AS4100 Steel Design Webinar Worked Examples
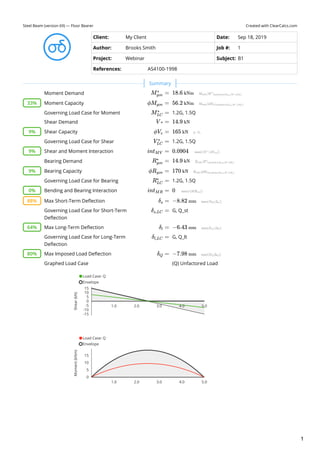
- 1. Created with ClearCalcs.comSteel Beam (version 69) — Floor Bearer Client: My Client Date: Sep 18, 2019 Author: Brooks Smith Job #: 1 Project: Webinar Subject: B1 References: AS4100-1998 Moment Demand Moment Capacity Governing Load Case for Moment 1.2G, 1.5Q Shear Demand Shear Capacity Governing Load Case for Shear 1.2G, 1.5Q Shear and Moment Interaction Bearing Demand Bearing Capacity Governing Load Case for Bearing 1.2G, 1.5Q Bending and Bearing Interaction Max Short-Term Deflection Governing Load Case for Short-Term Deflection G, Q_st Max Long-Term Deflection Governing Load Case for Long-Term Deflection G, Q_lt Max Imposed Load Deflection Graphed Load Case M =gov ∗ 18.6 kNm 33% ϕM =gov 56.2 kNm M =LC ∗ V =∗ 14.9 kN 9% ϕV =v 165 kN V =LC ∗ 9% int =MV 0.0904 R =gov ∗ 14.9 kN 9% ϕR =gov 170 kN R =LC ∗ 0% int =MR 0 88% δ =s −8.82 mm δ =s,LC 64% δ =l −6.43 mm δ =l,LC 80% δ =Q −7.98 mm (Q) Unfactored Load Load Case: Q Envelope 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Shear(kN) -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 Load Case: Q Envelope 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Moment(kNm) 0 5 10 15 Summary 1
- 2. Member Type Beam Orientation / Loading Direction Total Beam Length Deflection Limit Span Criterion Span Type (Interior or Cantilever) Short-Term Service ( ) Long-Term Service ( ) Imposed Load Q ( ) 300 300 300 Deflection Limit Absolute Criterion Maximum Spacing of Lateral Restraints Position of Supports from Left Support Type Position ( ) Length of Bearing ( ) Restraint Type Pinned 0 150 P: Partial (Lateral at Non-critical Flange + Partial Torsional) Pinned 5000 150 P: Partial (Lateral at Non-critical Flange + Partial Torsional) Maximum Interior Span Maximum Cantilever Distributed Loads Label Load Width ( ) Permanent Load ( ) Imposed Load ( ) Start Location ( ) End Location ( ) Floor Load 2000 0.5 1.5 0 5000 Height of Loads Application Include Self Weight Self Weight Character of Imposed Load Wind Class Ultimate Free Stream Dynamic Pressure Serviceability Free Stream Dynamic Pressure Net Downward Pressure Coefficient Net Uplift Pressure Coefficient Short-Term LC: Q Envelope 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Deflection(mm) -8 -6 -4 -2 0 Distance from Left of Beam (m) 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Floor Load 3 0 5 m 3 kN/m 7.5 kN 7.5 kN 180 UB 22.2 - Gr.300PLUS Major Axis / Loaded from Top L = 5000 mm D =lim L/ L/ L/ Interior Spans Δ =max 10 mm L =L 600 mm r = mm mm L =maxspan 5000 mm L =maxcant 0 mm w = mm kPa kPa mm mm Top Flange Yes SW = 0.218 kN/m Floors: Offices N1 q =u 0.69 kPa q =s 0.41 kPa C =pt,down↓ 0 C =pt,up↑ 0 Key Properties Permanent & Imposed Loads (AS1170.1) Wind and Other Loads (AS1170.x) 2
