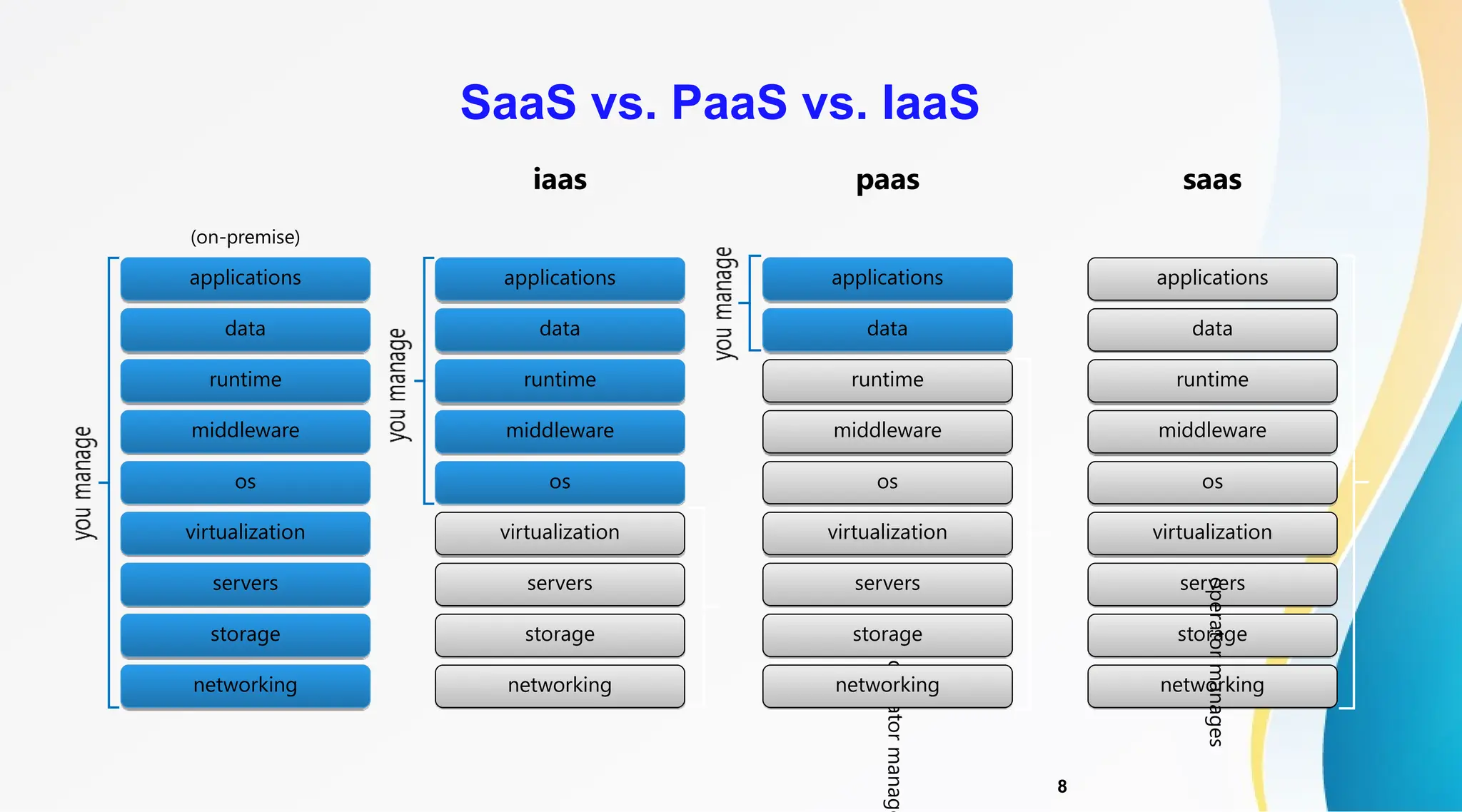
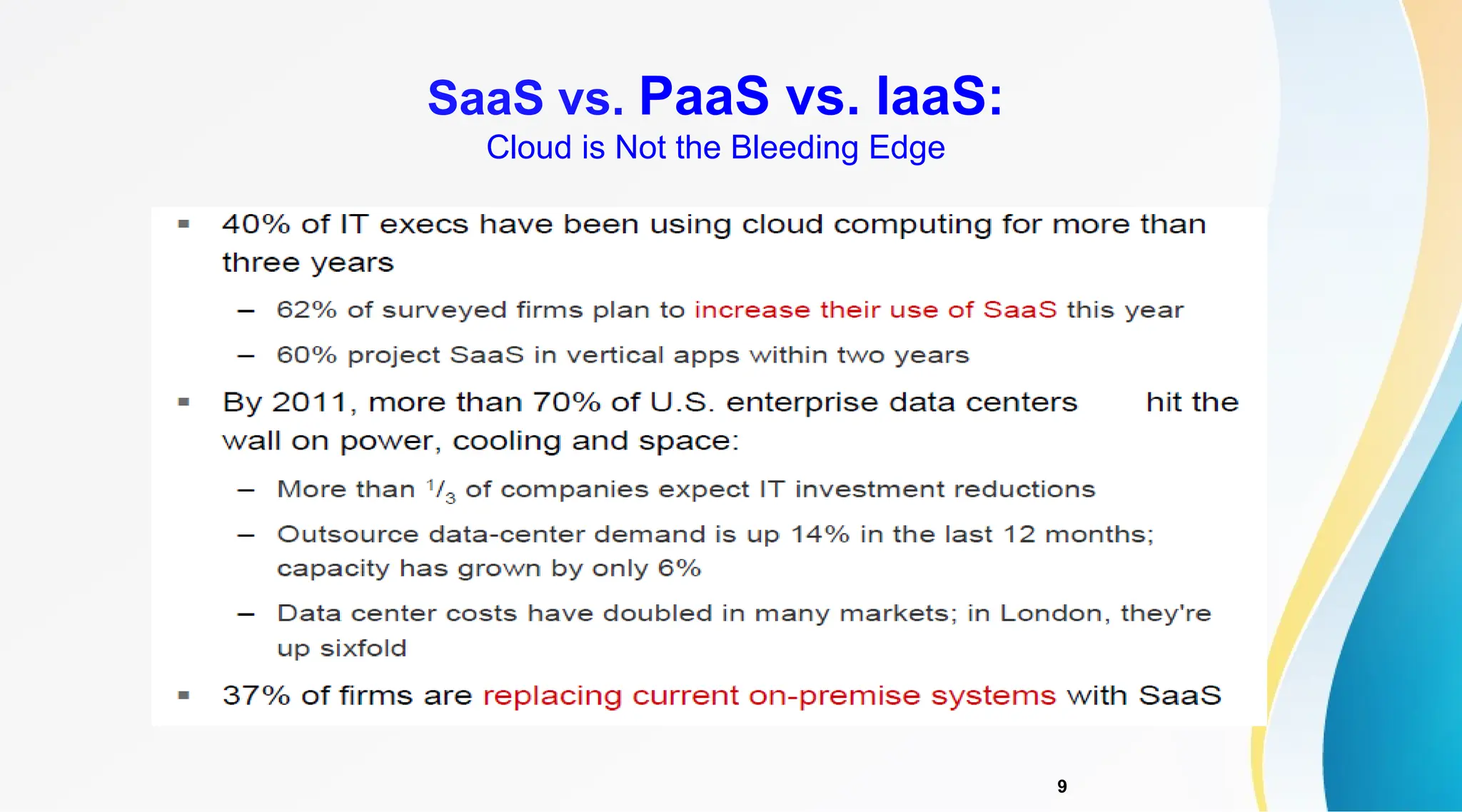
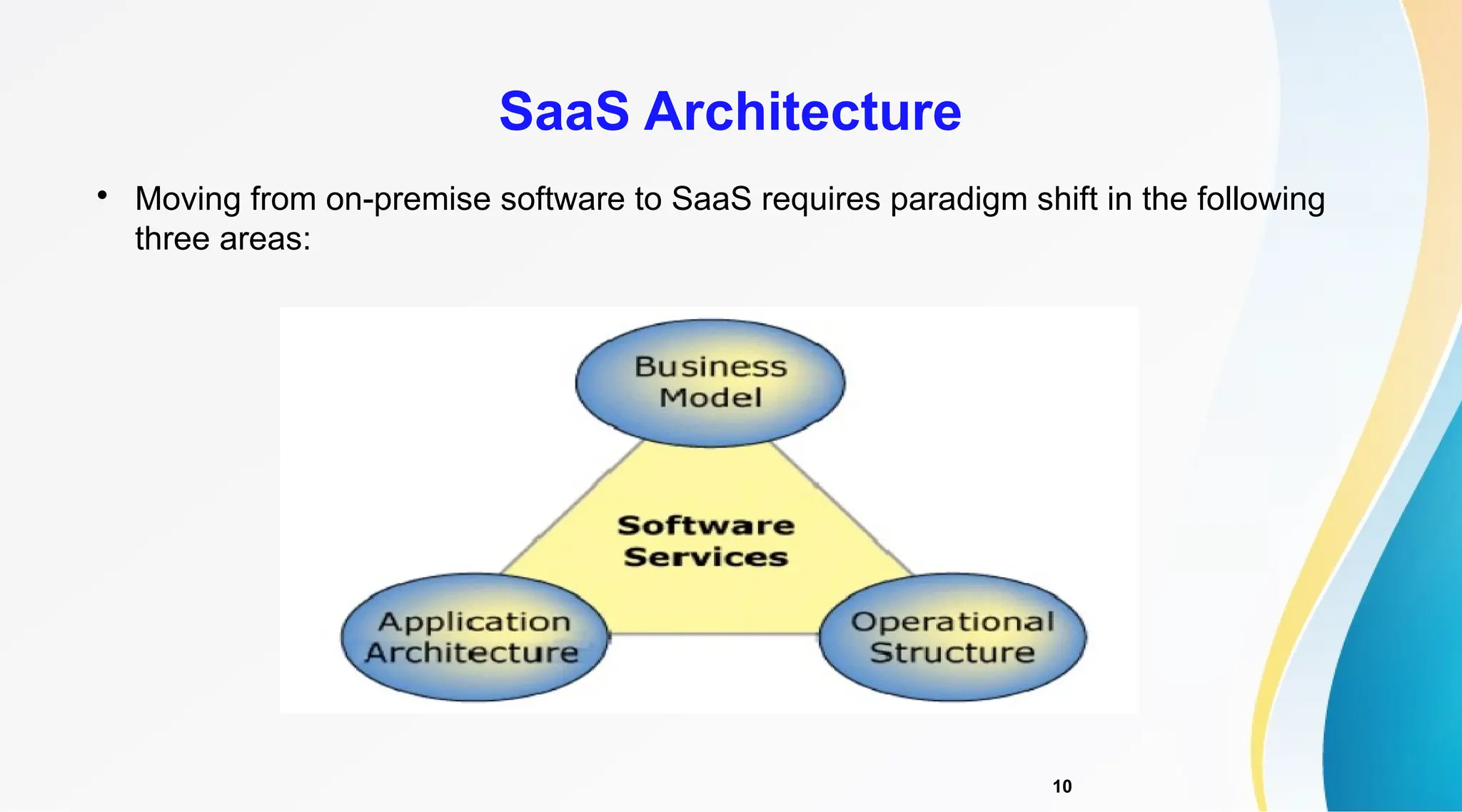
