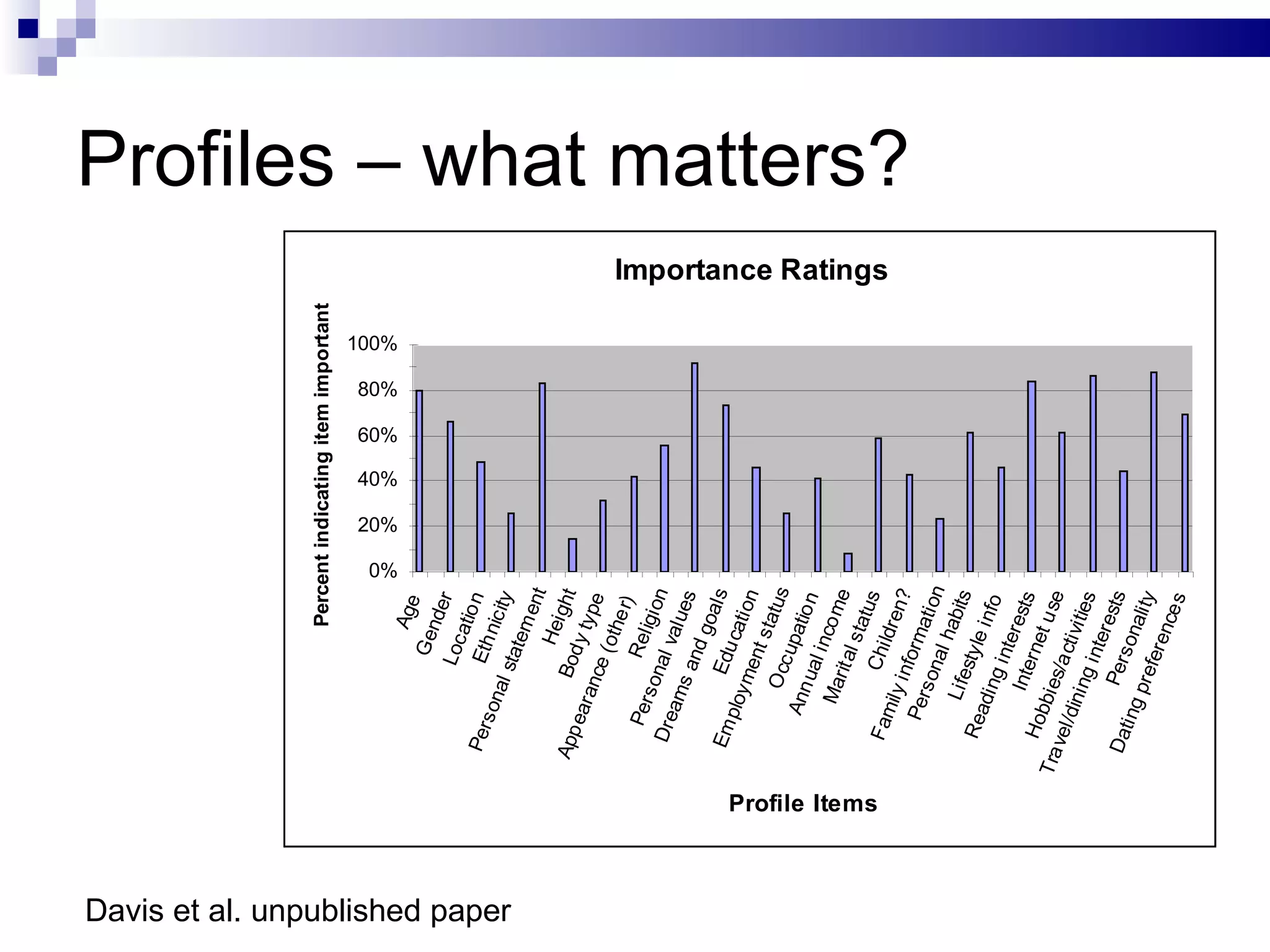
