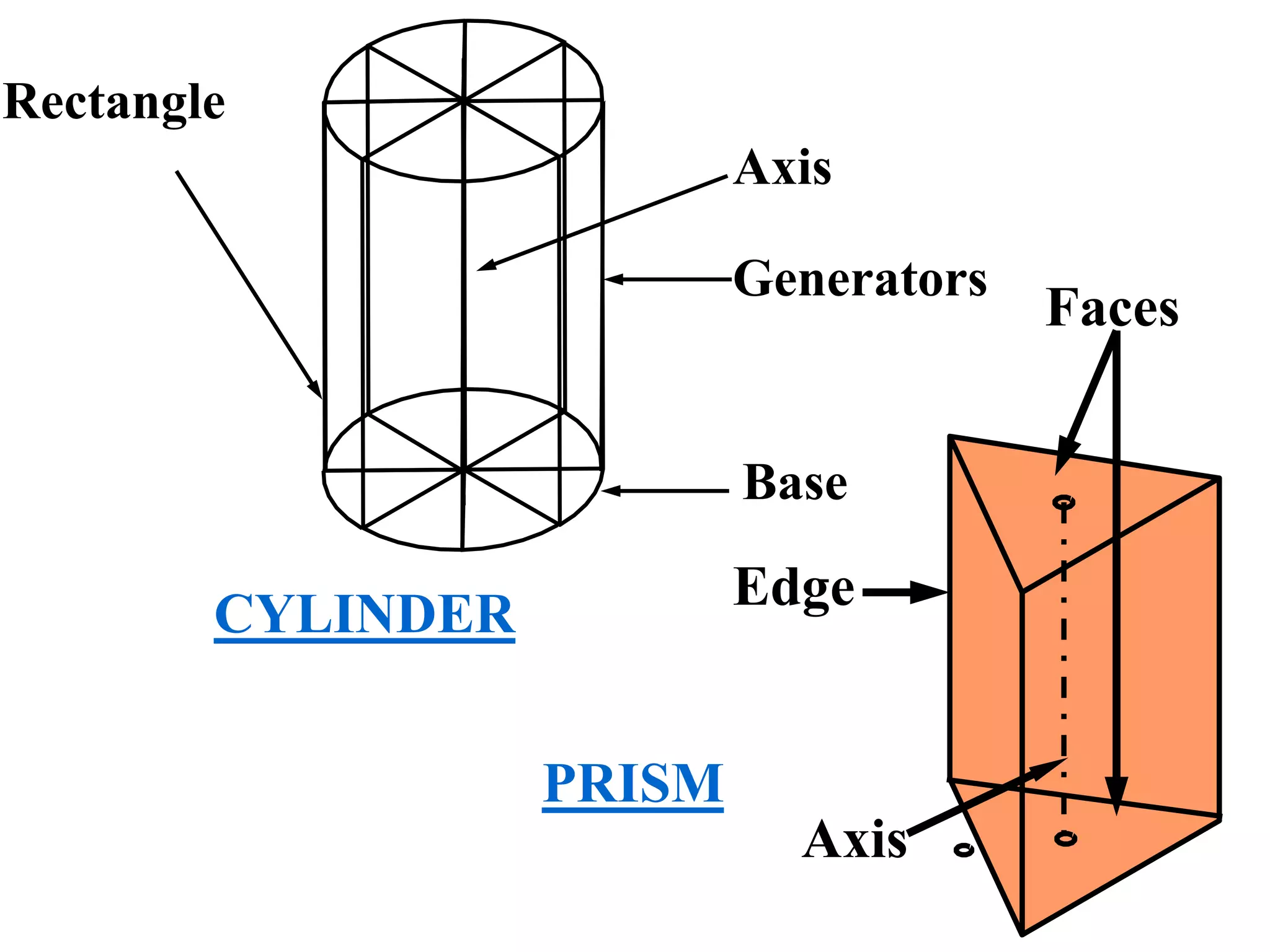
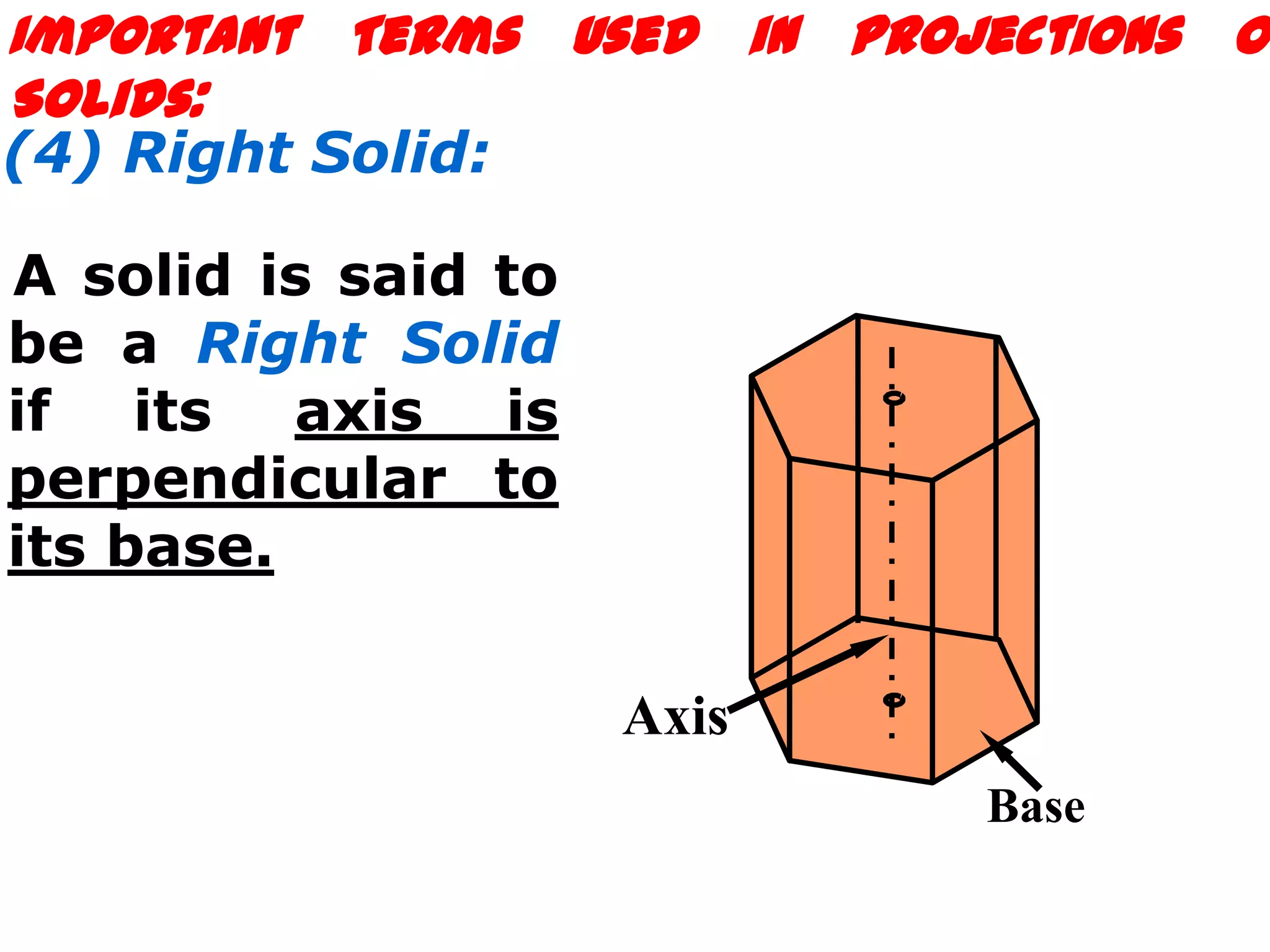
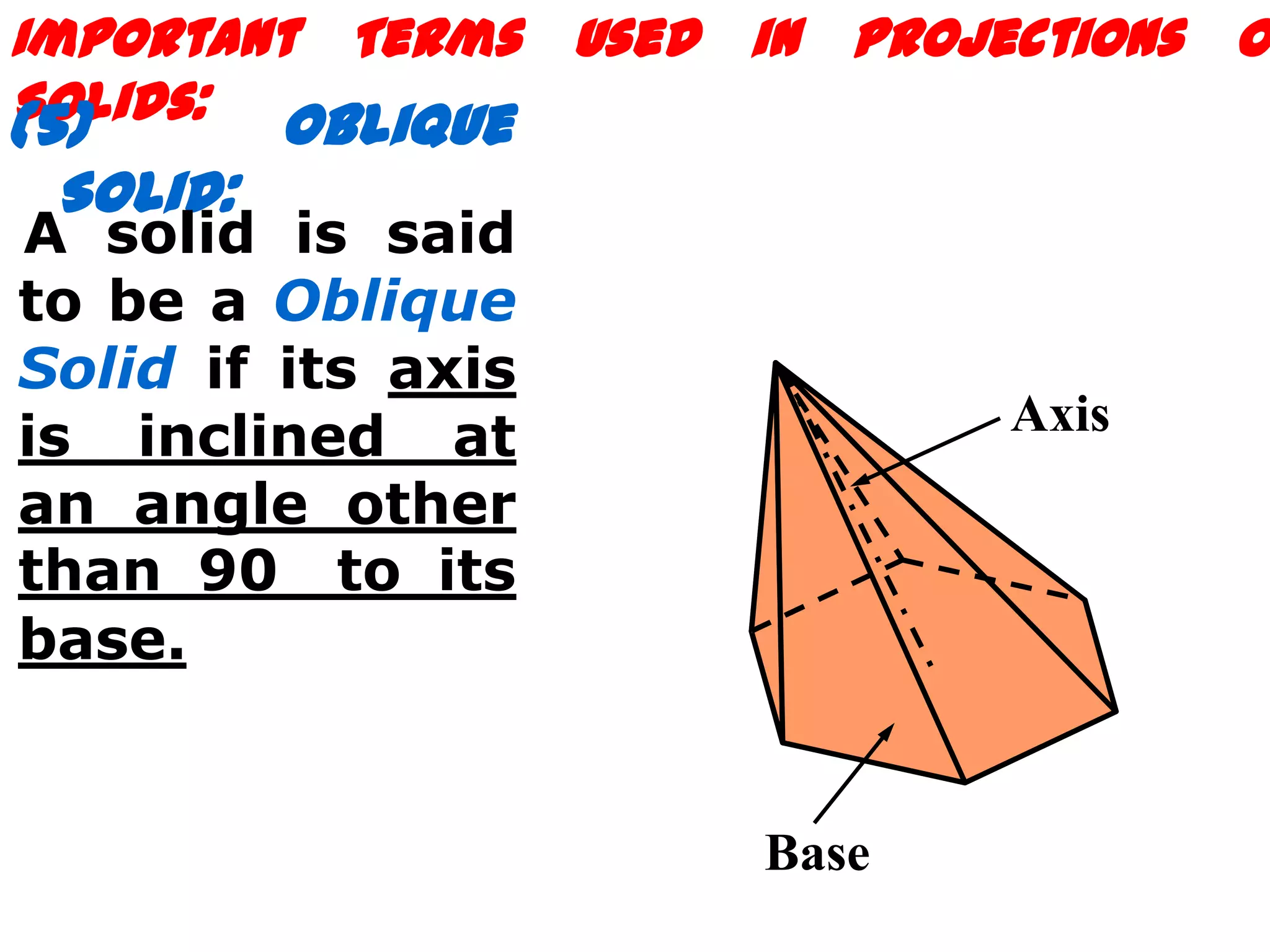
