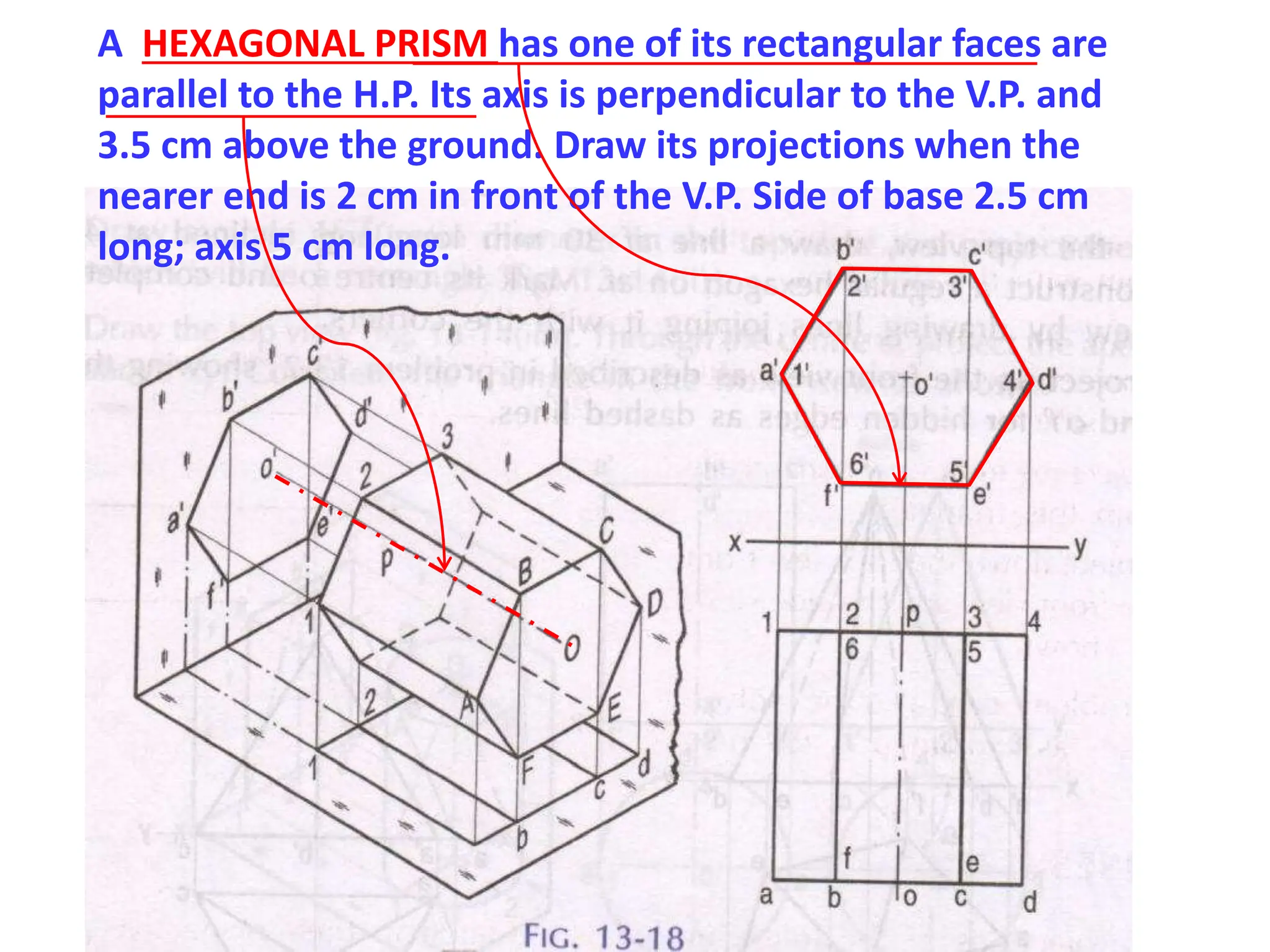
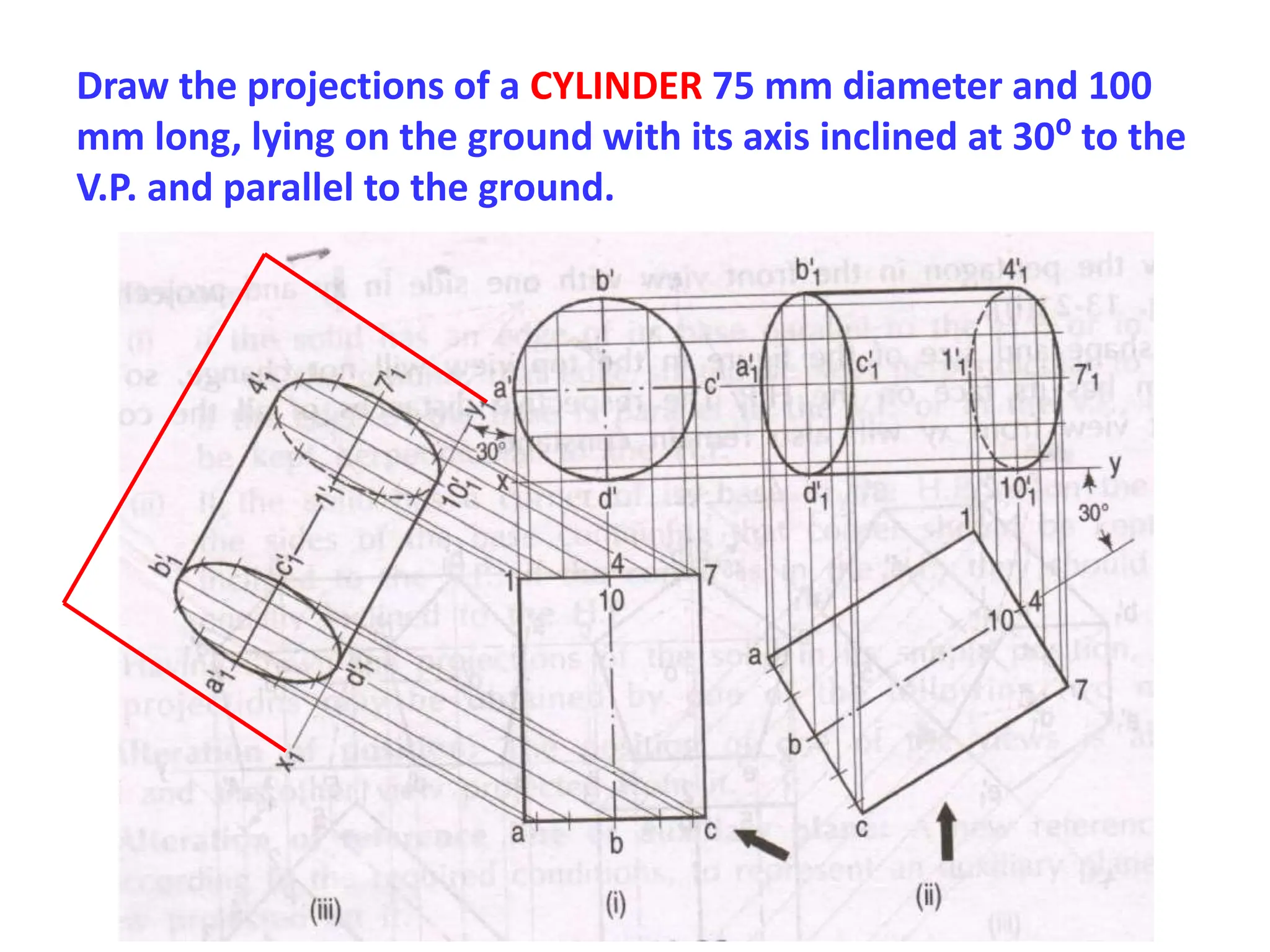
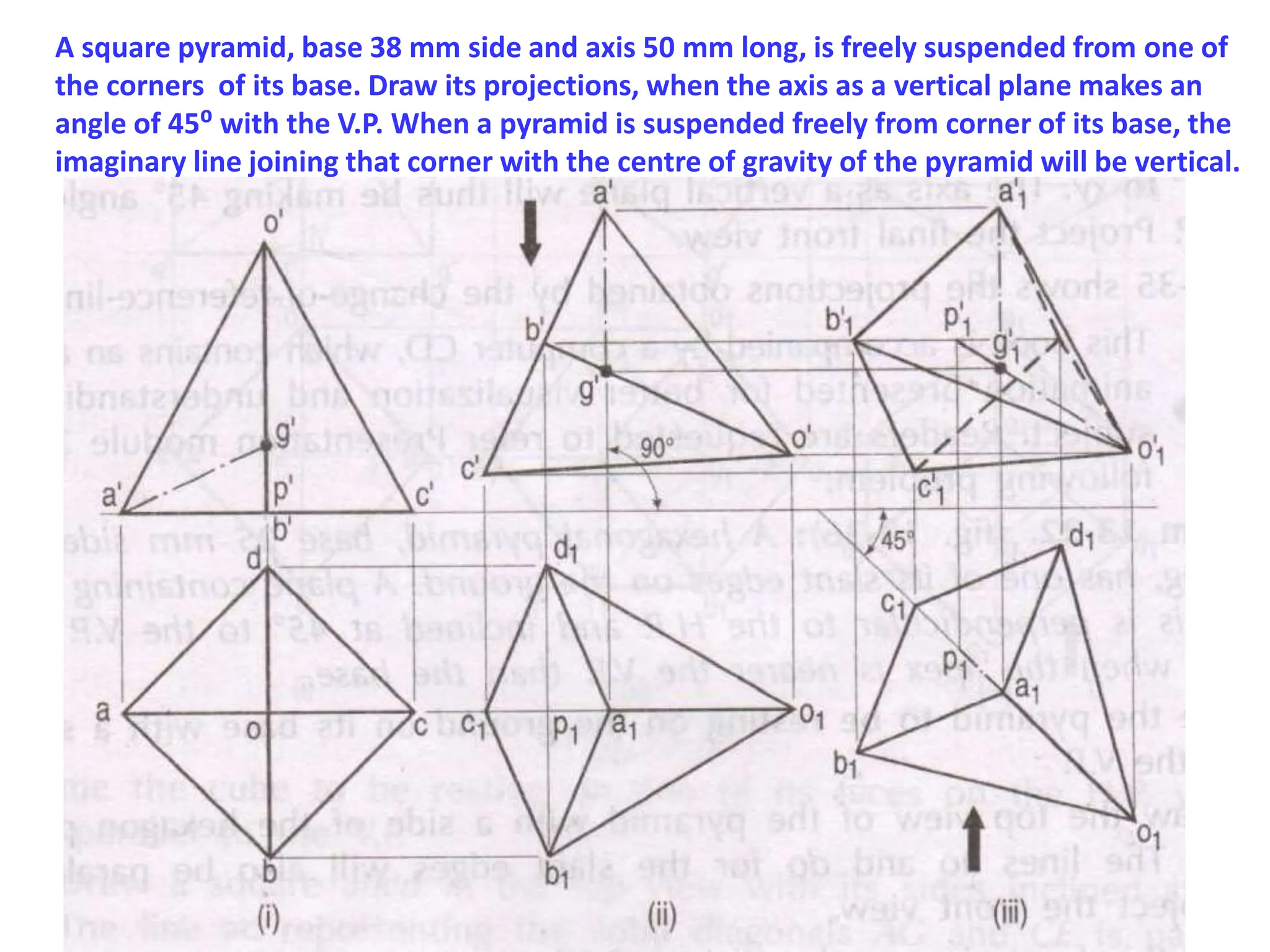
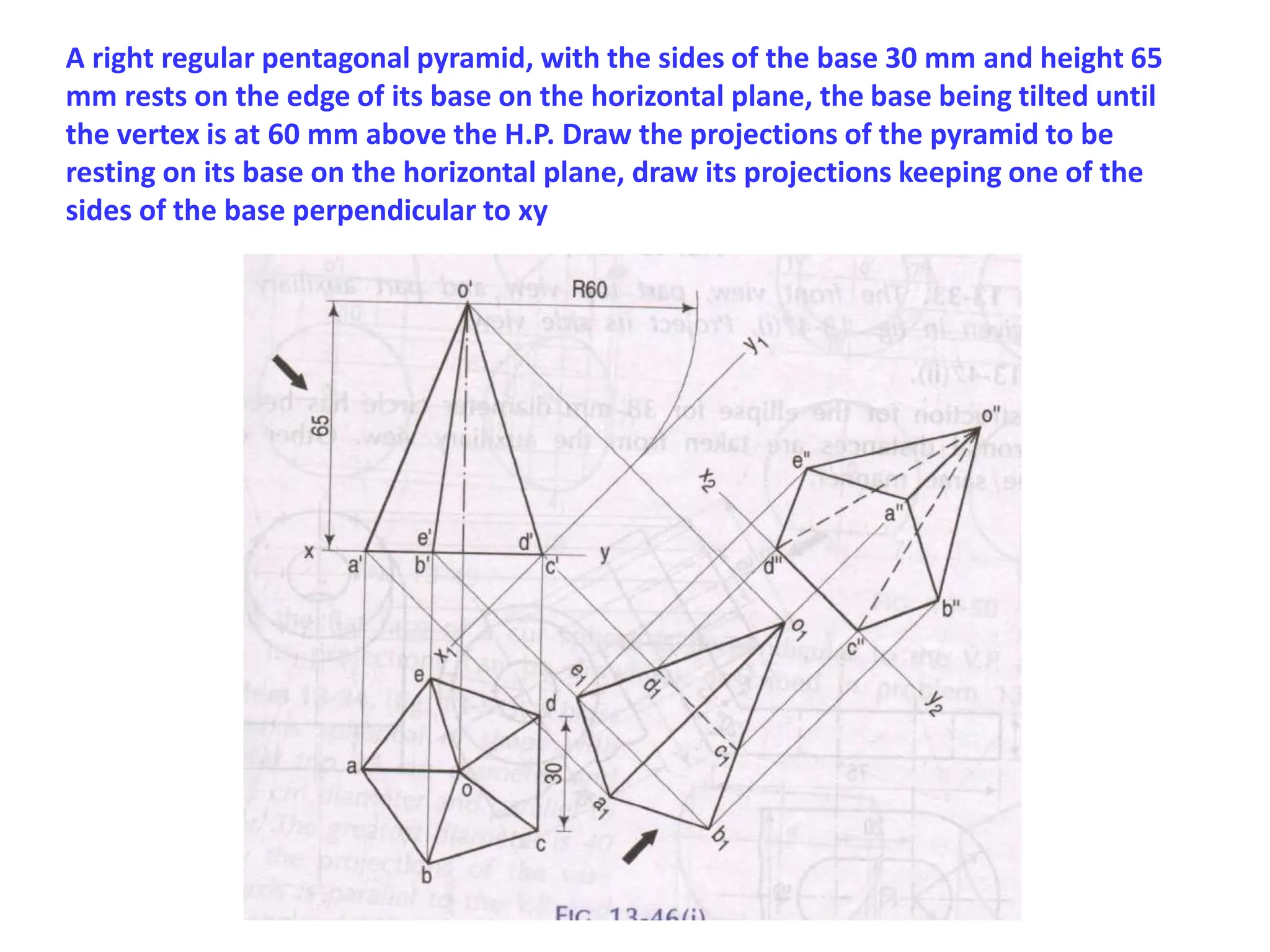
The document provides instructions for drawing the orthographic projections of various geometric solids, including prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. It includes over 30 examples of different solids in various orientations relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. For each example, it specifies the geometric properties of the solid and its position for the requested projections.