- 3. Wind Tributary/Load Width Other Distributed Loads Label Load Type Start Magnitude ( ) End Magnitude ( ) Start Location ( ) End Location ( ) Downward Wind Wu,dn 0 0 0 5000 Uplift Wind Wu,up 0 0 0 5000 Service Wind Ws 0 0 0 5000 Overall Breadth Maximum Beam Depth Overall Depth Number of Webs Depth Between Flanges Thickness of Web Web Slenderness Factor Web Yield Stress Breadth of Flange Thickness of Flange Flange Slenderness Factor Flange Yield Stress Ultimate Stress Gross Second Moment of Area Gross Second Moment of Area Gross Elastic Section Modulus Gross Plastic Section Modulus Effective Section Modulus (per manufacturer) Modulus of Elasticity Gross Axial Stiffness Gross Member Stiffness Shear Modulus of Elasticity Character of Imposed Load Factors Imposed Load Type Short-Term Factor Long-Term Factor Combination Factor Earthquake Factor 0.7 0.4 0.4 0.3 1 0.6 0.4 0.3 LW =wind 450 mm w =other kN/m kN/m mm mm b = 90 mm d =max 500 mm d = 179 mm n =w 1 d =l 159 mm t =w 6 mm d /t =l w 26.5 f =y,w 320 MPa b =f 90 mm t =f 10 mm b /t =f1 f 4.2 f =y,f 320 MPa f =u 440 MPa I = 15300000 mm3 I =perp 1220000 mm3 Z = 171000 mm3 S = 195000 mm3 Z =e 195000 mm3 E = 200000 MPa EA = 564000 kN ∗ mm/mm EI = 3060 kNm2 G =S 80000 MPa CharQ = Distributed Concentrated Member Properties Load Case Analysis (AS1170.0) 3
- 4. Strength Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Shear ( ) Moment ( ) Max Reaction ( ) 1.35G 8.22 -4.11 5.14 4.11 1.2G, 1.5Q 29.8 14.9 18.6 14.9 1.2G, 1.5Q_lt 16.3 8.15 10.2 8.15 1.2G, Wu_down, Q_comb 13.3 -6.65 8.32 6.65 0.9G, Wu_up 5.48 -2.74 3.42 2.74 G, Eu, Q_E 10.6 -5.29 6.62 5.29 1.2G, Su, Q_comb 13.3 -6.65 8.32 6.65 Short-term Service Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Deflection ( ) G, Ws 6.09 -3.24 G, Q_st 16.6 -8.82 G, Ws, Q_lt 12.1 -6.43 G, Es, Q_lt 12.1 -6.43 G, Ss, Q_lt 12.1 -6.43 Long-term Service Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Deflection ( ) G 6.09 -3.24 G, Q_lt 12.1 -6.43 G, Ss, Q_lt 12.1 -6.43 Unfactored Load Load Type Total Load ( ) Shear ( ) Moment ( ) Max Reaction ( ) Short-Term Deflection ( ) G 6.09 -3.04 3.81 3.04 -3.24 Q_dist 15 7.5 9.37 7.5 -7.98 Shear Capacity Factor Nominal Shear Yield Capacity Shear Buckling Coefficient Nominal Shear Buckling Capacity Nominal Shear Capacity in Uniform Stress Distribution Nominal Shear Capacity Capacity Factor Flange Element Slenderness Flange Element Yield Slenderness Limit Flange Element Plastic Slenderness Limit Section Compactness in Bending Compact Effective Section Modulus Section Moment Capacity Maximum Flange Area Reduction By Holes kN kN kNm kN kN mm kN mm kN kN kNm kN mm ϕ = 0.9 V =w 183 kN α =v 7.48 V =b 183 kN V =u 183 kN V =v 183 kN ϕ = 0.9 λ =e,f 4.75 λ =ey,f 14 λ =ep,f 8 compact =f Z =e 195000 kNm M =s 62.4 kNm A =f,holes 14.4 % Unfactored Load Analysis (AS1170.0) Shear Capacity (AS4100-1998, Section 5.11) Moment Section Capacity (AS4100-1998, Cl 5.3) 4
- 5. Moment Modification Factor Calculation Span Length ( ) Span Type Maximum Moment ( ) Q1 Moment ( ) Q2 Moment ( ) Q3 Moment ( ) M Mod. Factor 5000 Int 18.6 13.9 18.6 13.9 1.17 Slenderness Reduction Factor Span Length ( ) Span Type Twist Restraint Factor Lateral Rotation Restraint Factor Load Height Factor Effective Length ( ) Reference Buckling Moment ( ) Slenderness Reduction Factor 5000 PP 1.15 1 1.4 969 252 0.901 Nominal Moment Utilisation Span Length ( ) Span Type Moment Demand ( ) Member Moment Capacity ( ) Factored Moment Capacity ( ) Moment Utilisation 5000 PP 18.6 65.7 56.2 0.332 Consider Proportioning Method? Yes Flange Element Slenderness Flange Element Yield Slenderness Limit Compression Flange Effective Width Compression Flange Effective Area Flange Gross Area Minimum Flange Net Area Tension Flange Effective Area Minimum Flange Effective Area Distance Between Flange Centroids Moment Capacity of Flanges Alone Factored Moment Capacity of Flanges Alone Bending & Shear Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Moment Demand ( ) Factored Section Moment Capacity ( ) Shear Demand ( ) Shear Capacity Given Moment Interaction ( ) Shear Capacity Given Moment Utilisation 0 0 56.2 14.9 165 0.0904 5000 0 56.2 -14.9 165 0.0904 Capacity Factor Interior Bearing Criteria Flange Lateral Restraint Member Section Constant for Web Buckling Form Factor for Web Buckling Member Slenderness Reduction Factor for Web Position ( ) Geometric Slenderness Factor Factor Factor Factor Factor Slenderness Reduction 0 133 150 12.9 156 0.466 0.743 0.273 5 133 150 12.9 156 0.466 0.743 0.273 α =m mm kNm kNm kNm kNm α =s mm mm kNm M =table mm kNm kNm kNm PM =flag λ =e 4.75 λ =ey 14 b ∣d =fe e 90 mm A =fc 8100 mm2 A =fg 900 mm2 A =fn,min 770 mm2 A =ft 900 mm2 A =fm 900 mm2 d =f 169 mm M =f 48.7 kNm ϕM =f 43.8 kNm r = mm kNm kNm kN kN ϕ = 0.9 B =d 105 mm One Flange Only α =b 0.5 k =f 1 mm α =c,table mm Moment Capacity (AS4100-1998, Cl 5.1 & 5.6.1-2) Shear - Bending Moment Interaction (AS4100, Cl 5.12) Bearing Capacity (AS4100, Cl 5.13) 5
- 6. Bearing Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Interior Location? ( ) Reaction ( ) Bearing Yield Capacity ( ) Bearing Buckling Capacity ( ) Factored Bearing Capacity ( ) Bearing Utilisation ( ) 0 1 14.9 480 188 170 0.0879 5000 1 14.9 480 188 170 0.0879 Bending & Bearing Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Reaction ( ) Factored Bearing Capacity ( ) Governing Moment Demand ( ) Factored Moment Capacity ( ) Bending & Bearing Utilisation 0 14.9 170 0 56.2 0 5000 14.9 170 0 56.2 0 Short-Term Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Short-Term Deflection ( ) Short-term Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 5000 Int -8.82 10 0.882 Long-Term Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Long-Term Deflection ( ) Long-term Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 5000 Int -6.43 10 0.643 Imposed Load Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Imposed Load Deflection ( ) Imposed Load Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 5000 Int -7.98 10 0.798 Comments Steel Beam Analysis and Design to AS4100-1998 (R2016). Assumes: (1) Beam is of uniform cross-section along its full length, (2) Detailing requirements are checked separately, (3) Net areas are equal to the gross area with maximum allowed holes. R =table mm kN kN kN kN kN kN r = mm kN kN kNm kNm D =ST mm mm mm D =LT mm mm mm D =Q mm mm mm Bending & Bearing Capacity (AS4100, Cl 5.13.5) Deflection Analysis Comments Assumptions 6