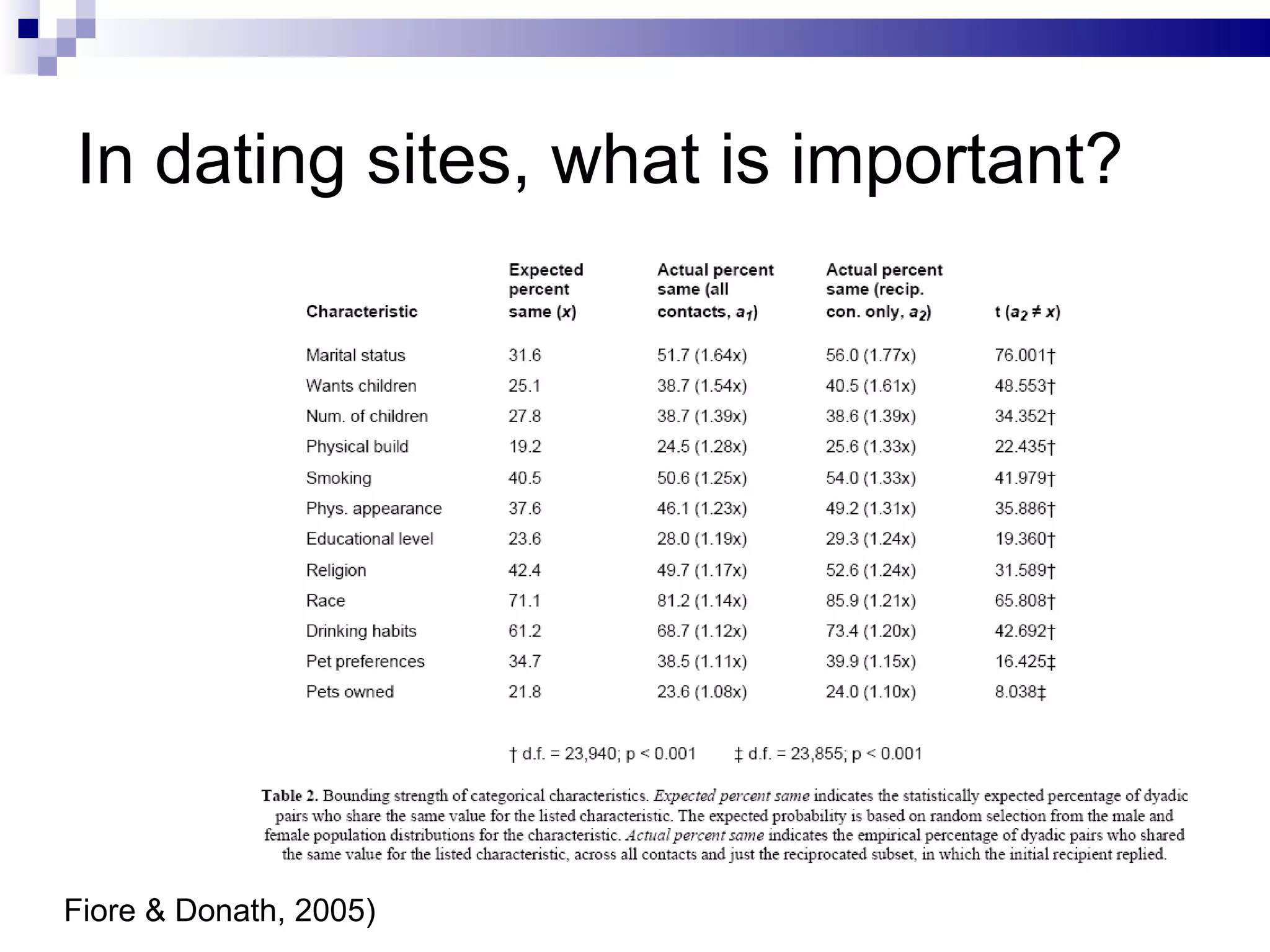
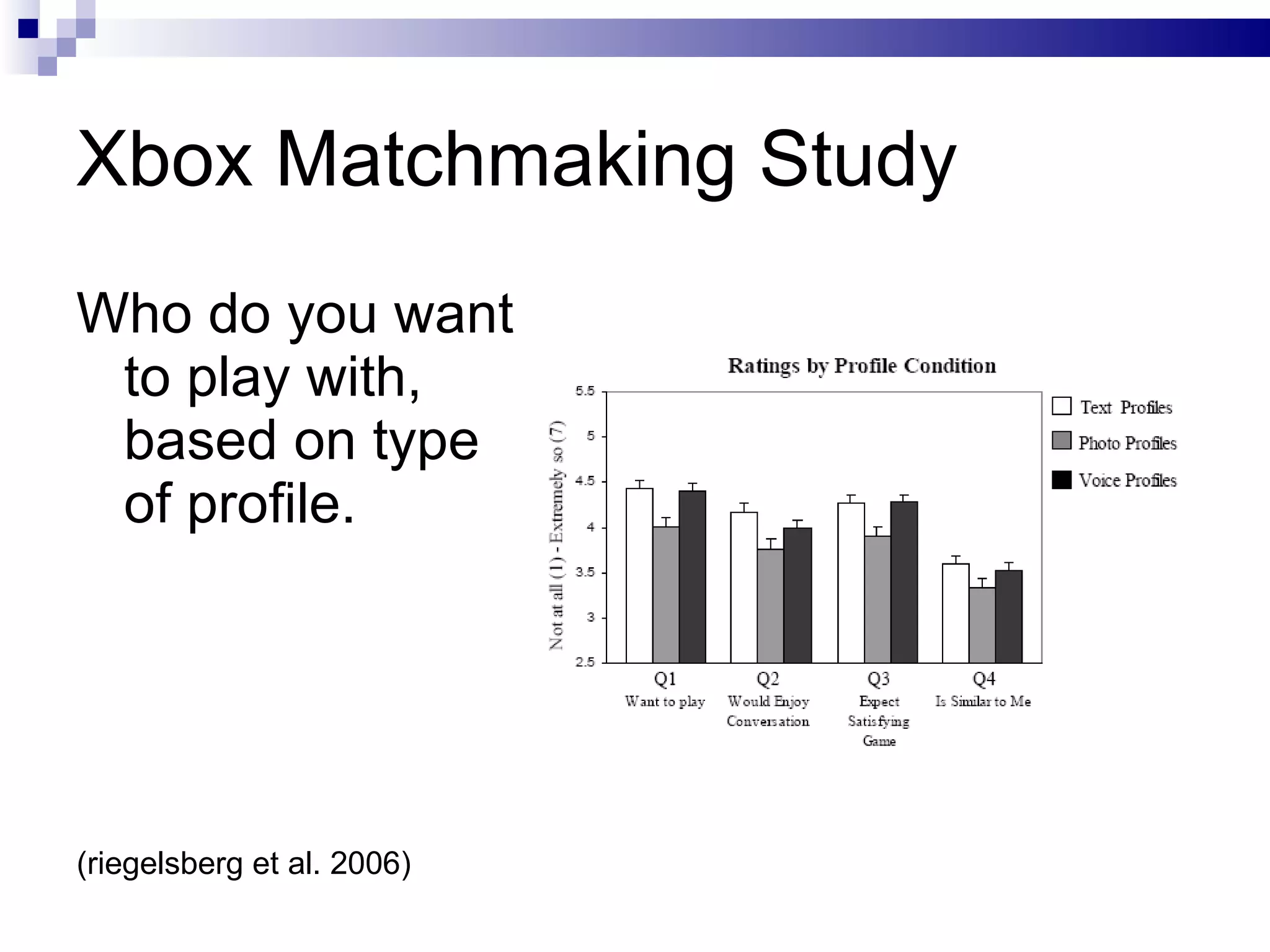
