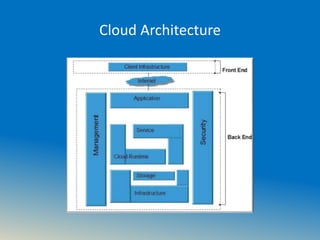
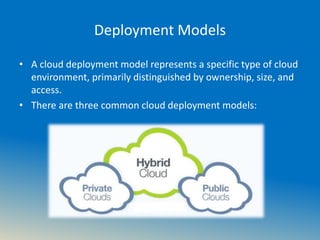
The document discusses cloud computing, including what it is, its history and benefits. It defines cloud as the delivery of computing services over the internet and discusses common cloud characteristics like on-demand self-service and rapid elasticity. It describes the different cloud models including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS). The document also provides an overview of Microsoft Azure, a flexible cloud platform, and concludes by noting that while cloud computing offers benefits, security remains a challenge that could slow adoption.