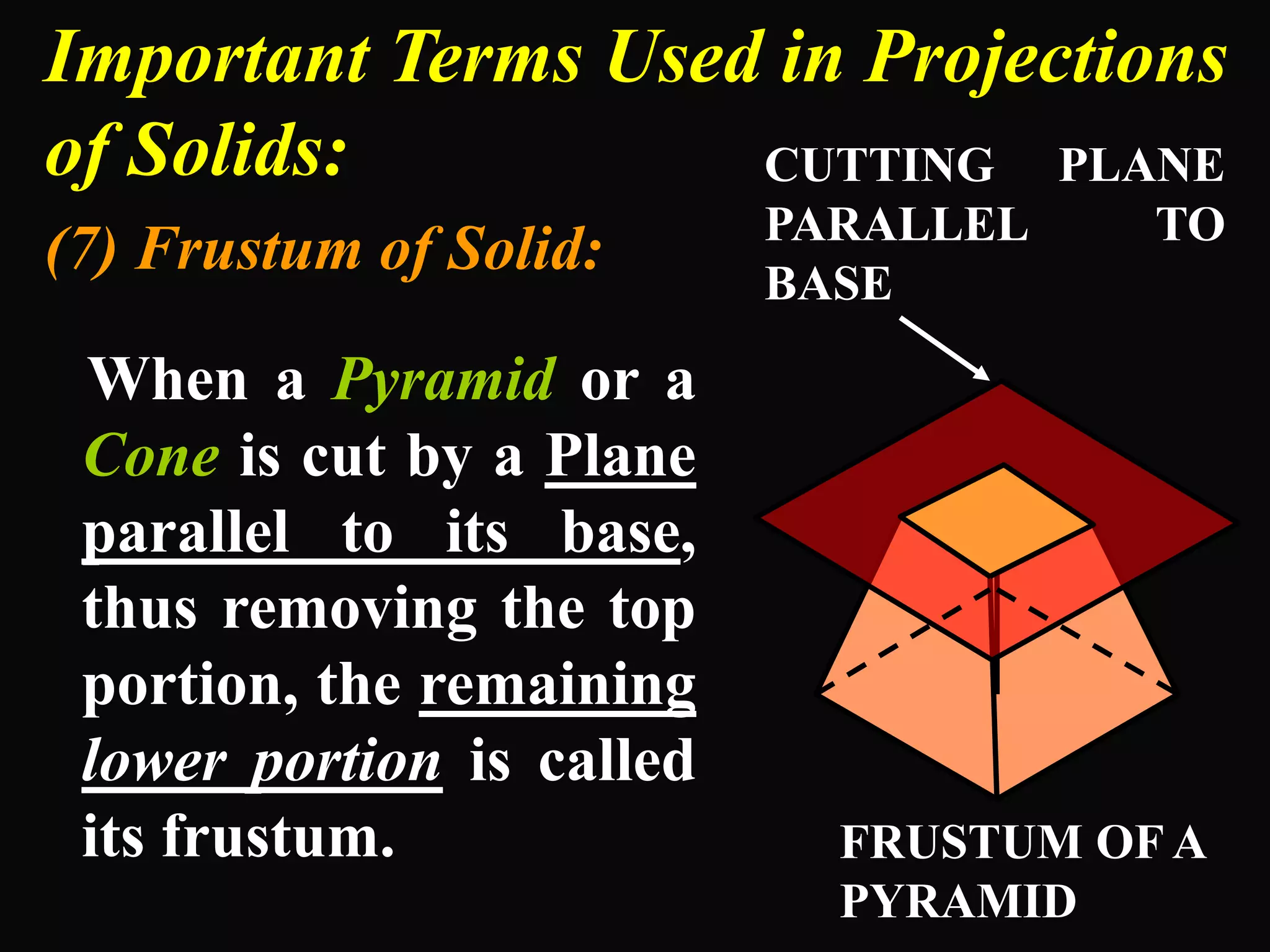
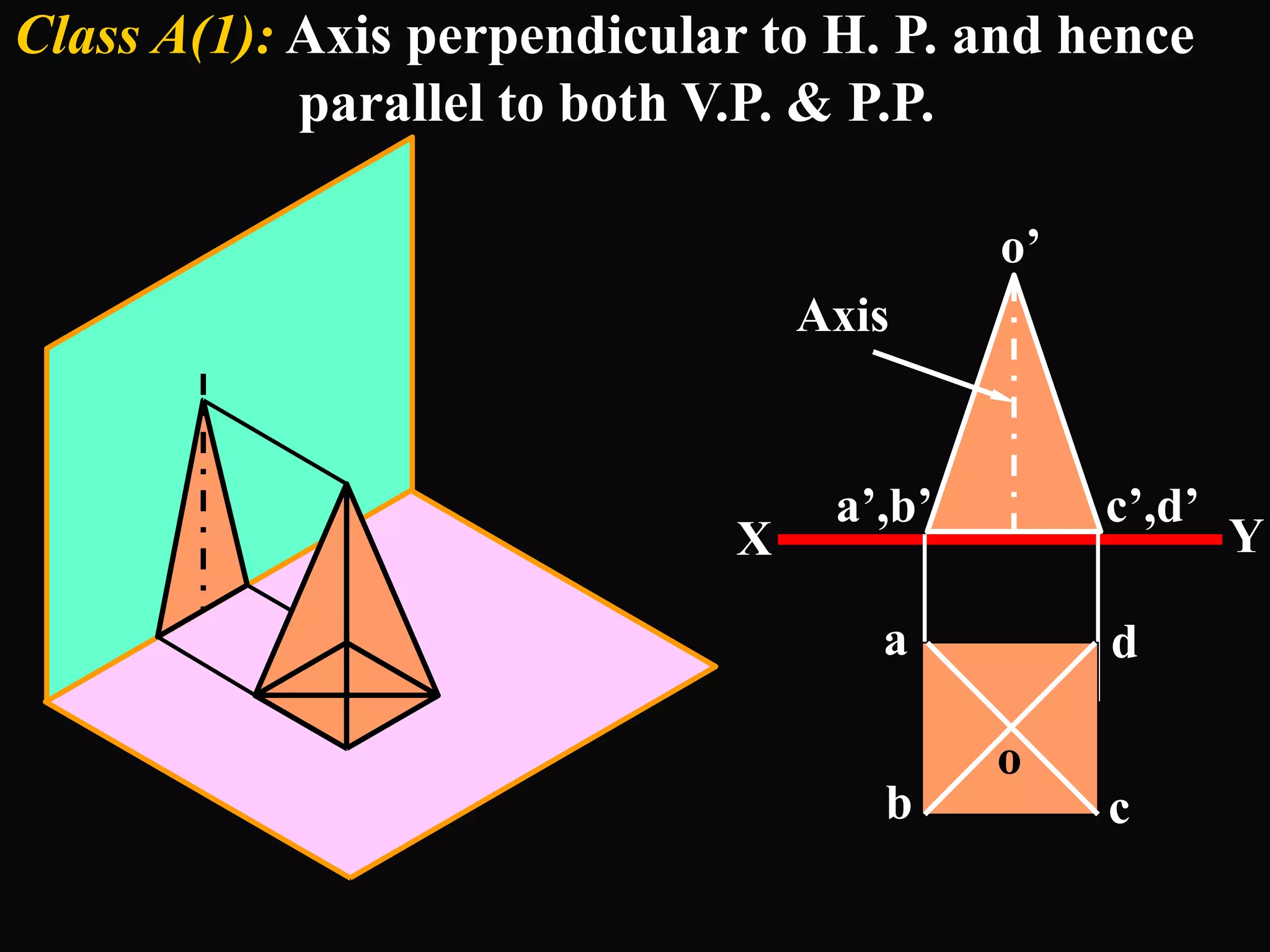
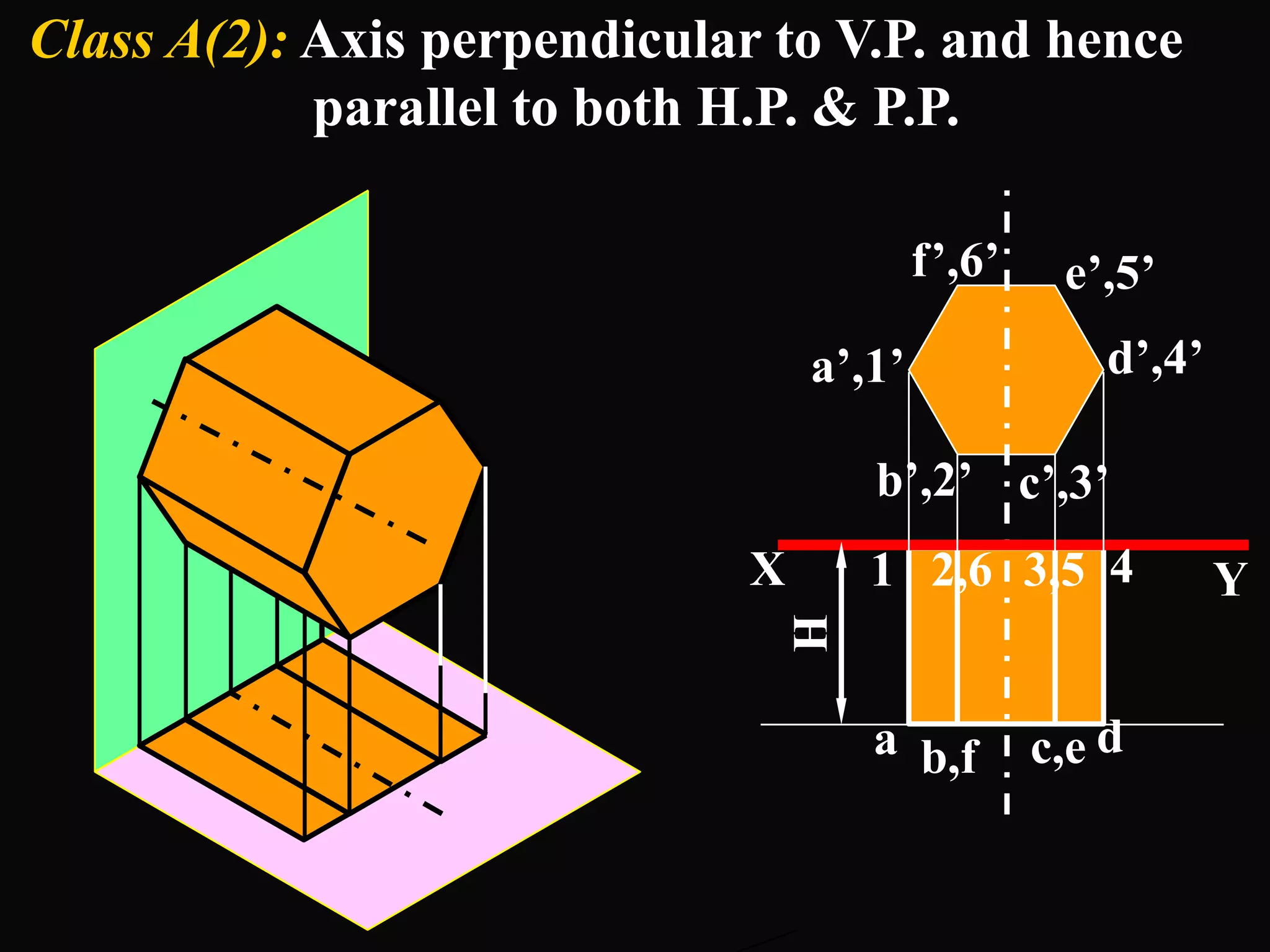