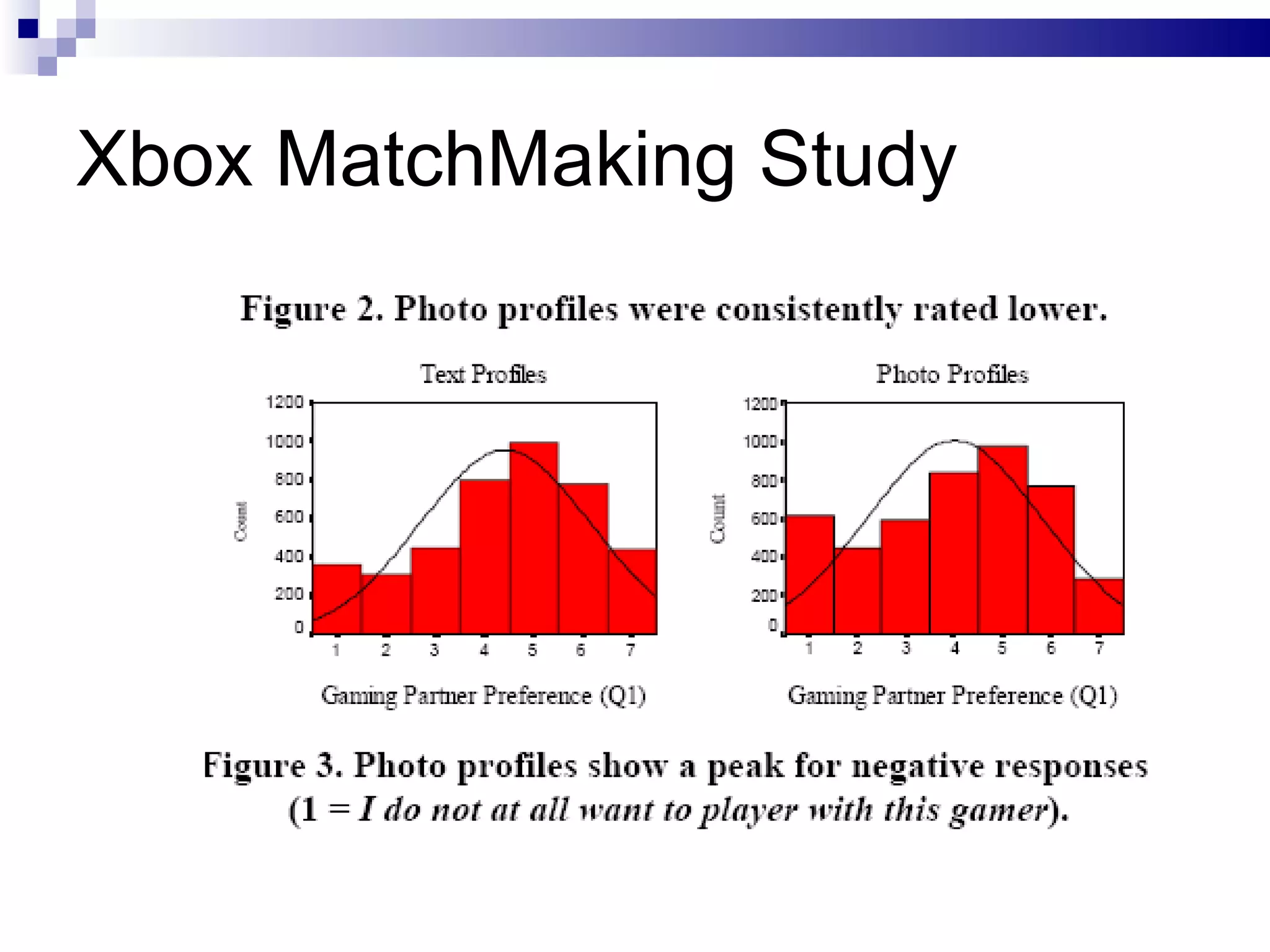