- 7. Created with ClearCalcs.comSteel Beam (version 69) — Floor Bearer Client: My Client Date: Sep 18, 2019 Author: Brooks Smith Job #: 1 Project: Webinar Subject: B2 References: AS4100-1998 Moment Demand Moment Capacity Governing Load Case for Moment 1.2G, 1.5Q Shear Demand Shear Capacity Governing Load Case for Shear 1.2G, 1.5Q Shear and Moment Interaction Bearing Demand Bearing Capacity Governing Load Case for Bearing 1.2G, 1.5Q Bending and Bearing Interaction Max Short-Term Deflection Governing Load Case for Short-Term Deflection G, Q_st Max Long-Term Deflection Governing Load Case for Long-Term Deflection G, Q_lt Max Imposed Load Deflection Graphed Load Case M =gov ∗ −79.1 kNm 26% ϕM =gov 300 kNm M =LC ∗ V =∗ −38 kN 8% ϕV =v 500 kN V =LC ∗ 8% int =MV 0.0759 R =gov ∗ 69.6 kN 61% ϕR =gov 115 kN R =LC ∗ 0% int =MR 0 91% δ =s −9.12 mm δ =s,LC 69% δ =l −6.86 mm δ =l,LC 75% δ =Q −7.54 mm (Q) Unfactored Load Load Case: Q Envelope 5 10 15 20 Shear(kN) -40 -20 0 20 Load Case: Q Envelope 5 10 15 20 Moment(kNm) -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 40 Summary 7
- 8. Member Type Beam Orientation / Loading Direction Total Beam Length Deflection Limit Span Criterion Span Type (Interior or Cantilever) Short-Term Service ( ) Long-Term Service ( ) Imposed Load Q ( ) 300 300 300 150 150 150 Deflection Limit Absolute Criterion Maximum Spacing of Lateral Restraints Position of Supports from Left Support Type Position ( ) Length of Bearing ( ) Restraint Type Pinned 0 150 P: Partial (Lateral at Non-critical Flange + Partial Torsional) Pinned 4000 150 L: Lateral at Critical Flange Only Pinned 15000 150 P: Partial (Lateral at Non-critical Flange + Partial Torsional) Maximum Interior Span Maximum Cantilever Distributed Loads Label Load Width ( ) Permanent Load ( ) Imposed Load ( ) Start Location ( ) End Location ( ) Floor Load 2000 0.5 1.5 0 20000 Height of Loads Application Include Self Weight Self Weight Character of Imposed Load Wind Class Ultimate Free Stream Dynamic Pressure Serviceability Free Stream Dynamic Pressure Short-Term LC: Q Envelope 5 10 15 20 Deflection(mm) -8 -6 -4 -2 0 Distance from Left of Beam (m) 0 5 10 15 20 Floor Load 3 0 20 m 3 kN/m 0.719 kN 26.3 kN 33 kN 410 UB 53.7 - Gr.300PLUS Major Axis / Loaded from Top L = 20000 mm D =lim L/ L/ L/ Interior Spans Cantilevers Δ =max 10 mm L =L 600 mm r = mm mm L =maxspan 11000 mm L =maxcant 5000 mm w = mm kPa kPa mm mm Top Flange Yes SW = 0.527 kN/m Floors: Offices N1 q =u 0.69 kPa q =s 0.41 kPa Key Properties Permanent & Imposed Loads (AS1170.1) Wind and Other Loads (AS1170.x) 8
- 9. Net Downward Pressure Coefficient Net Uplift Pressure Coefficient Wind Tributary/Load Width Other Distributed Loads Label Load Type Start Magnitude ( ) End Magnitude ( ) Start Location ( ) End Location ( ) Downward Wind Wu,dn 0 0 0 20000 Uplift Wind Wu,up 0 0 0 20000 Service Wind Ws 0 0 0 20000 Overall Breadth Maximum Beam Depth Overall Depth Number of Webs Depth Between Flanges Thickness of Web Web Slenderness Factor Web Yield Stress Breadth of Flange Thickness of Flange Flange Slenderness Factor Flange Yield Stress Ultimate Stress Gross Second Moment of Area Gross Second Moment of Area Gross Elastic Section Modulus Gross Plastic Section Modulus Effective Section Modulus (per manufacturer) Modulus of Elasticity