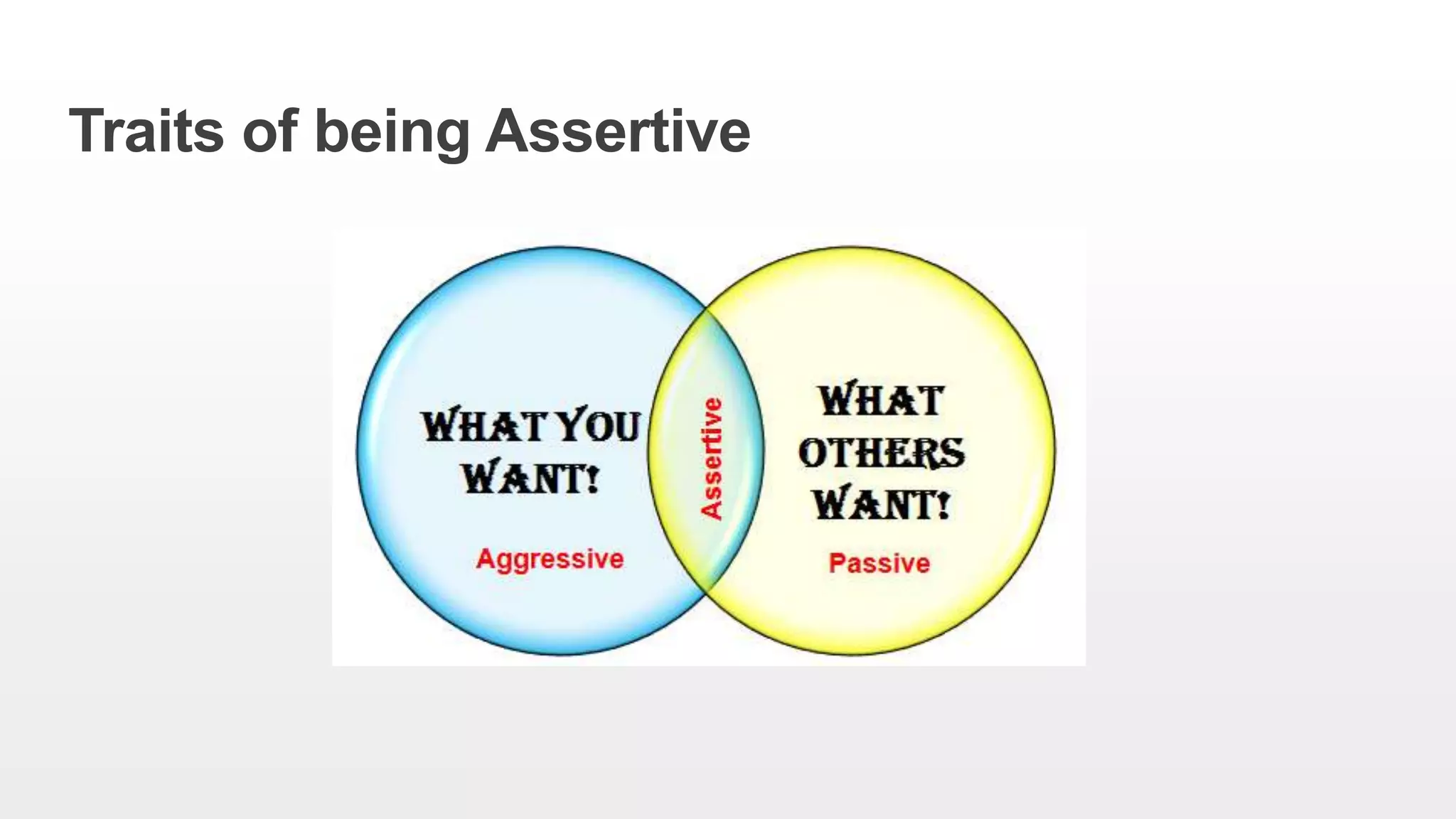
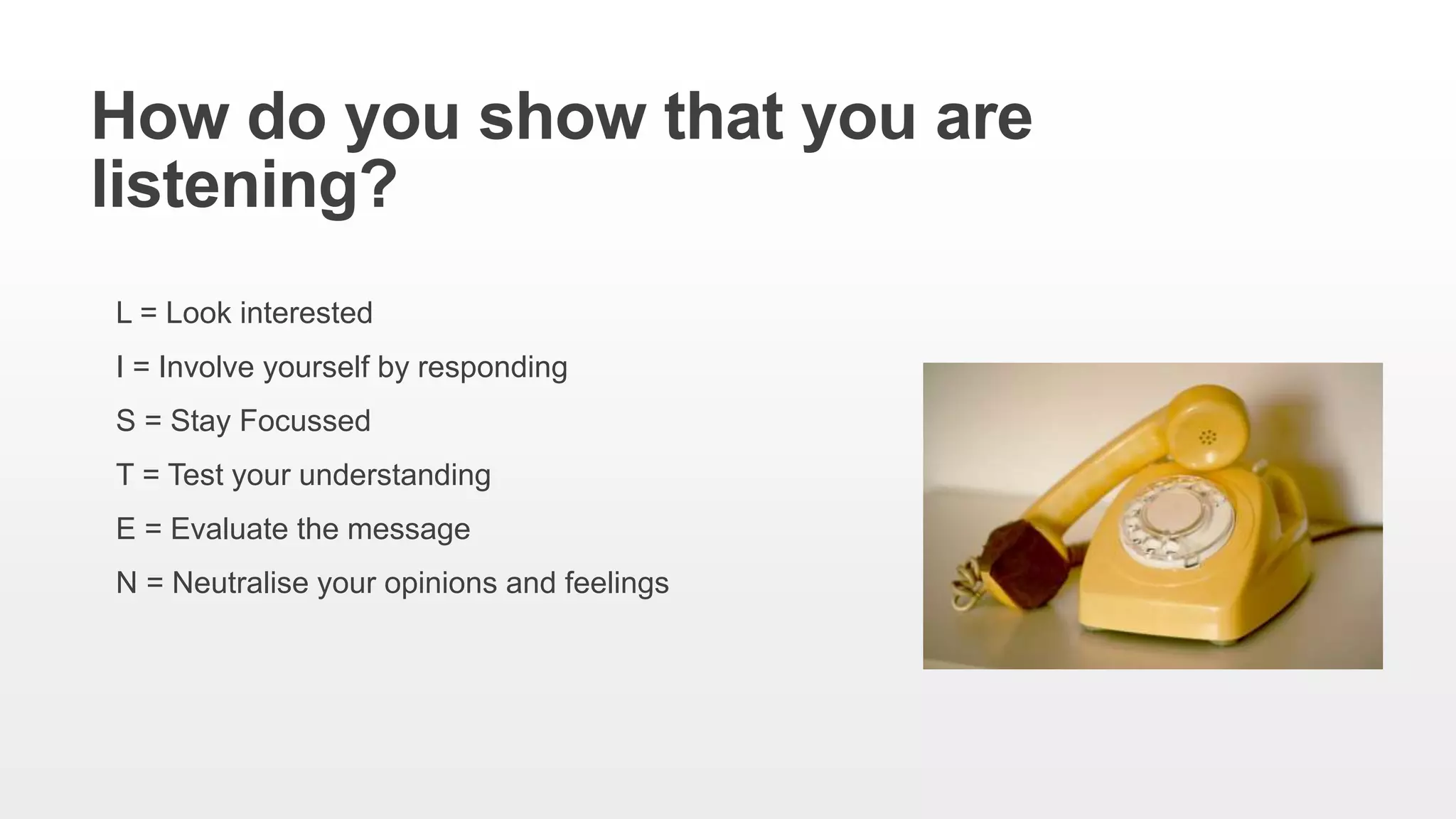
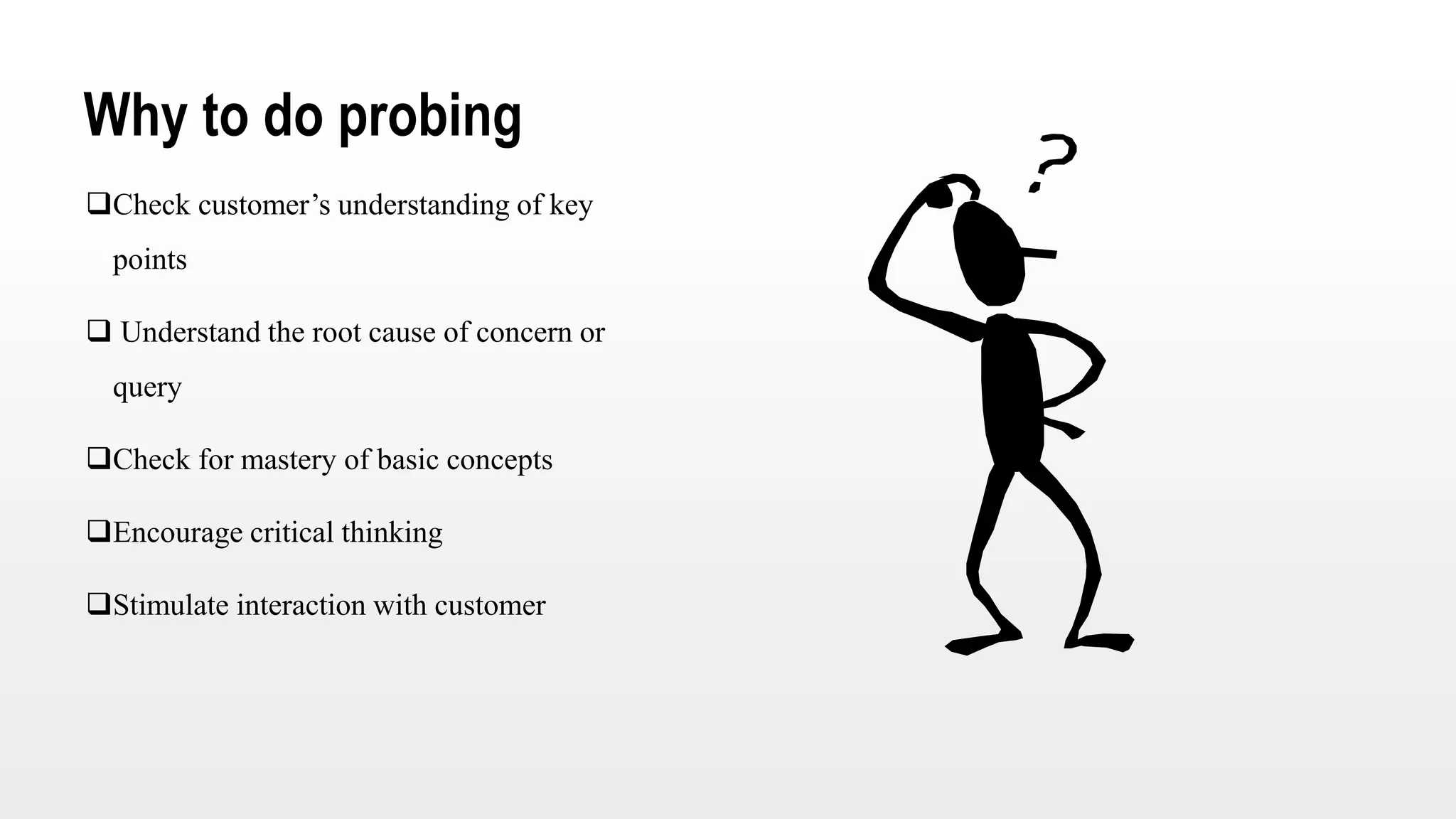