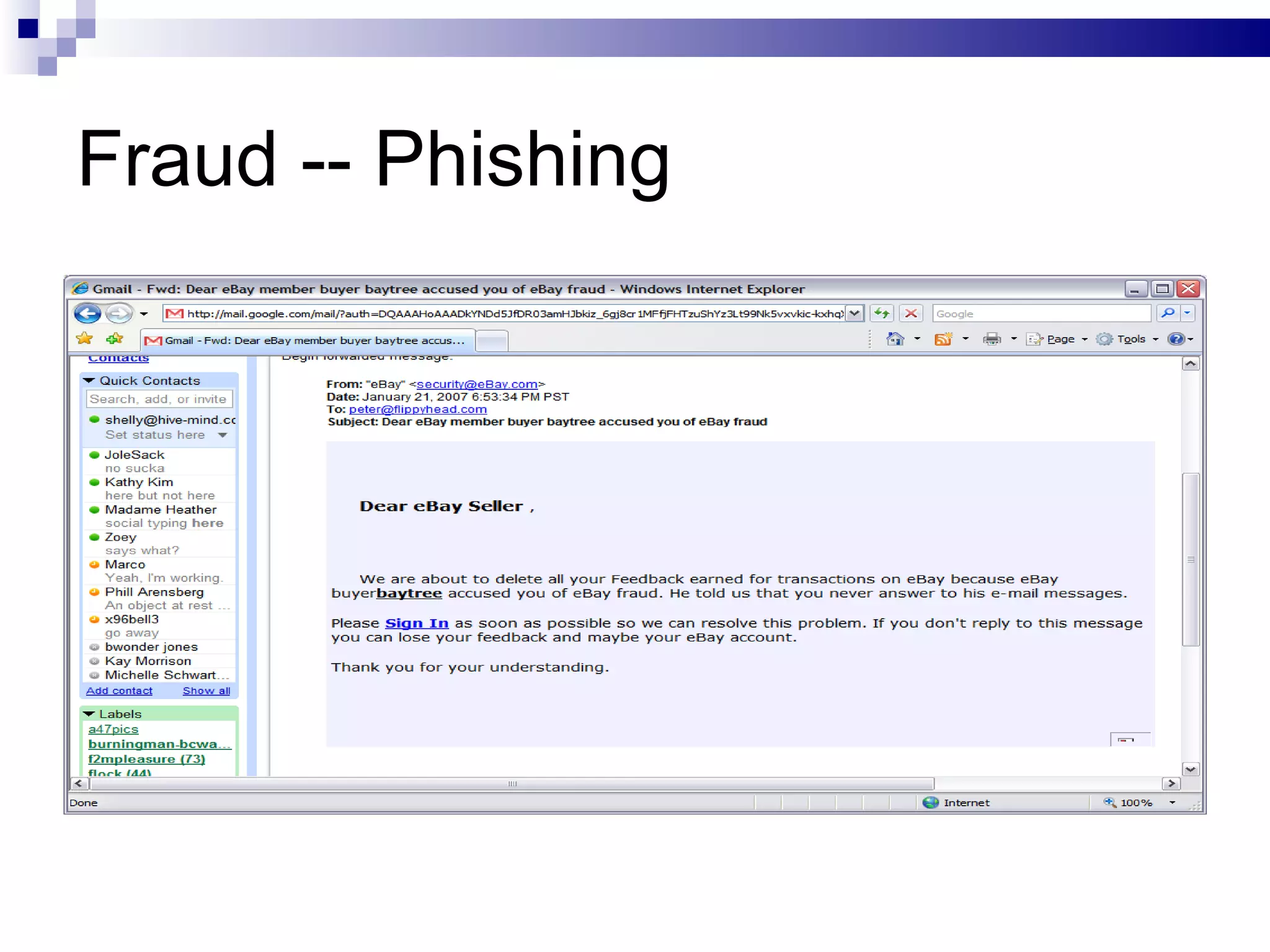
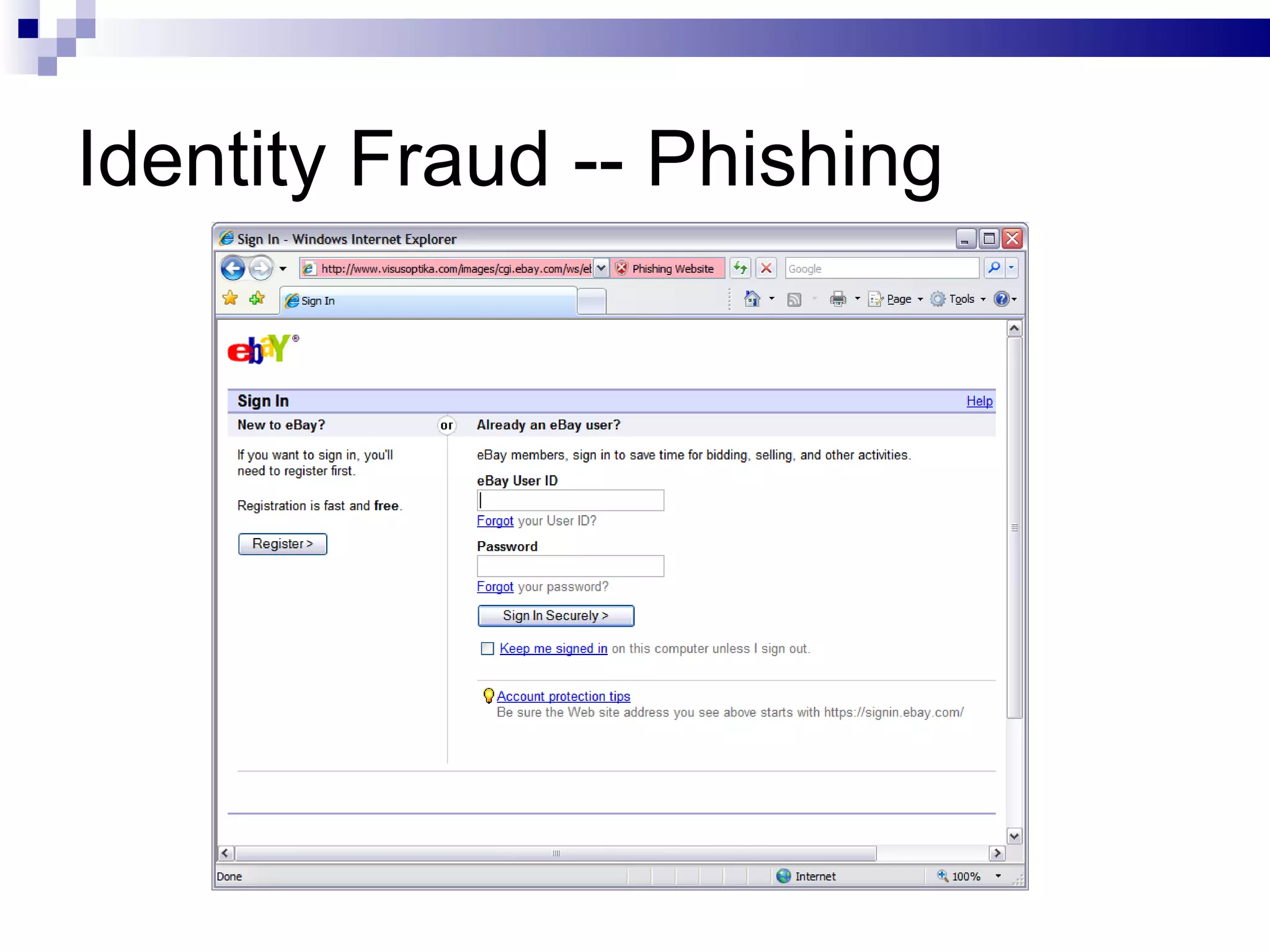