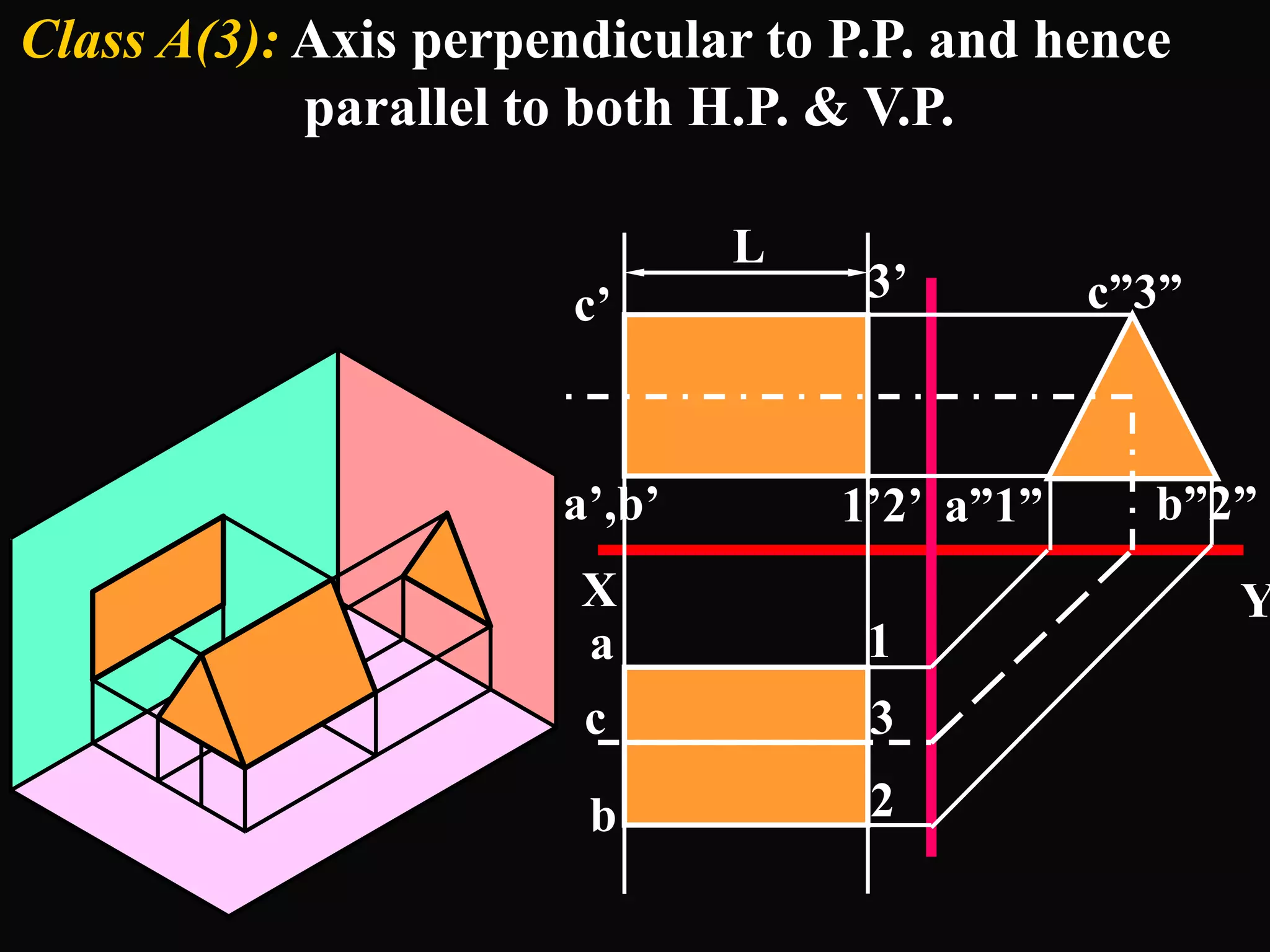
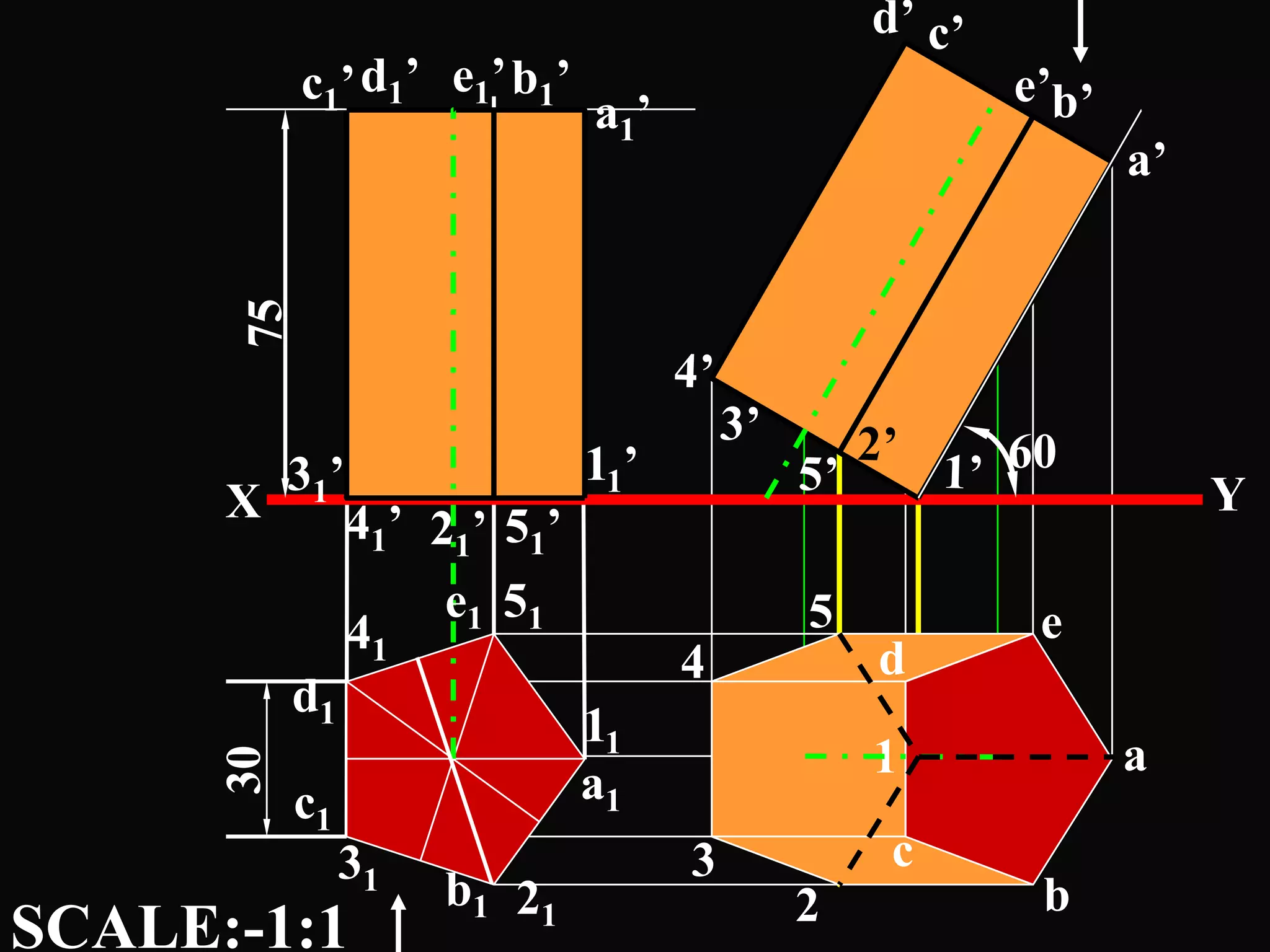
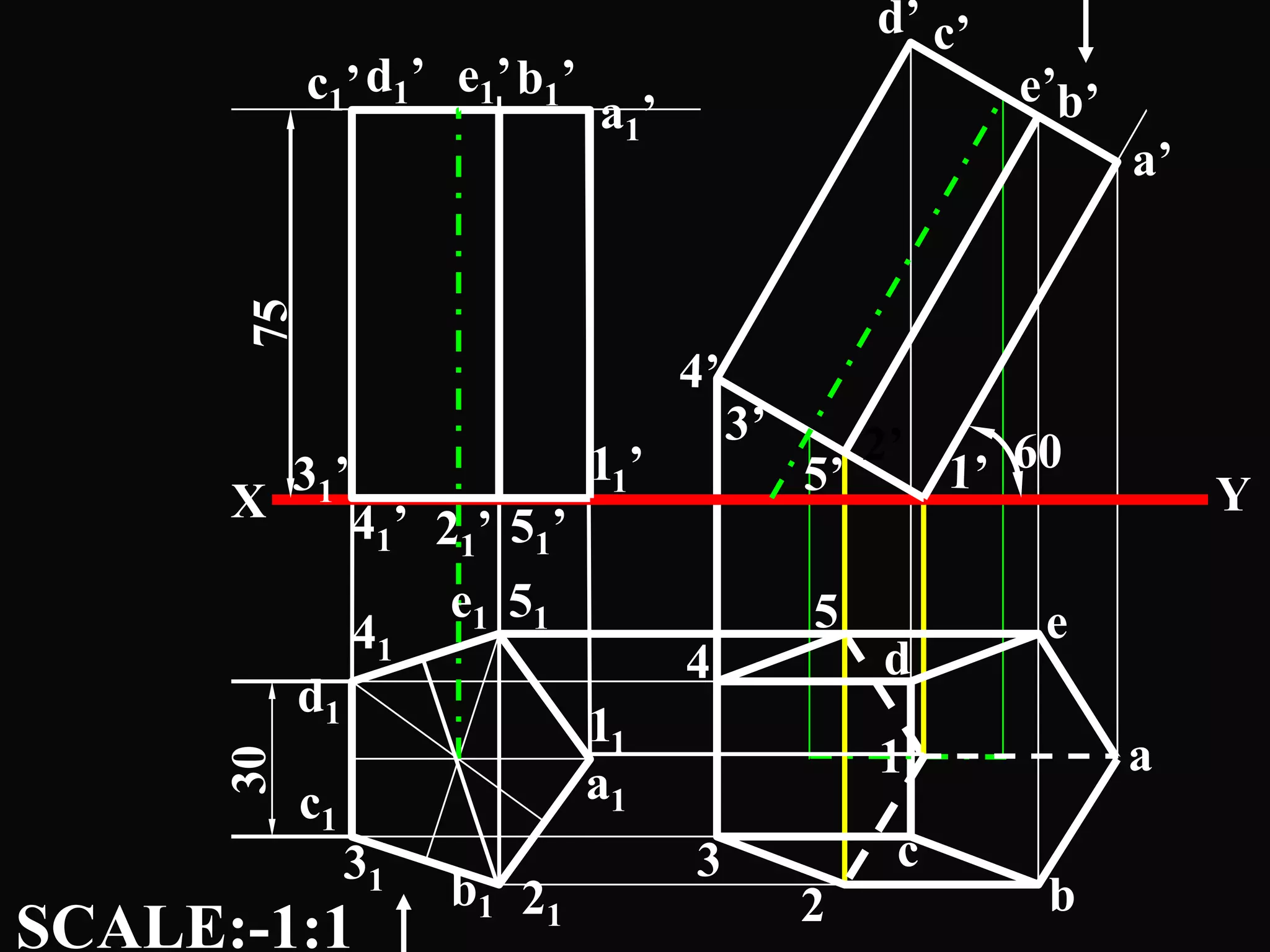
