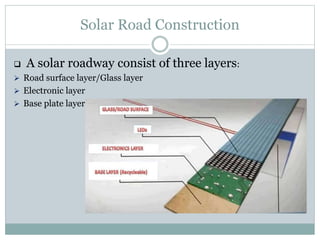
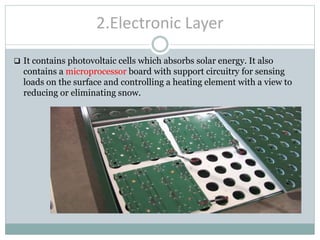
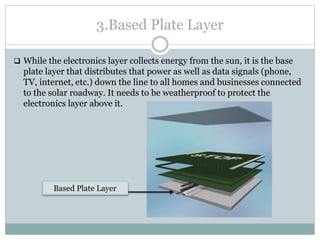
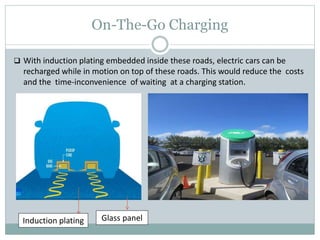
This document discusses the concept of solar roadways, which embed solar panels and LED lights below a tough glass surface to generate electricity and illuminate roads. A solar roadway consists of a glass top layer, an electronic layer containing photovoltaic cells and controls, and a base plate layer that distributes power. Solar roadways could power electric vehicles through induction charging and provide an intelligent transportation system by programming LED lights. While maintenance costs are a concern, solar roadways could meet a significant portion of India's electricity needs if implemented nationwide and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.