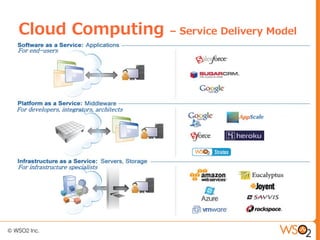
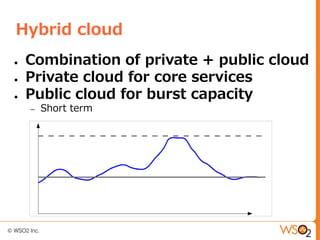
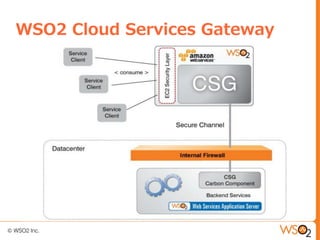
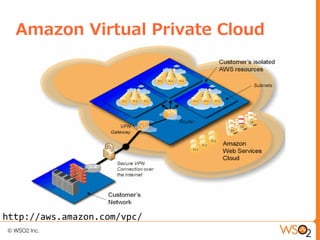
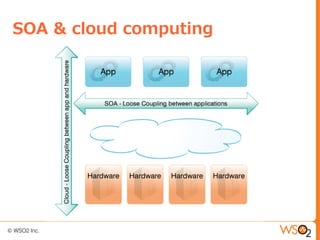
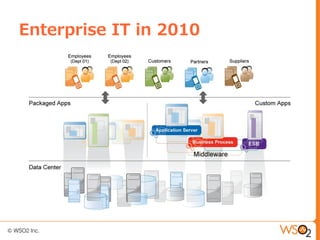
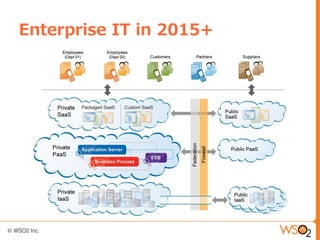
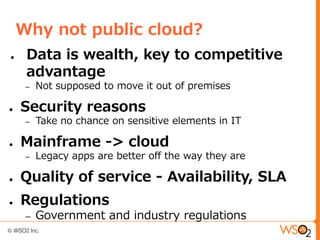
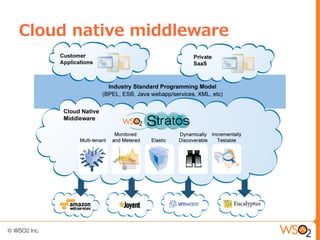
This document discusses setting up a private cloud and compares it to public cloud options. It defines cloud computing models including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). It then describes private, public, hybrid, and community cloud deployment models. The document focuses on setting up a private IaaS cloud using Ubuntu Enterprise Cloud (UEC) to provide infrastructure on an organization's own data centers. It notes the prerequisites for private cloud, and recommends also implementing a PaaS on top of the IaaS for a more complete platform to develop cloud native applications.