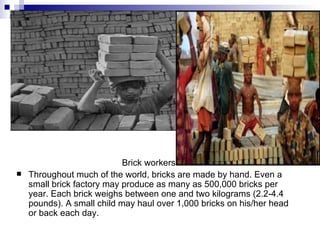
Child labour is a significant social and economic problem in India, where an estimated 20-50 million children work. Children as young as 6 years old work long hours in difficult conditions in various industries like carpet factories, brick kilns, quarries and shops. Poverty is a major driving factor, as many families rely on children's wages for survival. Laws prohibit child labour in hazardous occupations but enforcement remains a challenge. To fully address the issue, greater efforts are needed to reduce poverty, increase access to education and enforce child labour laws.