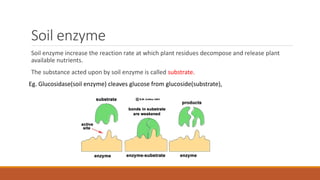
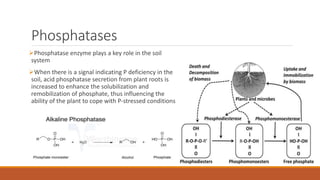
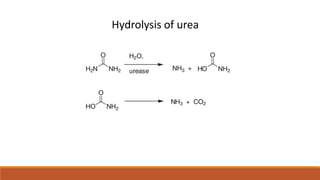
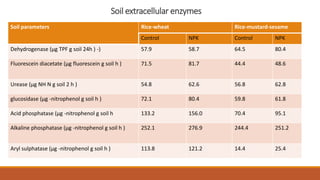
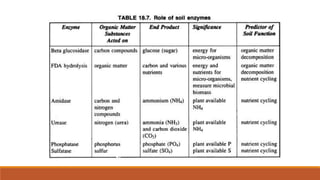
The document discusses the role and importance of soil enzymes in increasing nutrient availability through the decomposition of plant residues. It categorizes enzymes into types and classifications, including oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, and others, explaining their functions and significance in soil health and fertility. Additionally, it highlights how soil enzyme activity serves as a biological indicator of soil quality and ecosystem health.