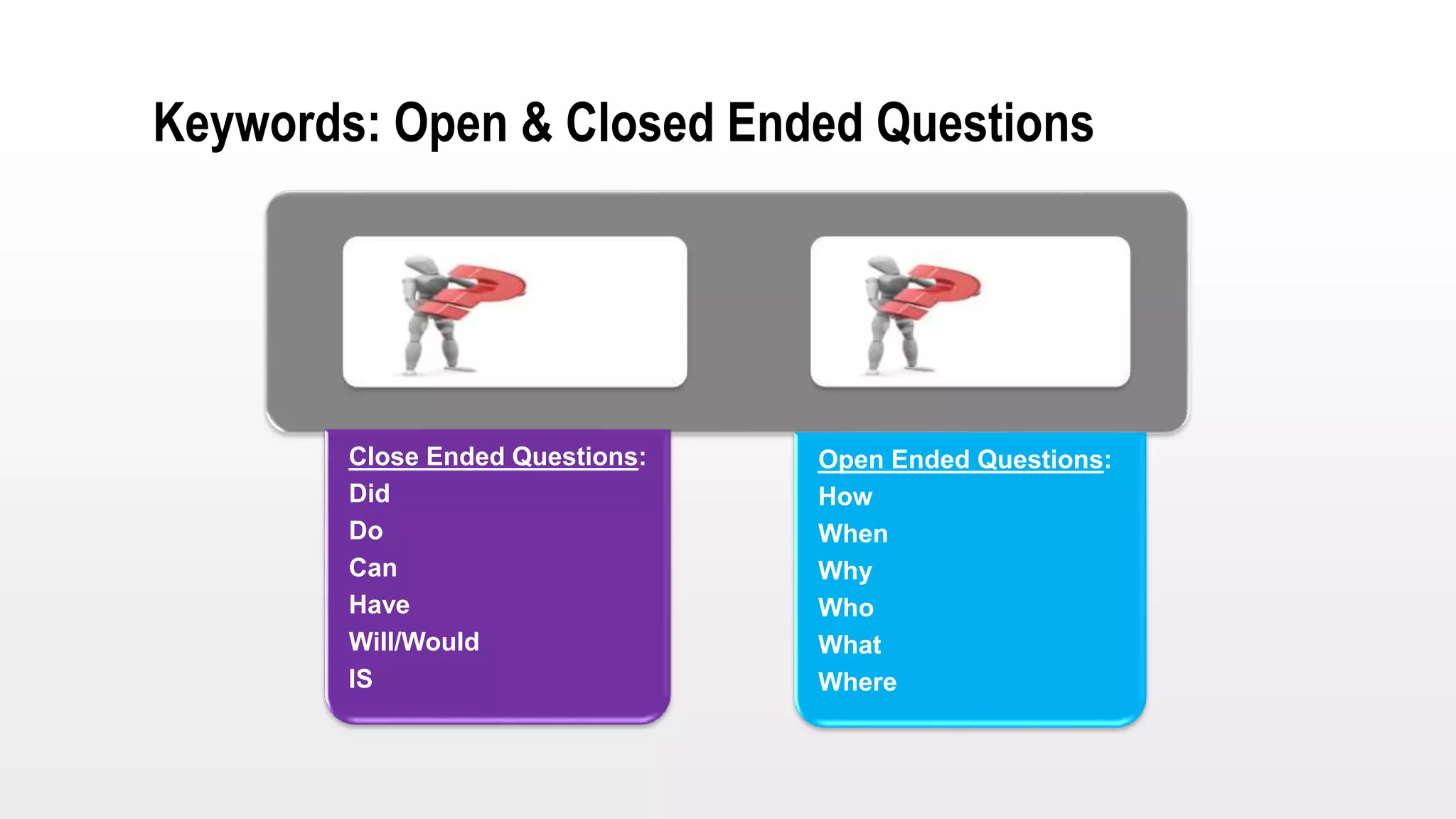
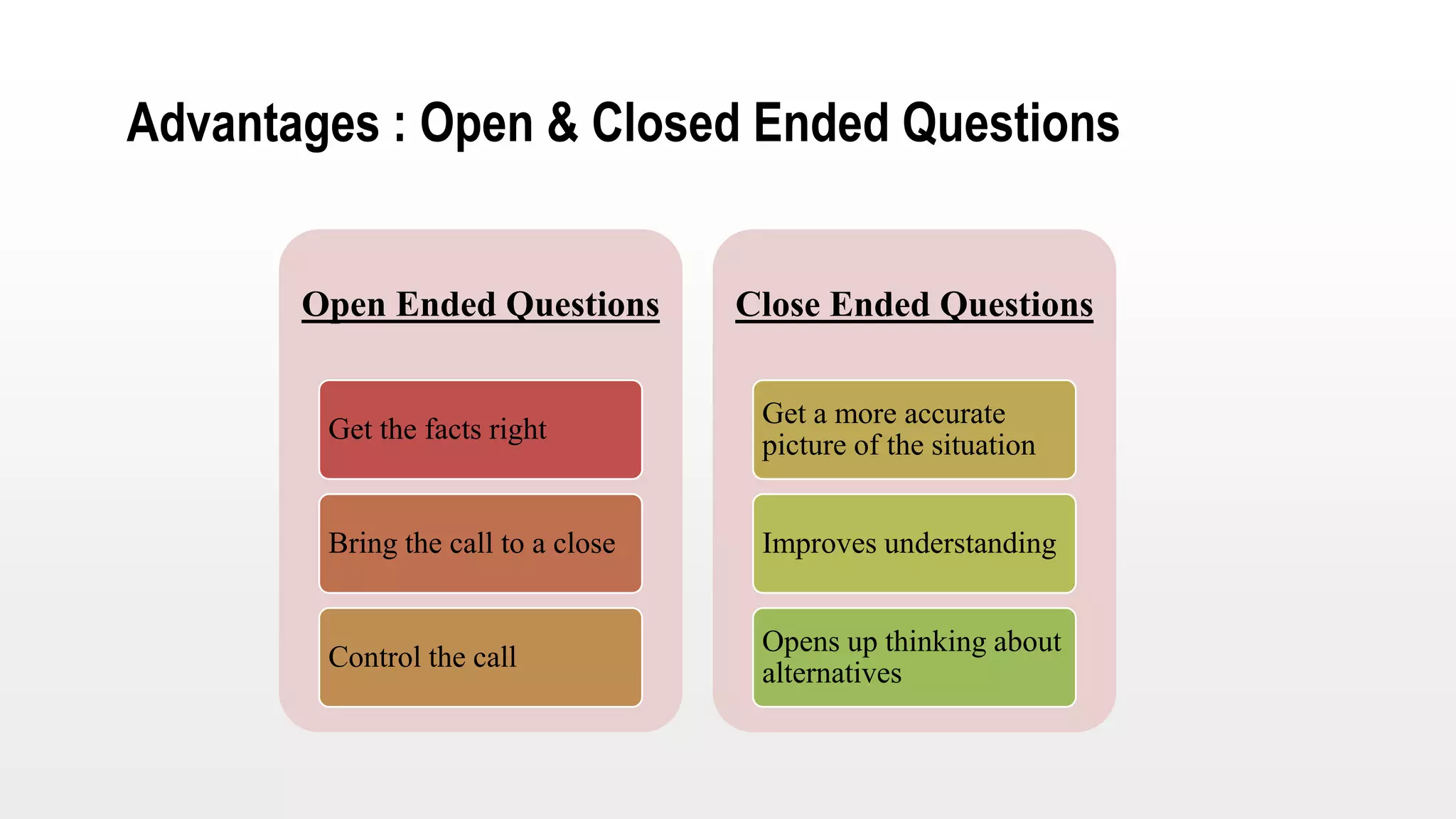