Gross Axial Stiffness Gross Member Stiffness Shear Modulus of Elasticity Character of Imposed Load Factors Imposed Load Type Short-Term Factor Long-Term Factor Combination Factor Earthquake Factor 0.7 0.4 0.4 0.3 1 0.6 0.4 0.3 C =pt,down↓ 0 C =pt,up↑ 0 LW =wind 450 mm w =other kN/m kN/m mm mm b = 178 mm d =max 500 mm d = 403 mm n =w 1 d =l 381 mm t =w 7.6 mm d /t =l w 50.1 f =y,w 320 MPa b =f 178 mm t =f 10.9 mm b /t =f1 f 7.82 f =y,f 320 MPa f =u 440 MPa I = 188000000 mm3 I =perp 10300000 mm3 Z = 933000 mm3 S = 1060000 mm3 Z =e 1060000 mm3 E = 200000 MPa EA = 1380000 kN ∗ mm/mm EI = 37600 kNm2 G =S 80000 MPa CharQ = Distributed Concentrated Member Properties Load Case Analysis (AS1170.0) 9
- 10. Strength Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Shear ( ) Moment ( ) Max Reaction ( ) 1.35G 41.2 -12.4 -25.8 22.7 1.2G, 1.5Q 127 -38 -79.1 69.6 1.2G, 1.5Q_lt 72.6 -21.8 -45.4 39.9 1.2G, Wu_down, Q_comb 60.6 -18.2 -37.9 33.3 0.9G, Wu_up 27.5 -8.24 -17.2 15.1 G, Eu, Q_E 48.5 -14.6 -30.3 26.7 1.2G, Su, Q_comb 60.6 -18.2 -37.9 33.3 Short-term Service Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Deflection ( ) G, Ws 30.5 -3.84 G, Q_st 72.5 -9.12 G, Ws, Q_lt 54.5 -6.86 G, Es, Q_lt 54.5 -6.86 G, Ss, Q_lt 54.5 -6.86 Long-term Service Load Cases Load Case Total Load ( ) Deflection ( ) G 30.5 -3.84 G, Q_lt 54.5 -6.86 G, Ss, Q_lt 54.5 -6.86 Unfactored Load Load Type Total Load ( ) Shear ( ) Moment ( ) Max Reaction ( ) Short-Term Deflection ( ) G 30.5 -9.15 -19.1 16.8 -3.84 Q_dist 60 -18 -37.5 33 -7.54 Shear Capacity Factor Nominal Shear Yield Capacity Shear Buckling Coefficient Nominal Shear Buckling Capacity Nominal Shear Capacity in Uniform Stress Distribution Nominal Shear Capacity Capacity Factor Flange Element Slenderness Flange Element Yield Slenderness Limit Flange Element Plastic Slenderness Limit Section Compactness in Bending Non-compact Effective Section Modulus Section Moment Capacity Maximum Flange Area Reduction By Holes kN kN kNm kN kN mm kN mm kN kN kNm kN mm ϕ = 0.9 V =w 556 kN α =v 2.09 V =b 556 kN V =u 556 kN V =v 556 kN ϕ = 0.9 λ =e,f 8.85 λ =ey,f 14 λ =ep,f 8 compact =f Z =e 1040000 kNm M =s 333 kNm A =f,holes 14.4 % Unfactored Load Analysis (AS1170.0) Shear Capacity (AS4100-1998, Section 5.11) Moment Section Capacity (AS4100-1998, Cl 5.3) 10
- 11. Moment Modification Factor Calculation Span Length ( ) Span Type Maximum Moment ( ) Q1 Moment ( ) Q2 Moment ( ) Q3 Moment ( ) M Mod. Factor 4000 Int -44.6 -1.63 -9.72 -24 2.5 11000 Int -79.1 17.8 34.1 2 2.5 5000 Cant -79.1 -45.6 -20.6 -5.23 1.25 Slenderness Reduction Factor Span Length ( ) Span Type Twist Restraint Factor Lateral Rotation Restraint Factor Load Height Factor Effective Length ( ) Reference Buckling Moment ( ) Slenderness Reduction Factor 4000 PL 1.47 1 1.4 1230 2660 0.967 11000 PL 1.47 1 1.4 1230 2660 0.967 5000 PP 1.23 1 1.4 1040 3750 0.987 Nominal Moment Utilisation Span Length ( ) Span Type Moment Demand ( ) Member Moment Capacity ( ) Factored Moment Capacity ( ) Moment Utilisation 4000 PL -44.6 806 300 0.149 11000 PL -79.1 806 300 0.264 5000 PP -79.1 411 300 0.264 Consider Proportioning Method? Yes Flange Element