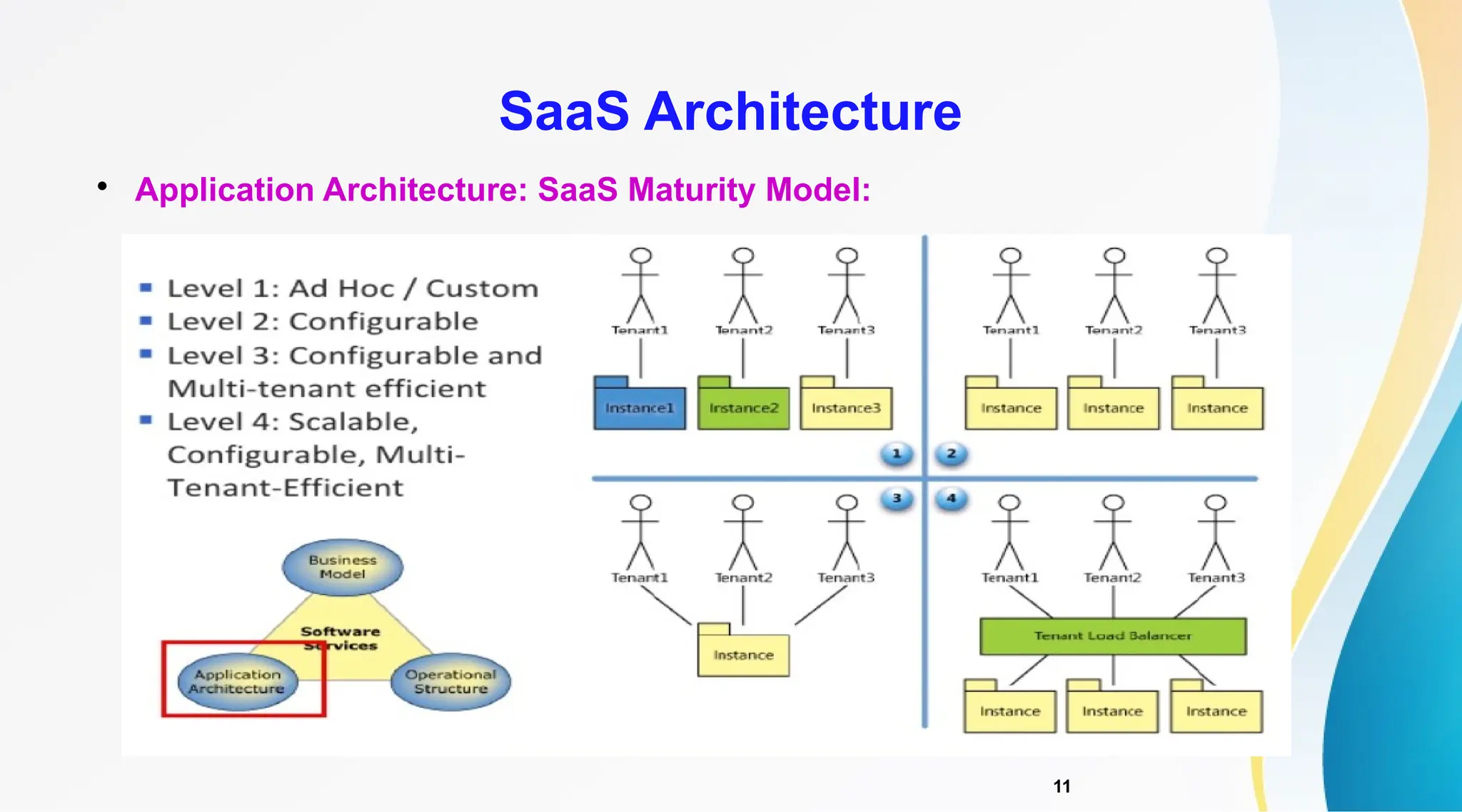
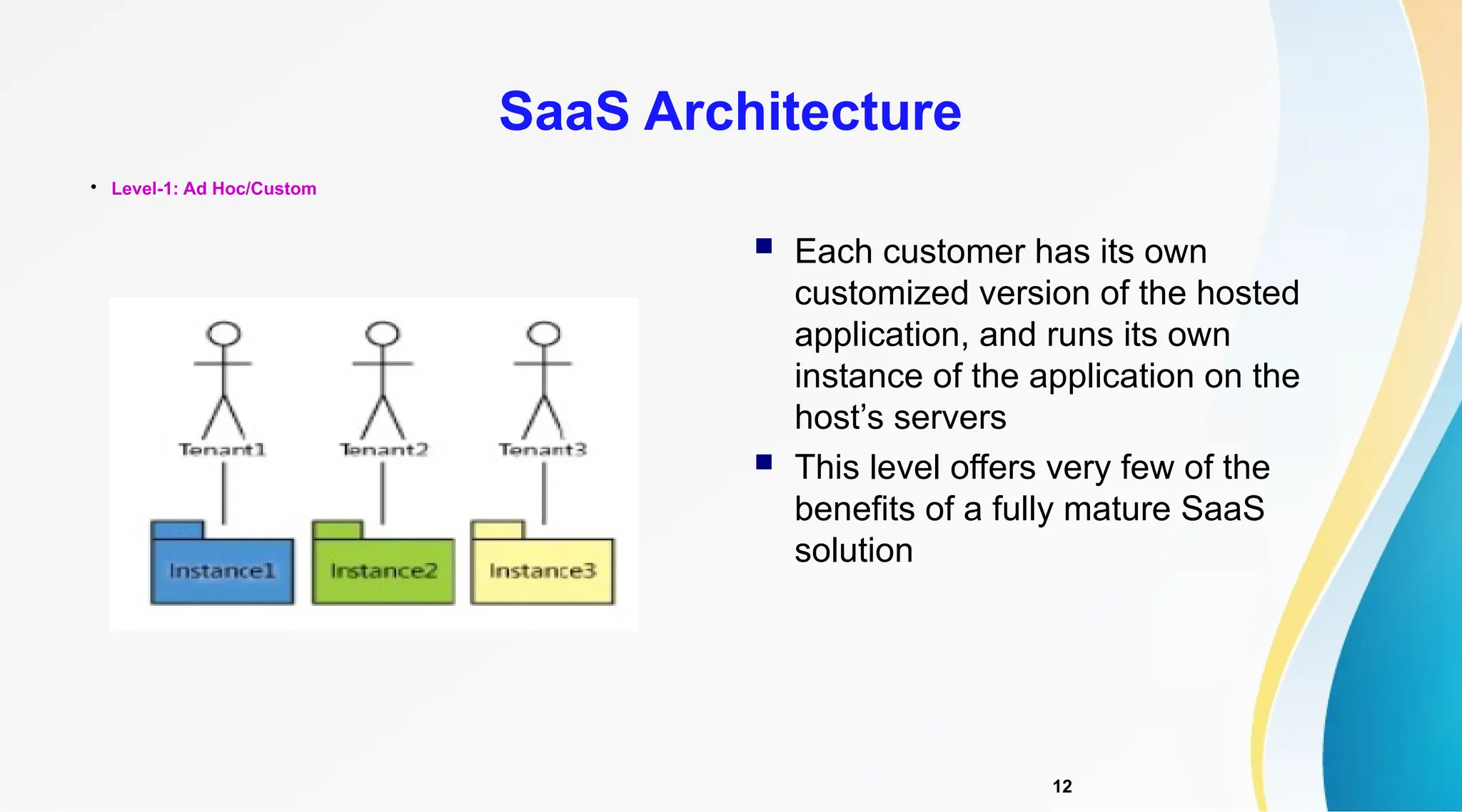
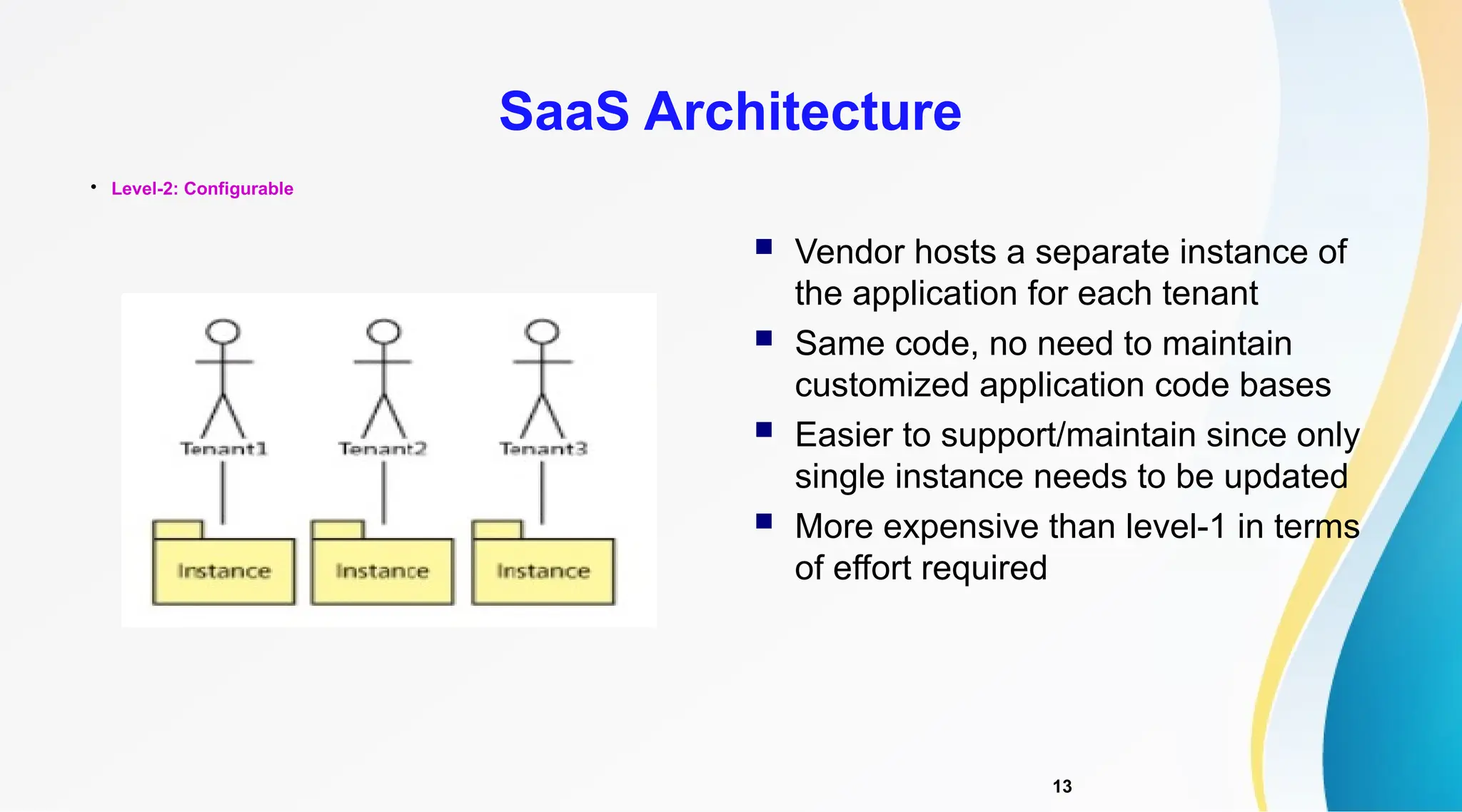
