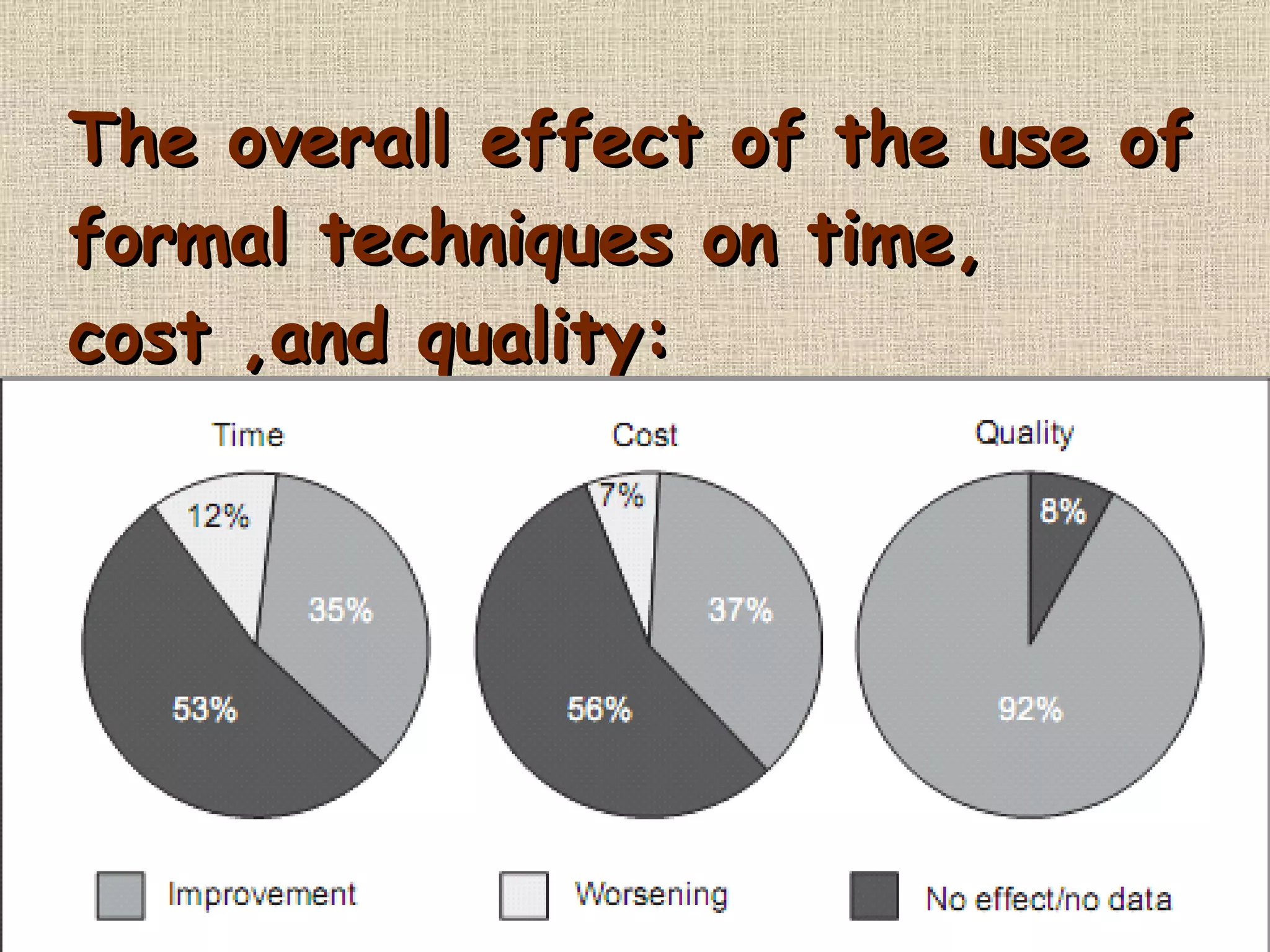
Formal methods are mathematically based techniques for specifying, designing, and verifying software systems. Formal specifications precisely state what software should do without describing how. Formal verification rigorously proves an algorithm's correctness against a specification using logical rules. While formal methods reduce errors, the cost of full formalization is often prohibitive for industry; lightweight formal methods employing partial specification and focused analysis are alternatives.