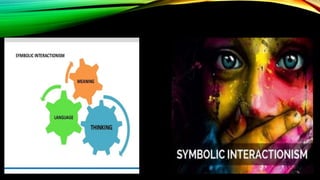
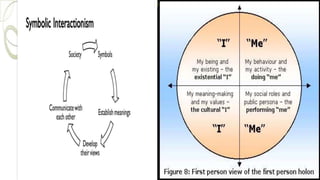
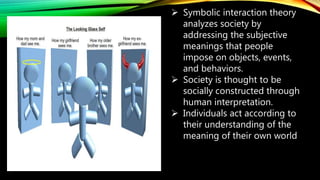
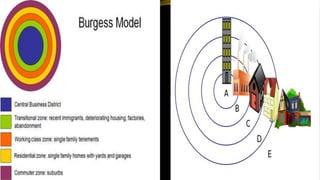
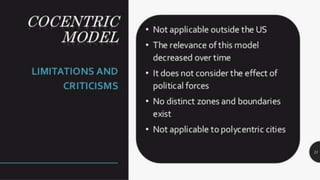
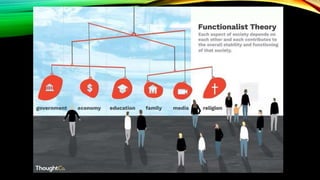
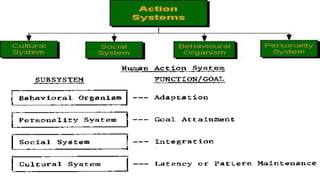
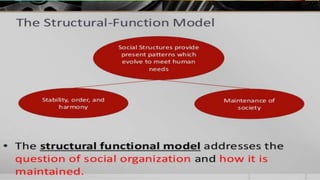
This document provides an overview of sociological foundations of education and symbolic interactionism. It discusses key thinkers in the development of symbolic interactionism like George Herbert Mead and Ernest Watson Burgess. Mead developed the theory through his unpublished works that were later published by his students. Burgess created the concentric zone theory to explain socioeconomic divides within cities with population density decreasing as distance from the central business district increases. The document also outlines the three core principles of symbolic interactionism: meaning, language, and thought. It explains how individuals develop a sense of self through interacting with others and learning to see themselves from others' perspectives.