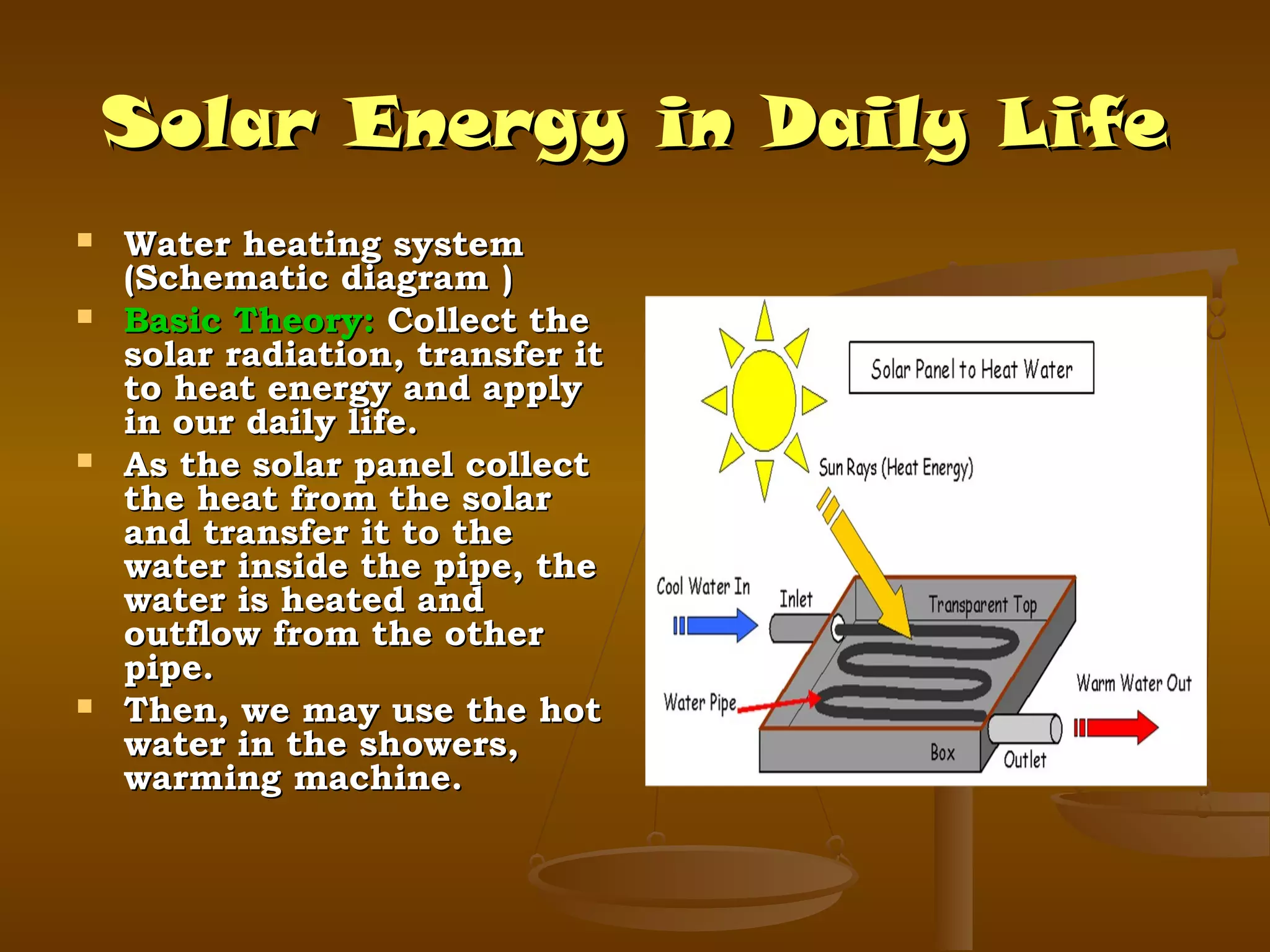
The document discusses solar energy, including its definition as radiant light and heat from the sun that is transformed into different types of energy. It is the most abundant renewable energy source and is commonly collected using solar panels. It has advantages like being long-lasting, silent and non-polluting, but disadvantages including high initial costs. Applications include powering houses, water heating, farming, and generating electricity through photovoltaic cells.