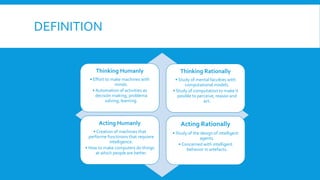
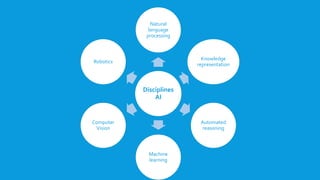
The document discusses various approaches to artificial intelligence (AI), focusing on understanding and replicating human thought processes. It outlines key methodologies such as the Turing Test for assessing intelligence, cognitive modeling for studying human reasoning, and the rational agent approach for autonomous decision-making. It highlights challenges and advantages in translating informal knowledge into formal logical notation, along with the limitations of rationality in practical scenarios.