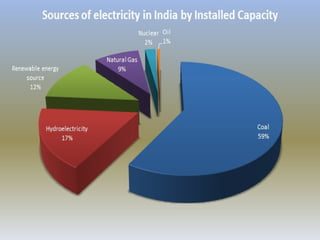
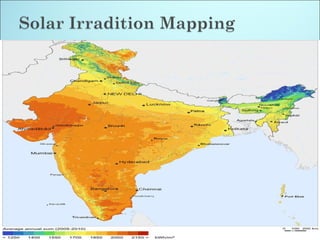
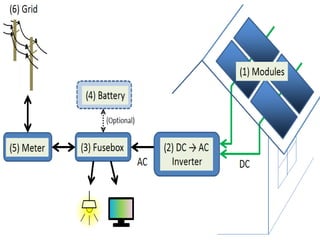
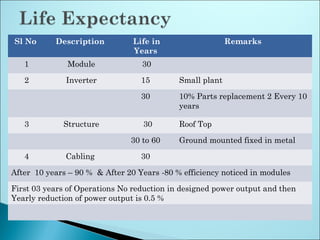
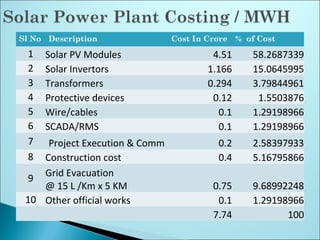
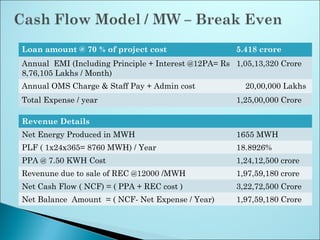
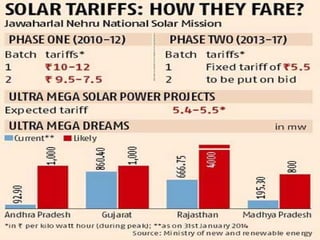
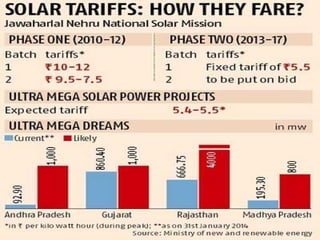
The document outlines the key steps in site identification and project pre-feasibility for solar power projects. These include identifying suitable land characteristics like soil type and drainage; assessing solar radiation and shadows; conducting geological, social, and evacuation feasibility studies; selecting technology; and performing financial pre-feasibility analysis. Key site requirements include plain land near substations with proper road access and drainage. Financial analysis covers costs, revenue, cash flows, and break-even time.