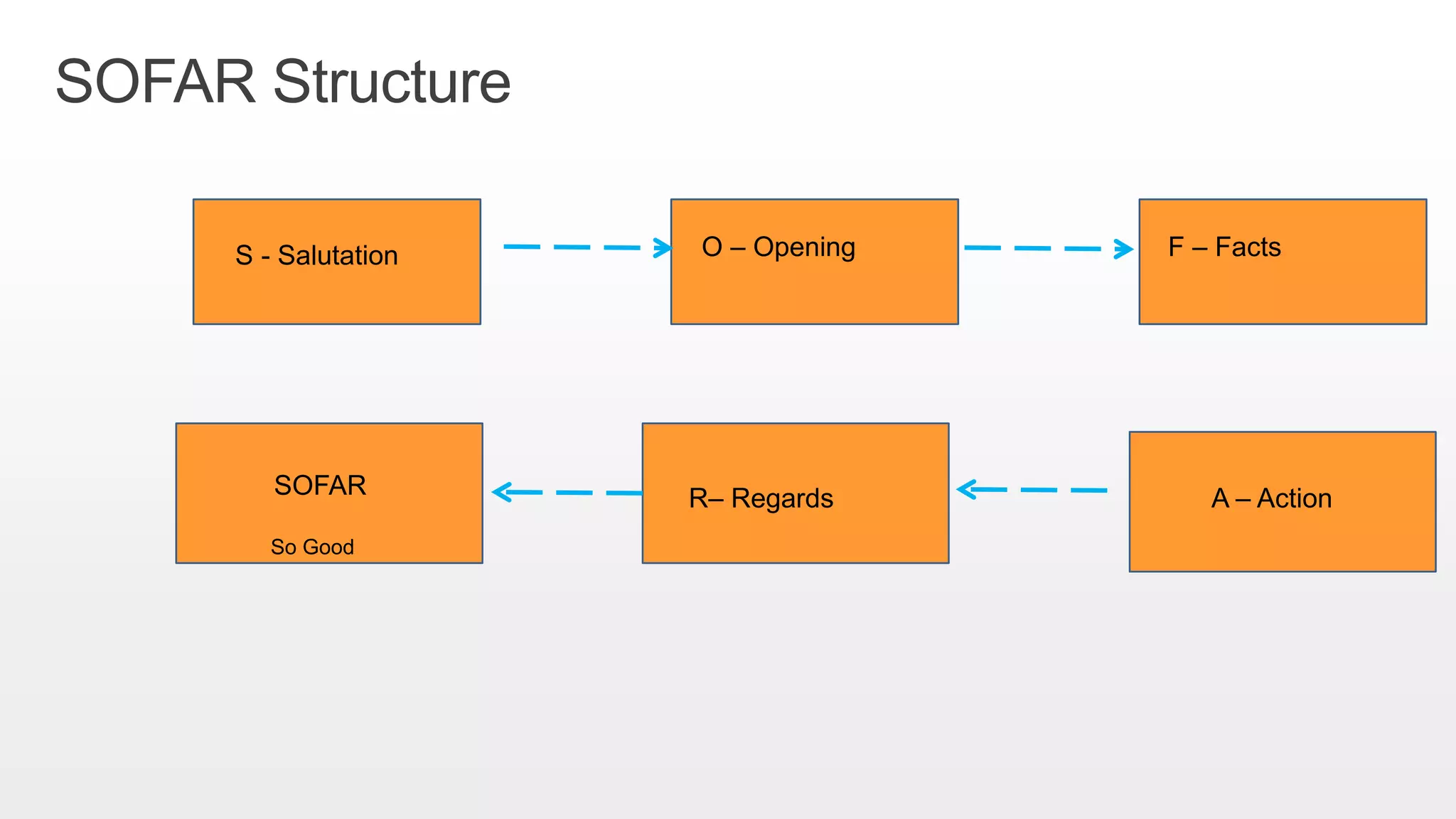
This document provides an overview of soft skills training related to communication. It discusses the importance of communication and defines various communication styles. The document outlines barriers to communication and effective verbal communication techniques. It also describes listening skills, questioning techniques, email etiquette, and telephone etiquette to ensure clear and effective communication.