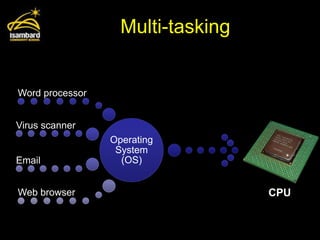
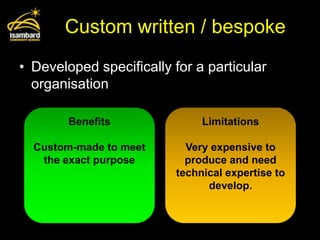
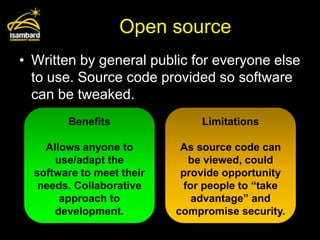
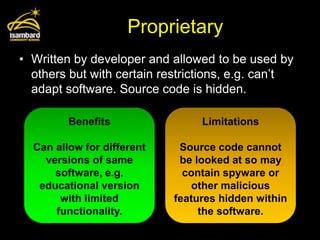
This document discusses operating systems and software development. It defines the main functions of an operating system as memory management, user interface, multi-tasking, peripheral management, and security. It also describes different types of software development including custom written, off-the-shelf, open source, and proprietary software. The document provides examples of benefits and limitations of each approach.

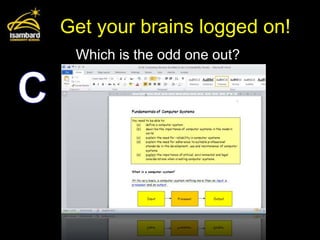



![User interface
• The OS provides the user with a way of
controlling the functions of the computer
without resorting to machine code.
• It can be:
Graphical (GUI – Graphic User Text-based [no mouse] (CLI –
Interface), e.g. Windows Command Line Interface), e.g. MS-DOS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/software-120126022744-phpapp01/85/Software-7-320.jpg)