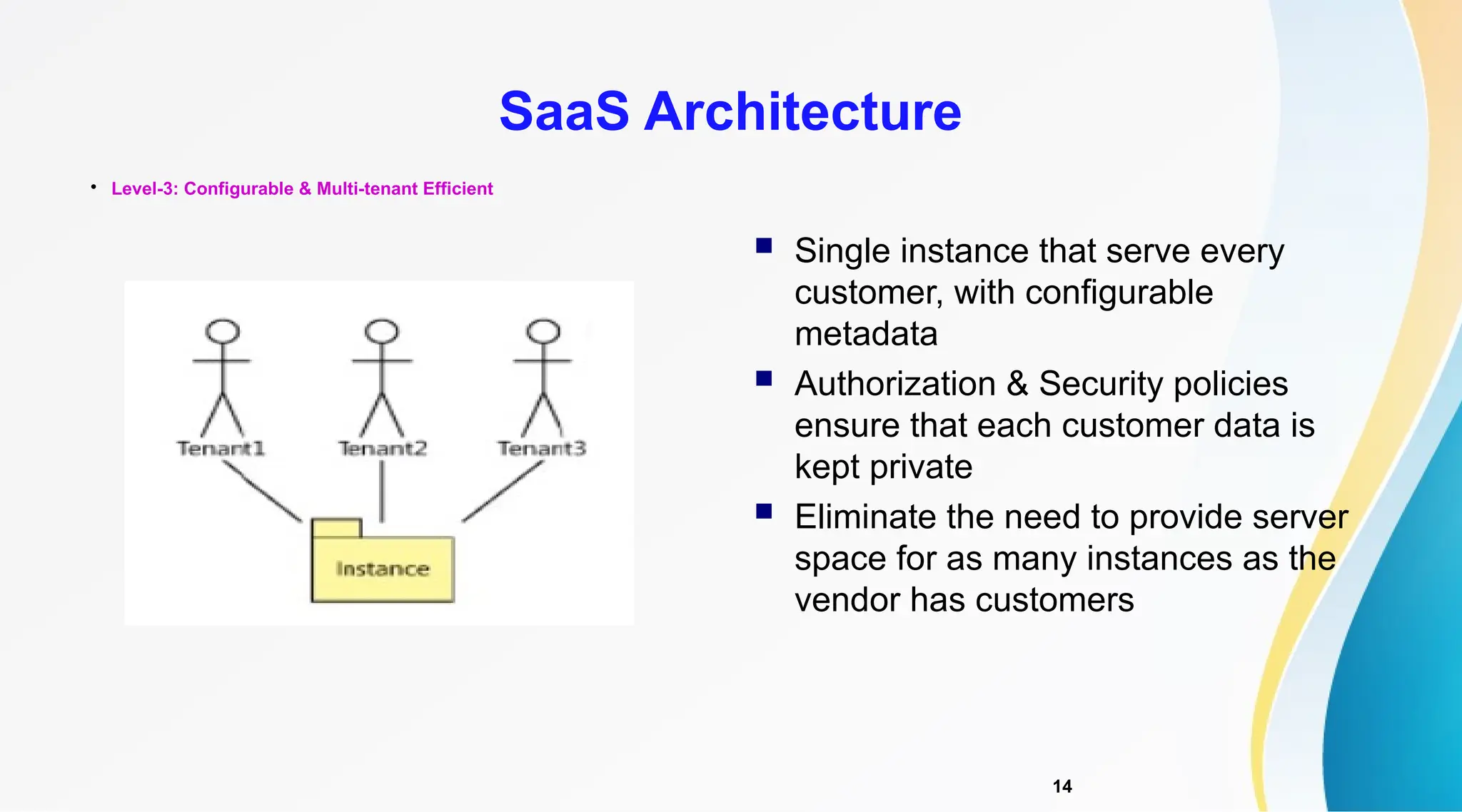
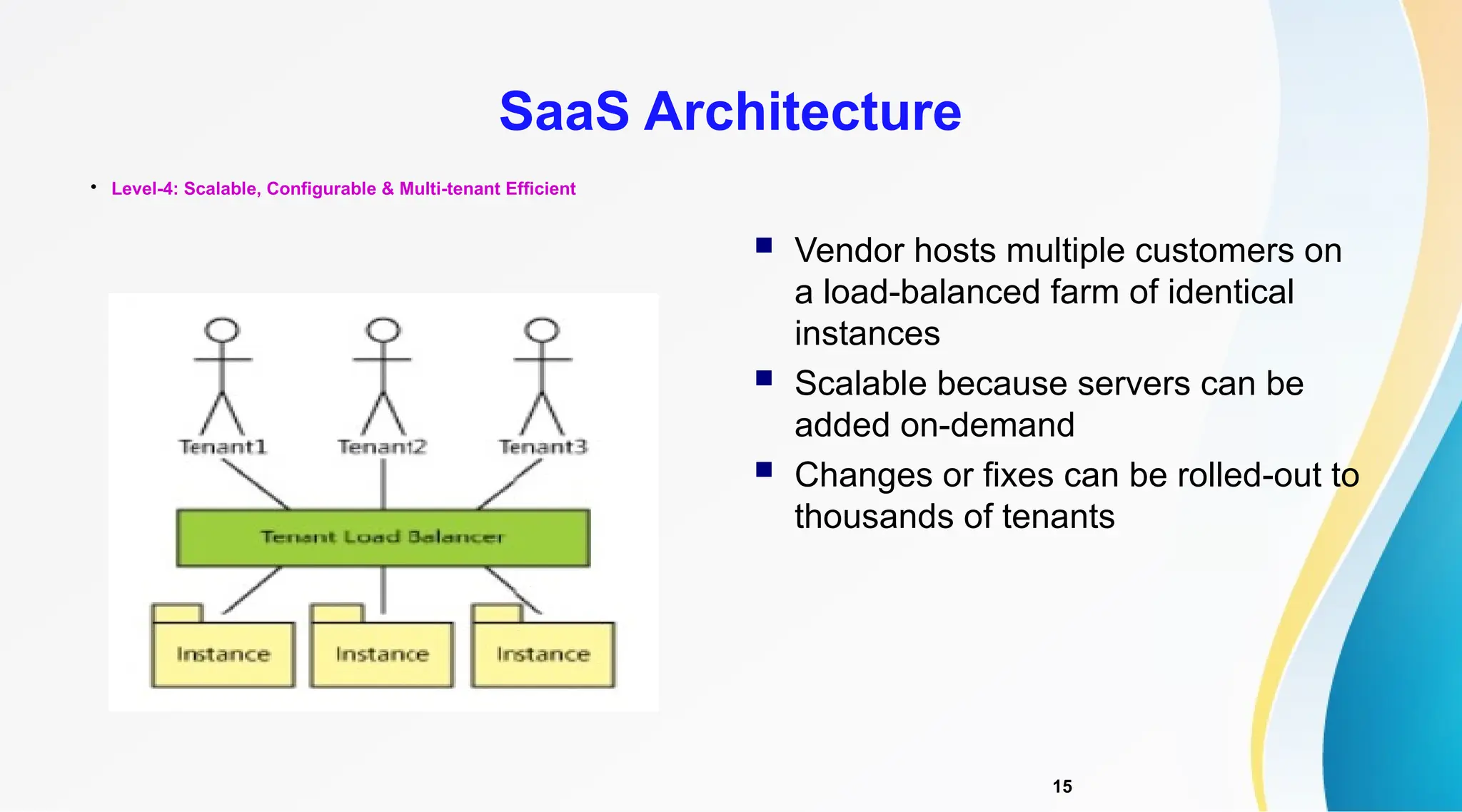
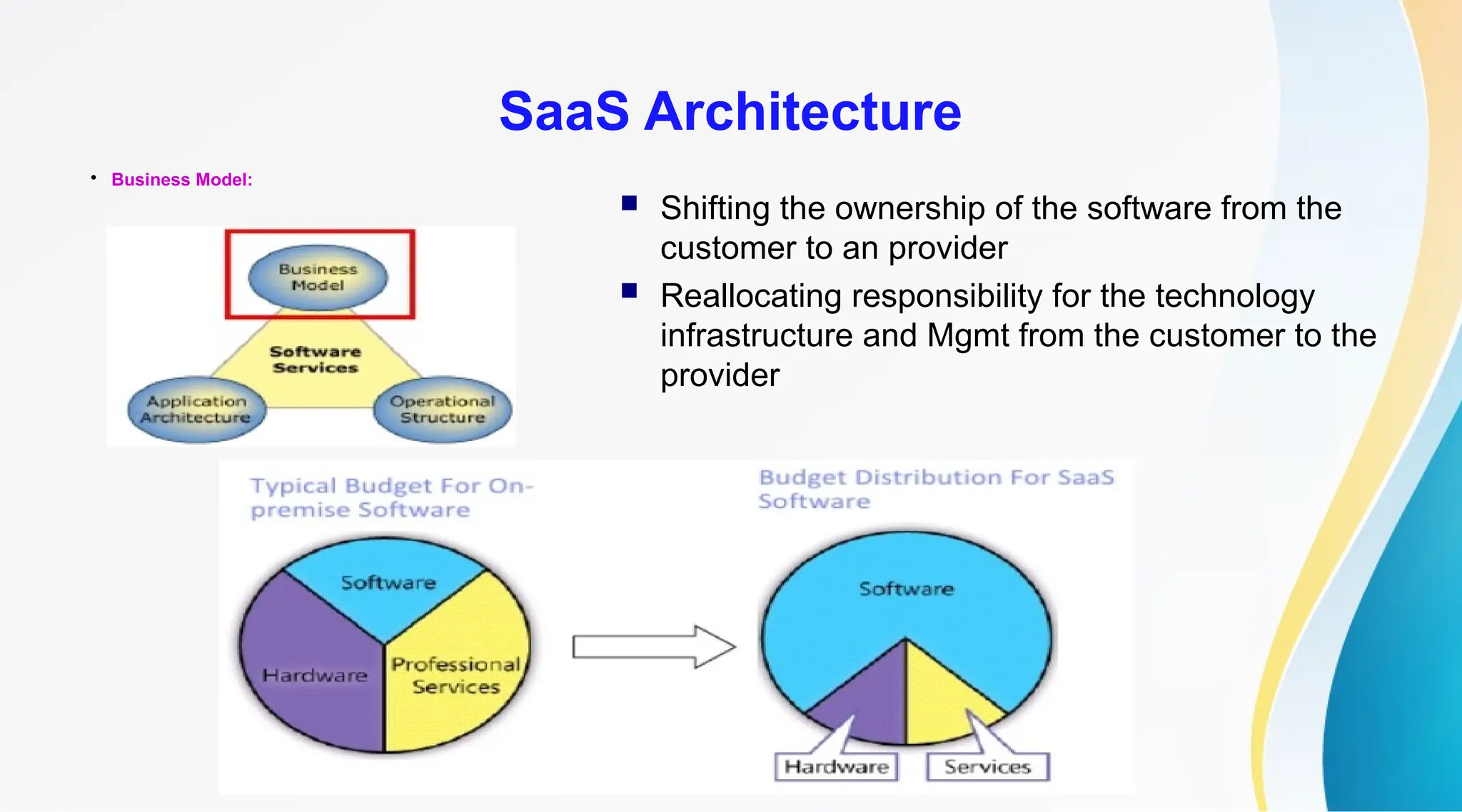