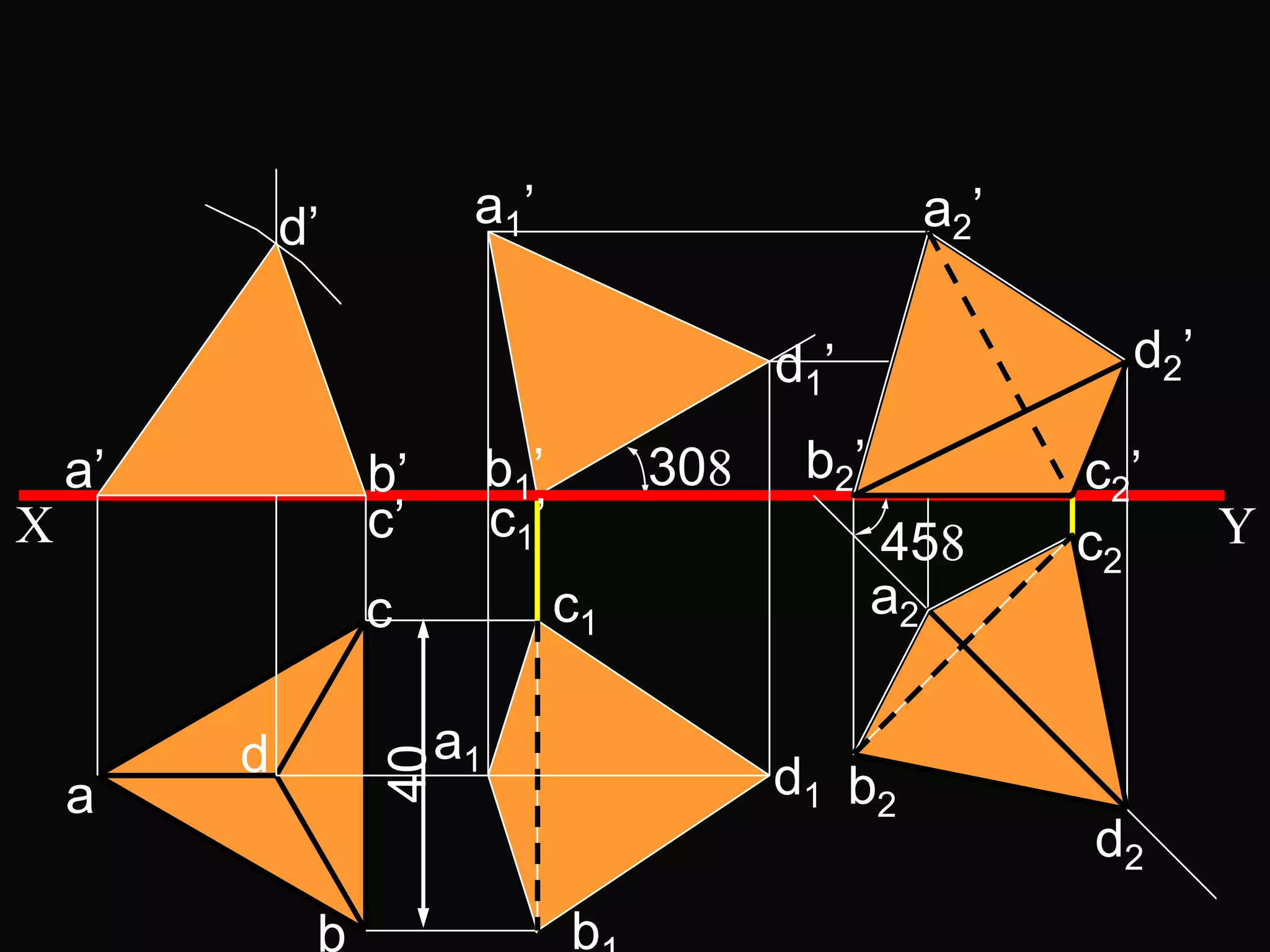
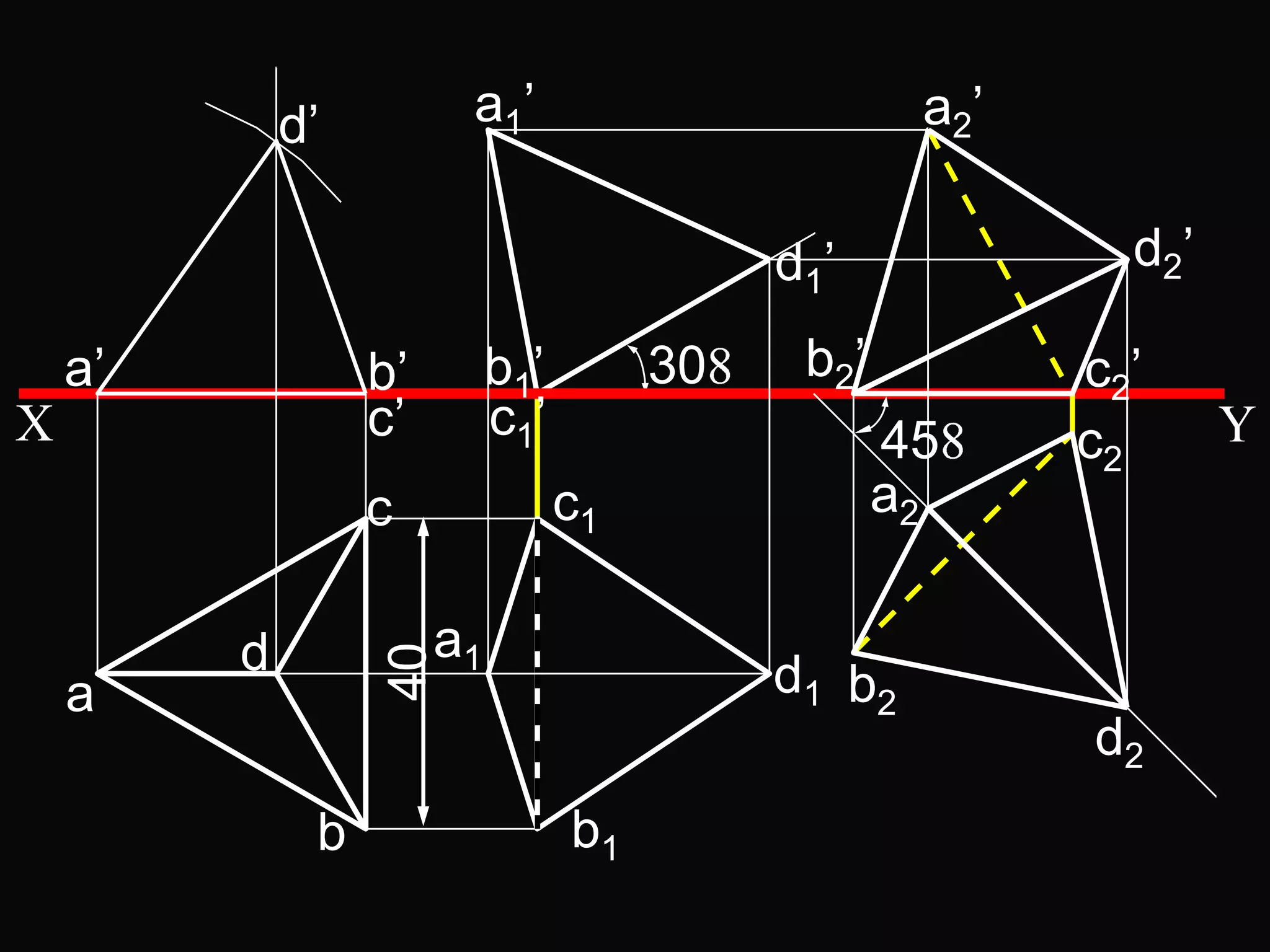
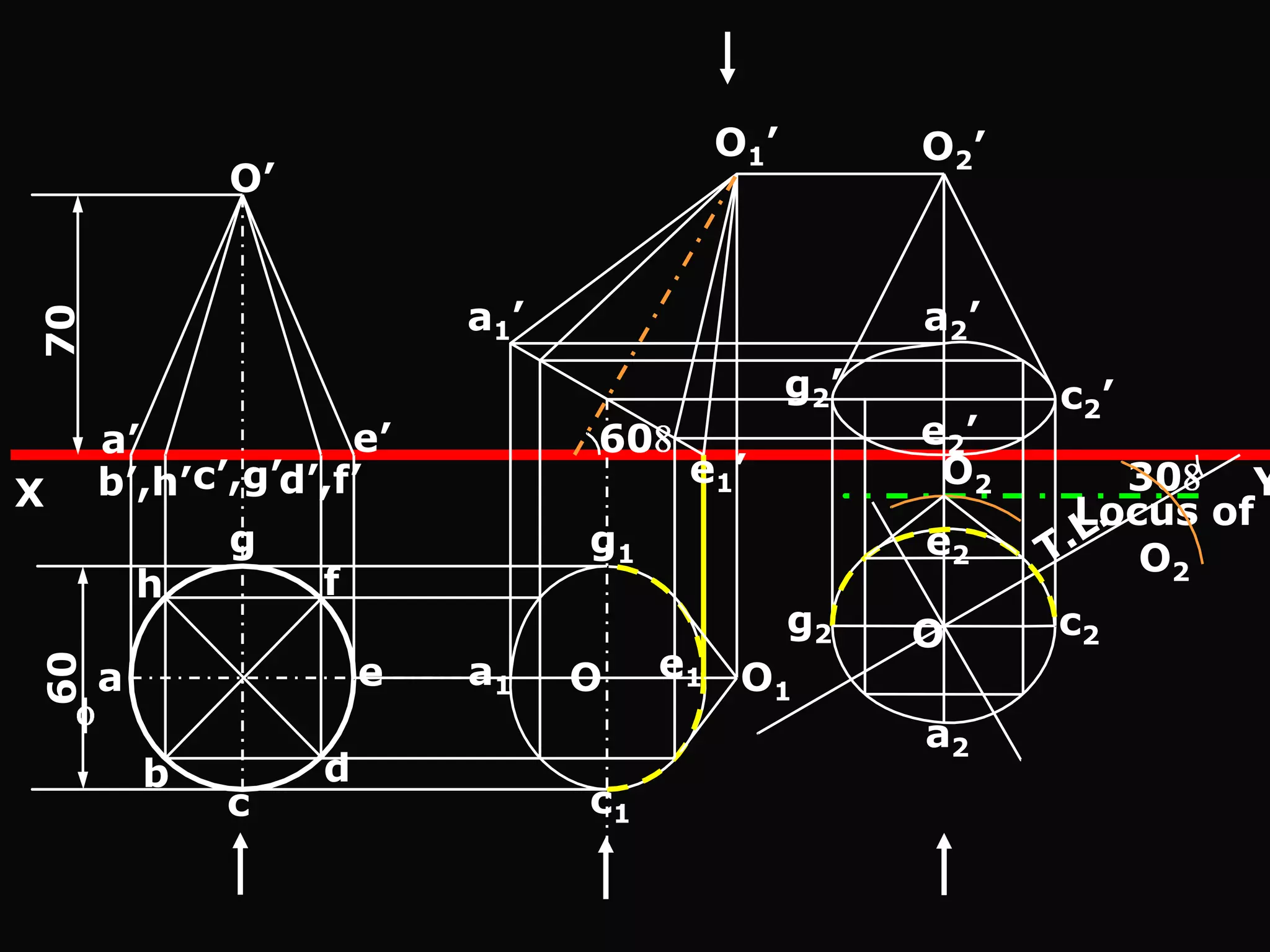
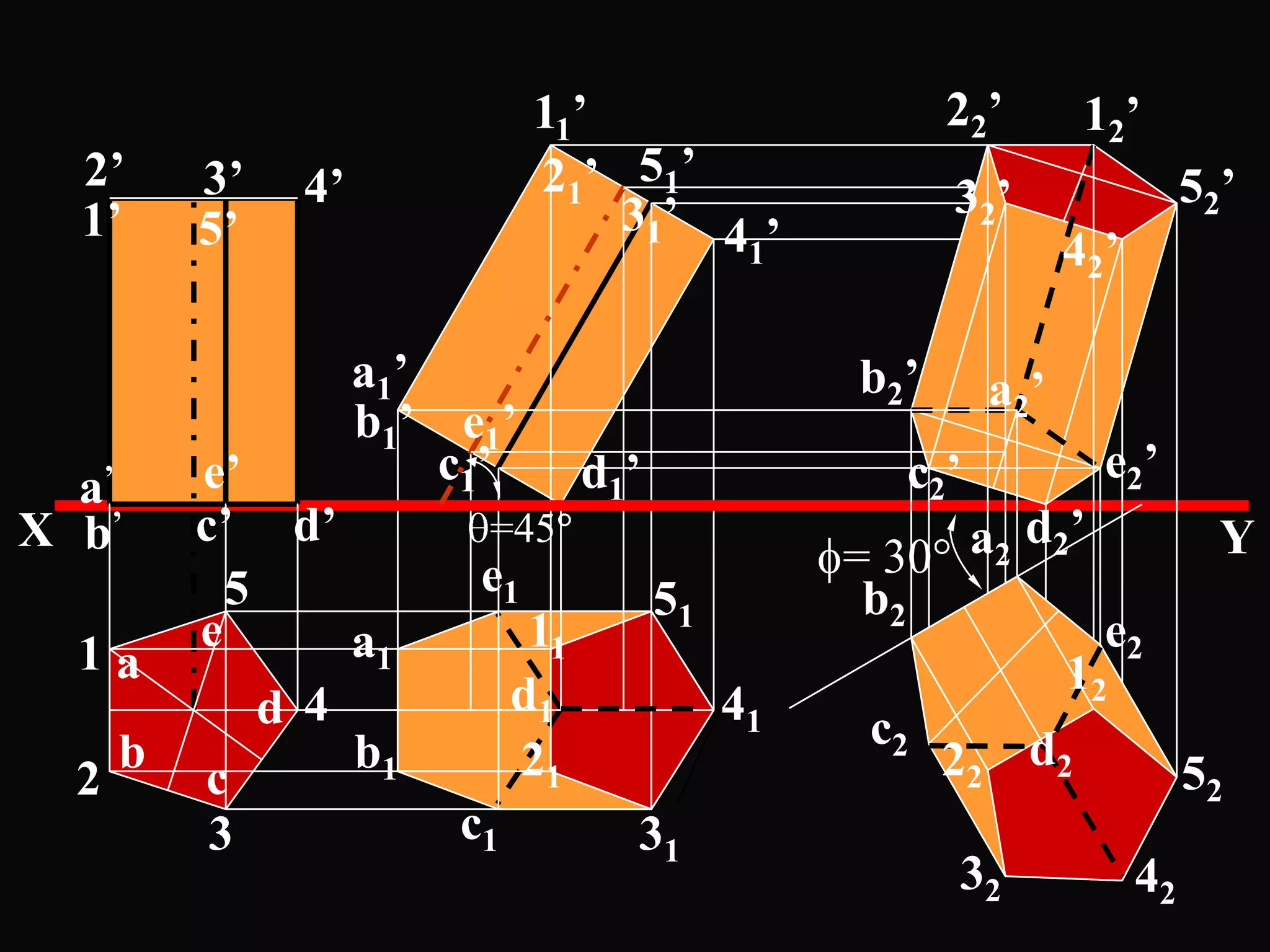
