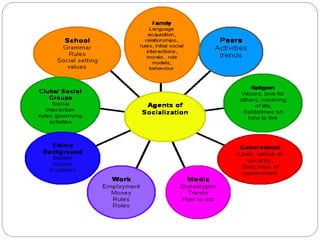
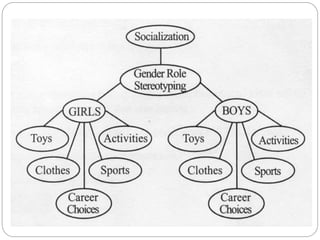
This document discusses human socialization and development. It states that while infants have the innate capacity for social learning, they cannot develop into social beings without interaction with other humans. The process by which people learn the roles and norms necessary to function in their society is called socialization. Socialization is influenced by both nature (heredity) and nurture (environmental and social influences). The family, school, peer groups, media, and religion are some of the key agents of socialization that teach people the culture and help them develop relationships. Severe social isolation can damage human development, as shown by cases of children deprived of social contact.