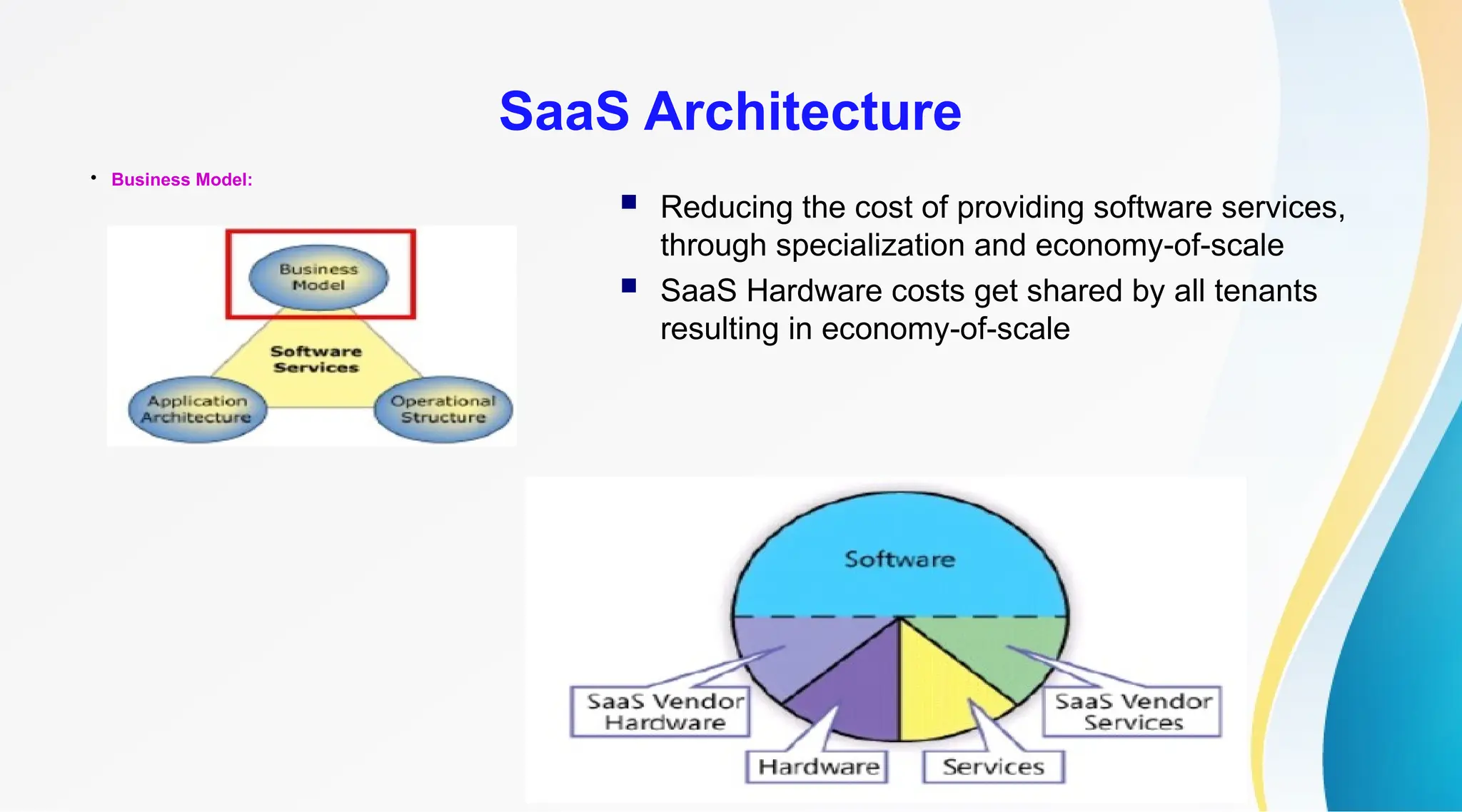
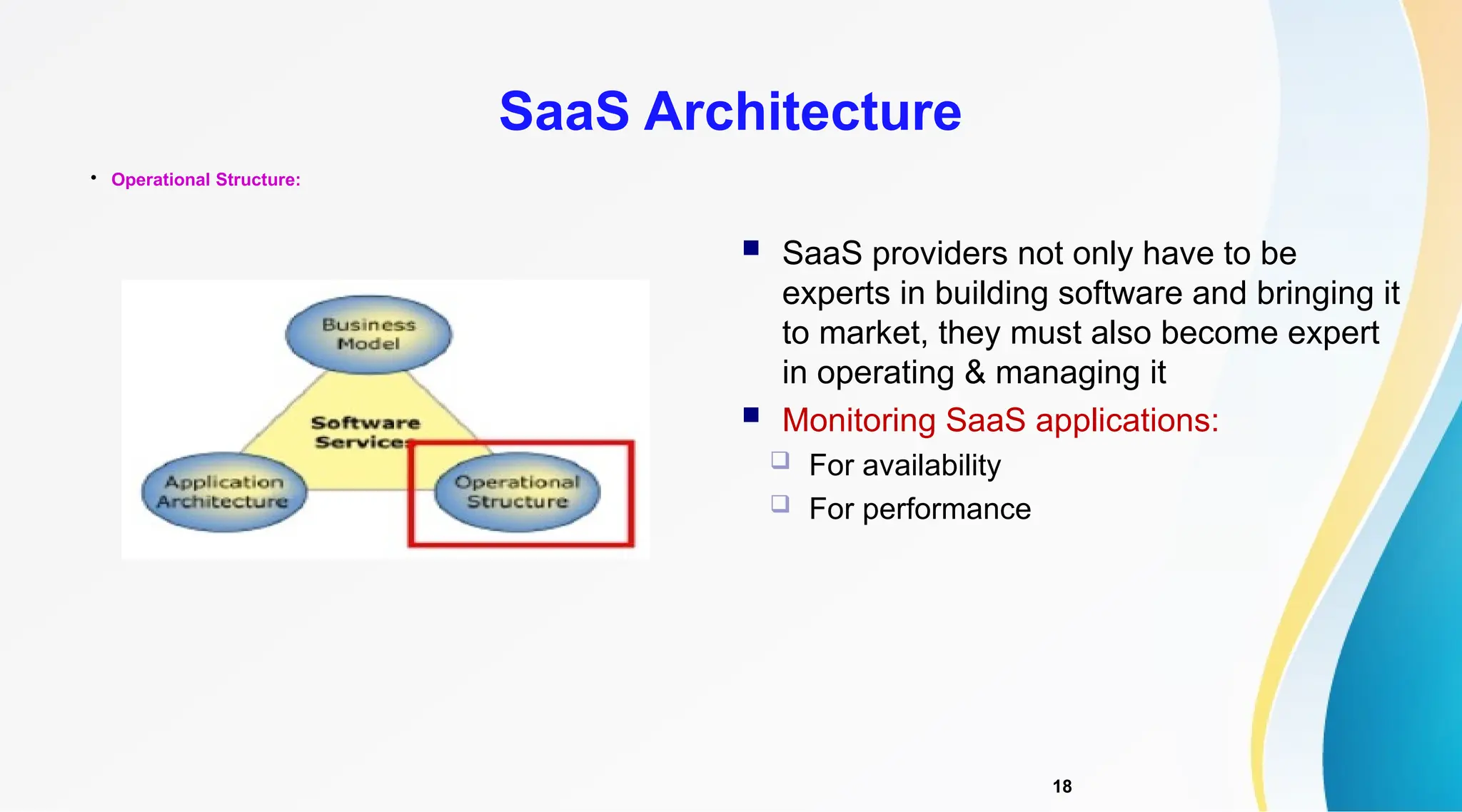
The document discusses Software as a Service (SaaS), its advantages for users and vendors, and comparisons with Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It outlines various SaaS architecture levels, highlights its applications across different business sectors like customer relationship management, human resources, and financial services, and provides examples of popular SaaS products. Overall, SaaS enables lowered costs and easier management for businesses by facilitating web-based software access without the need for significant hardware investments.