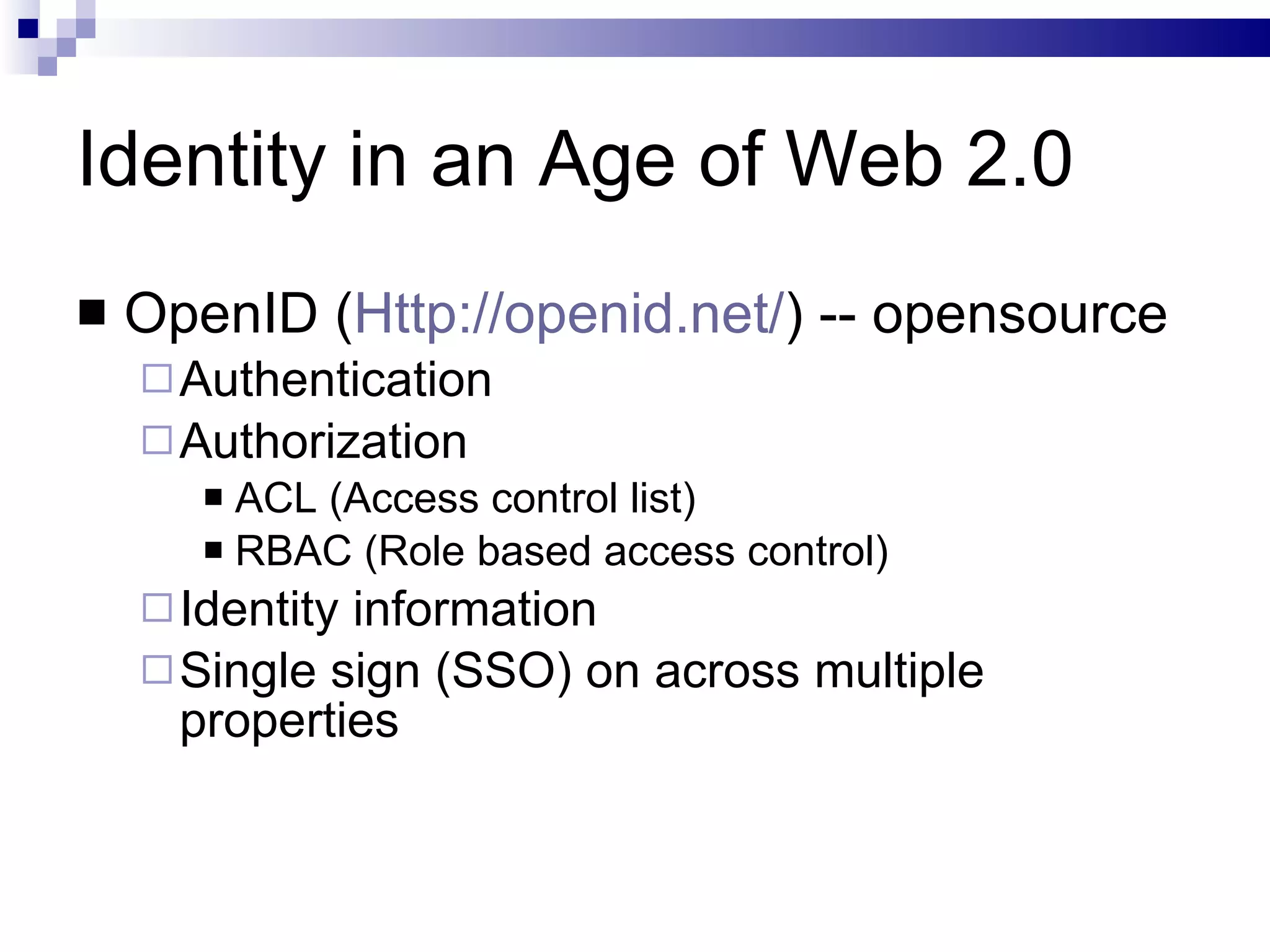
