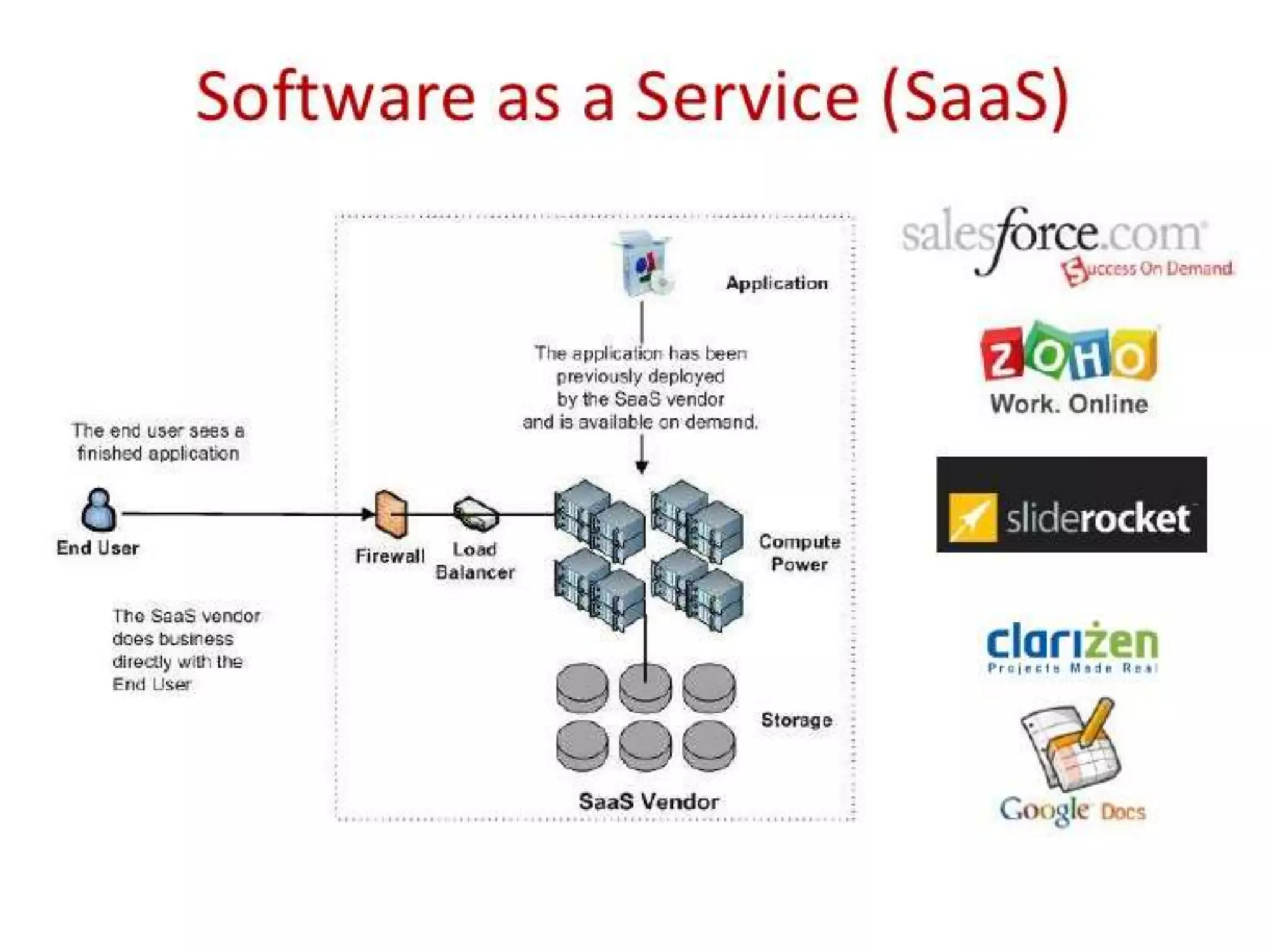
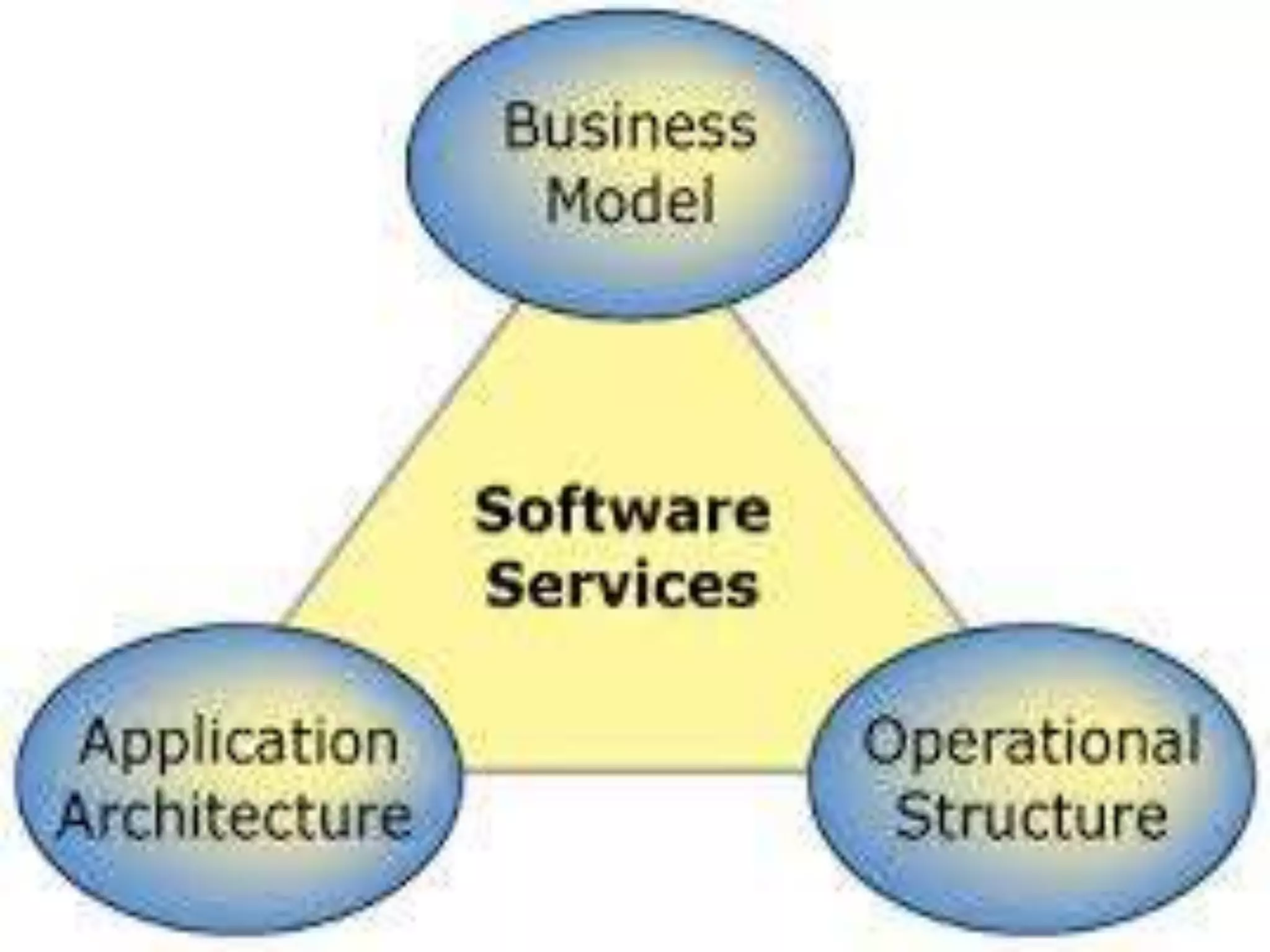
The document provides an overview of Software as a Service (SaaS), detailing its definition, characteristics, types, architecture, and major providers. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of SaaS, highlighting aspects such as ease of use, scalability, and security concerns. The conclusion emphasizes the importance and maturity of SaaS in modern application development and deployment.