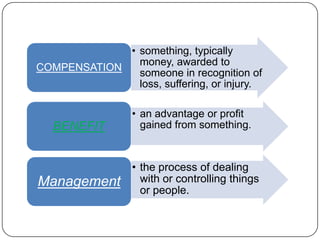
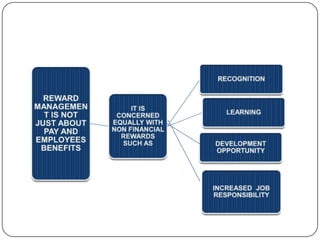
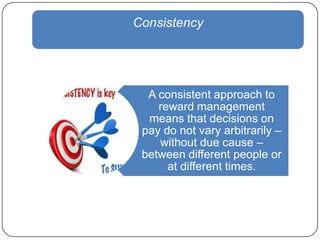
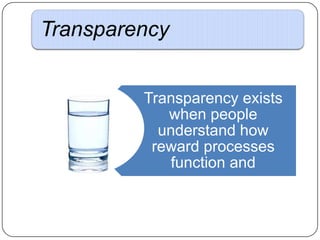
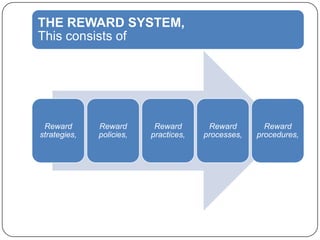
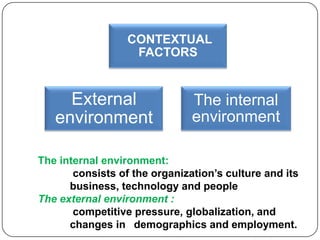
This document provides an overview of reward management (also known as compensation and benefit management). It defines reward management as dealing with strategies, policies and processes to recognize employee contributions both financially and non-financially. The aims of reward management are to motivate employees, align rewards with business goals, and develop a high-performance culture. These aims are achieved through developing strategies, policies and practices based on principles of fairness, equity, consistency and transparency. The key elements of a reward system include base pay, contingent pay, benefits, job evaluation, market analysis, grade structures and performance management. Factors influencing reward management include the organization's context and environment as well as conceptual factors related to strategic management and human behavior.