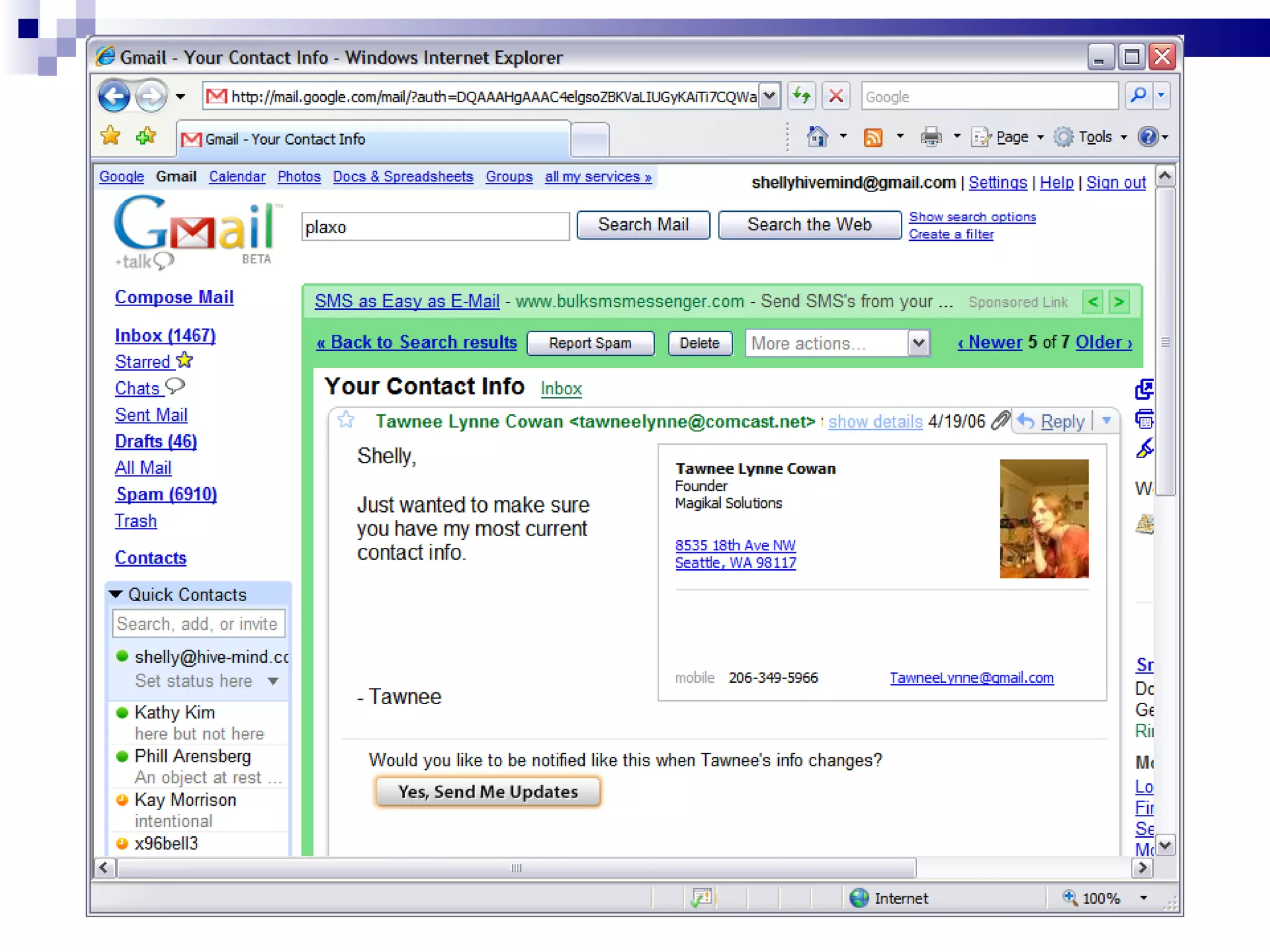