Slenderness Flange Element Yield Slenderness Limit Compression Flange Effective Width Compression Flange Effective Area Flange Gross Area Minimum Flange Net Area Tension Flange Effective Area Minimum Flange Effective Area Distance Between Flange Centroids Moment Capacity of Flanges Alone Factored Moment Capacity of Flanges Alone Bending & Shear Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Moment Demand ( ) Factored Section Moment Capacity ( ) Shear Demand ( ) Shear Capacity Given Moment Interaction ( ) Shear Capacity Given Moment Utilisation 0 0 300 1.52 500 0.00303 4000 -44.6 300 31.7 500 0.0633 15000 -79.1 300 -38 500 0.0759 Capacity Factor Interior Bearing Criteria Flange Lateral Restraint Member Section Constant for Web Buckling Form Factor for Web Buckling α =m mm kNm kNm kNm kNm α =s mm mm kNm M =table mm kNm kNm kNm PM =flag λ =e 8.85 λ =ey 14 b ∣d =fe e 178 mm A =fc 31700 mm2 A =fg 1940 mm2 A =fn,min 1660 mm2 A =ft 1940 mm2 A =fm 1940 mm2 d =f 392 mm M =f 243 kNm ϕM =f 219 kNm r = mm kNm kNm kN kN ϕ = 0.9 B =d 218 mm One Flange Only α =b 0.5 k =f 1 mm Moment Capacity (AS4100-1998, Cl 5.1 & 5.6.1-2) Shear - Bending Moment Interaction (AS4100, Cl 5.12) Bearing Capacity (AS4100, Cl 5.13) 11
- 12. Member Slenderness Reduction Factor for Web Position ( ) Geometric Slenderness Factor Factor Factor Factor Factor Slenderness Reduction 0 251 284 7.26 287 0.892 0.593 0.0896 4 251 284 7.26 287 0.892 0.593 0.0896 15 251 284 7.26 287 0.892 0.593 0.0896 Bearing Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Interior Location? ( ) Reaction ( ) Bearing Yield Capacity ( ) Bearing Buckling Capacity ( ) Factored Bearing Capacity ( ) Bearing Utilisation ( ) 0 1 1.52 622 128 115 0.0132 4000 1 55.5 622 128 115 0.483 15000 1 69.6 622 128 115 0.607 Bending & Bearing Capacity Per Support Position ( ) Reaction ( ) Factored Bearing Capacity ( ) Governing Moment Demand ( ) Factored Moment Capacity ( ) Bending & Bearing Utilisation 0 1.52 115 0 300 0 4000 55.5 115 -44.6 300 0 15000 69.6 115 -79.1 300 0 Short-Term Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Short-Term Deflection ( ) Short-term Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 4000 Int 0.358 10 0.0358 11000 Int -4.13 10 0.413 5000 Cant -9.12 10 0.912 Long-Term Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Long-Term Deflection ( ) Long-term Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 4000 Int 0.269 10 0.0269 11000 Int -3.11 10 0.311 5000 Cant -6.86 10 0.686 Imposed Load Deflection Per Span Span Length ( ) Span Type Imposed Load Deflection ( ) Imposed Load Deflection Limit ( ) Deflection Utilisation 4000 Int 0.296 10 0.0296 11000 Int -3.42 10 0.342 5000 Cant -7.54 10 0.754 Comments Steel Beam Analysis and Design to AS4100-1998 (R2016). Assumes: (1) Beam is of uniform cross-section along its full length, (2) Detailing requirements are checked separately, (3) Net areas are equal to the gross area with maximum allowed holes. α =c,table mm R =table mm kN kN kN kN kN kN r = mm kN kN kNm kNm D =ST mm mm mm D =LT mm mm mm D =Q mm mm mm Bending & Bearing Capacity (AS4100, Cl 5.13.5) Deflection Analysis Comments Assumptions 12