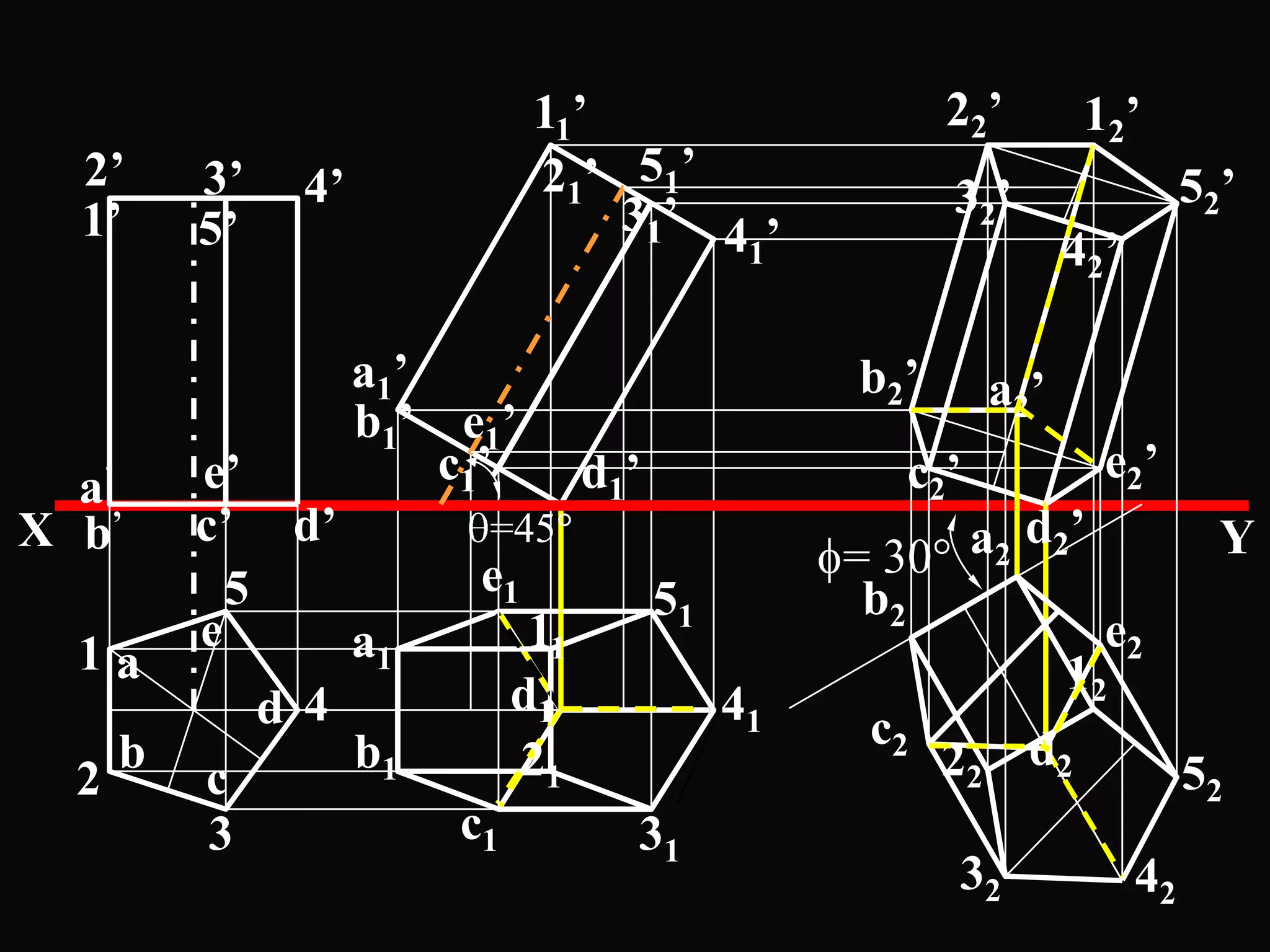
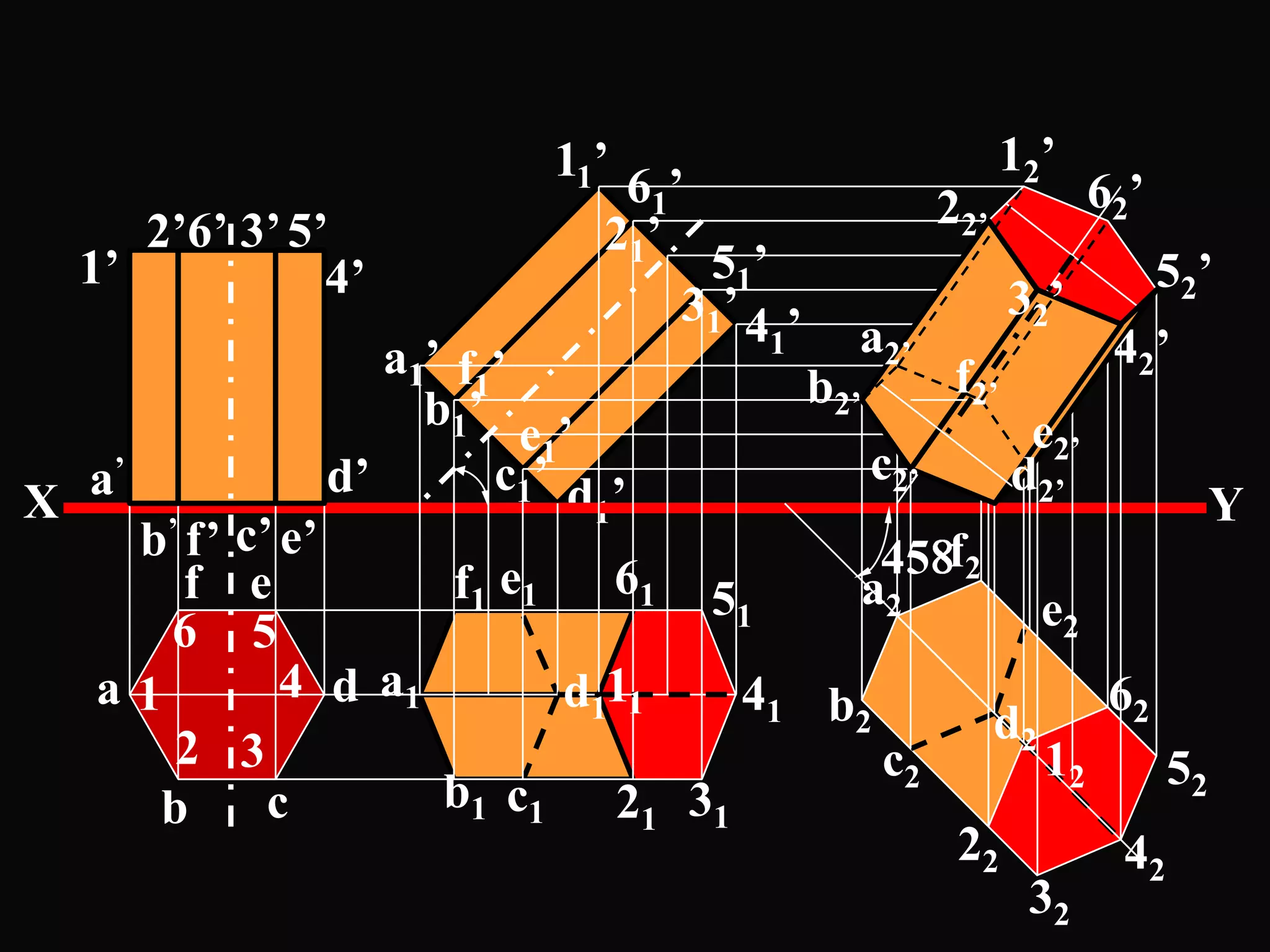
The document describes different types of geometric solids including prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, spheres and their variations. It defines key terms used for these solids such as axis, apex, base, edge, face, frustum and truncated. It also discusses different orientations of solids relative to planes and provides examples of drawing projections of solids in various positions and orientations.