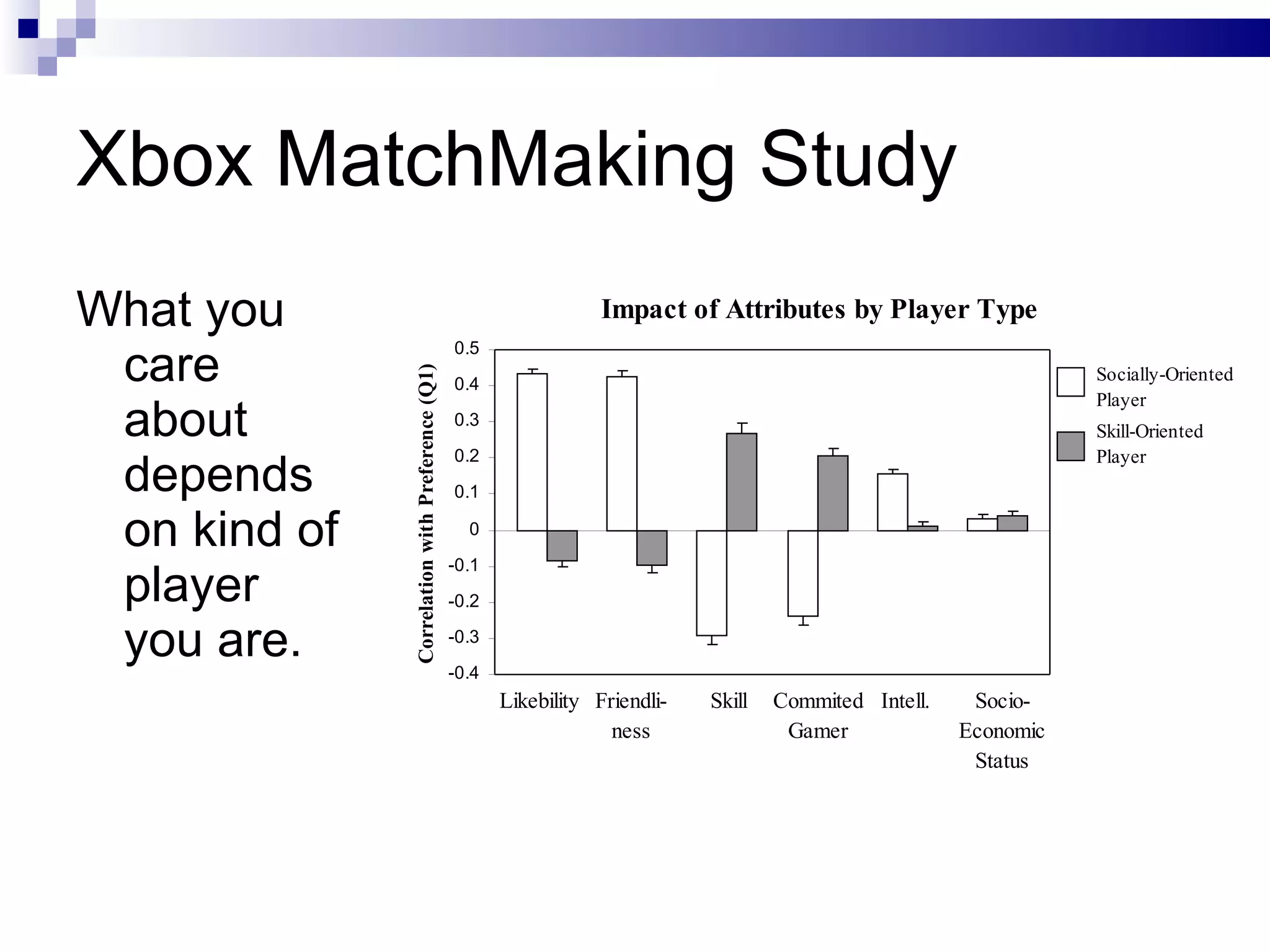
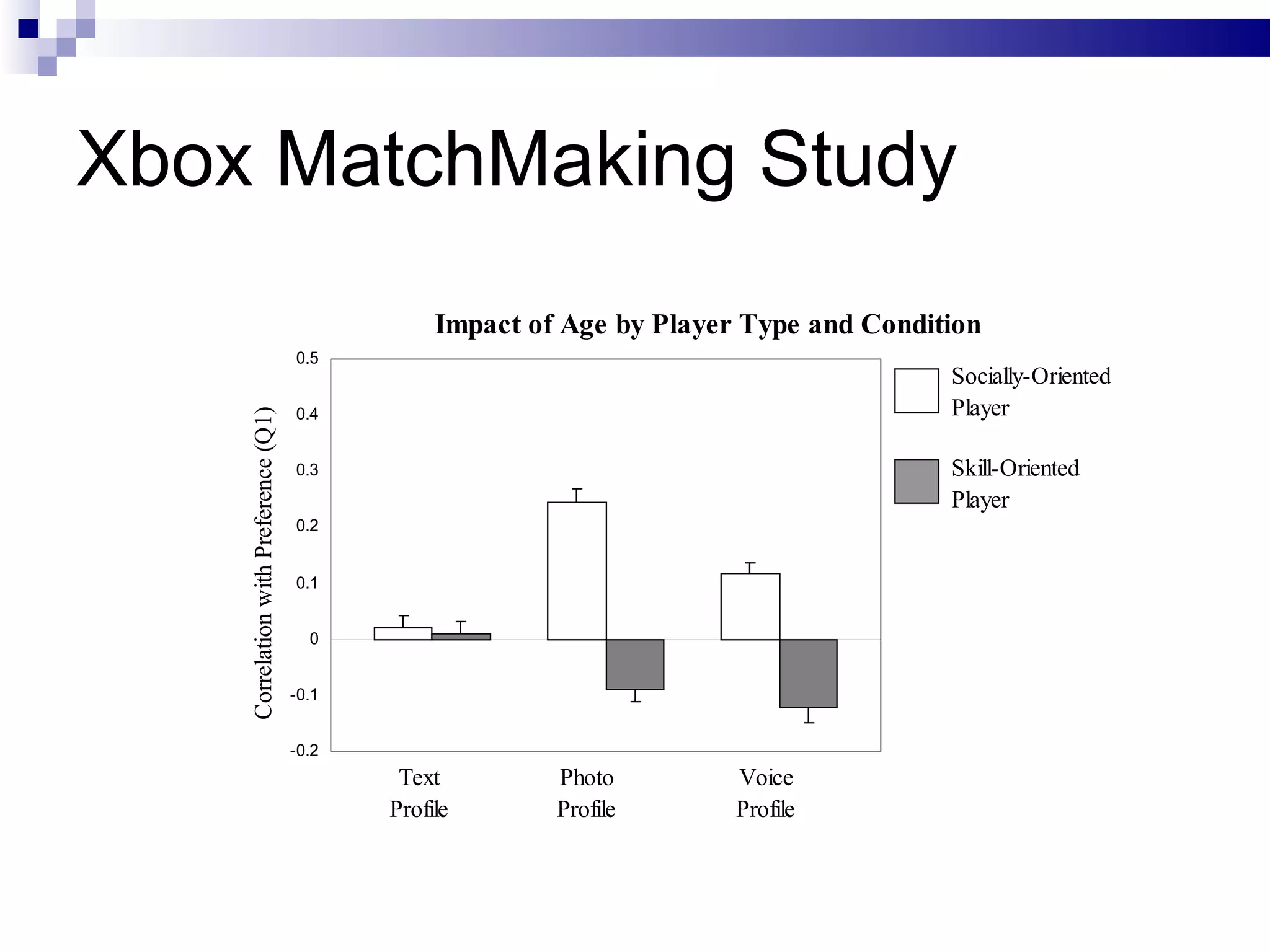
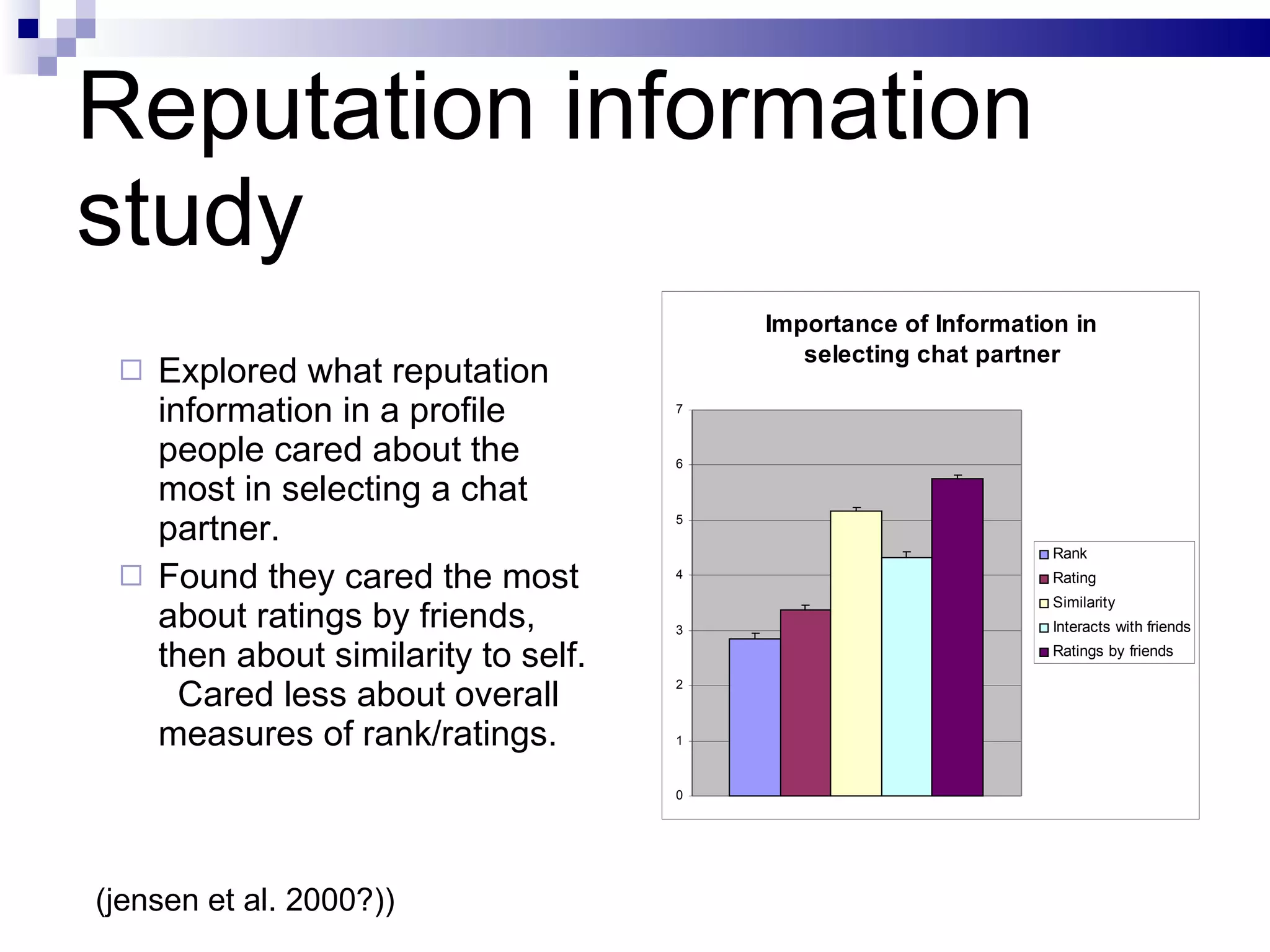
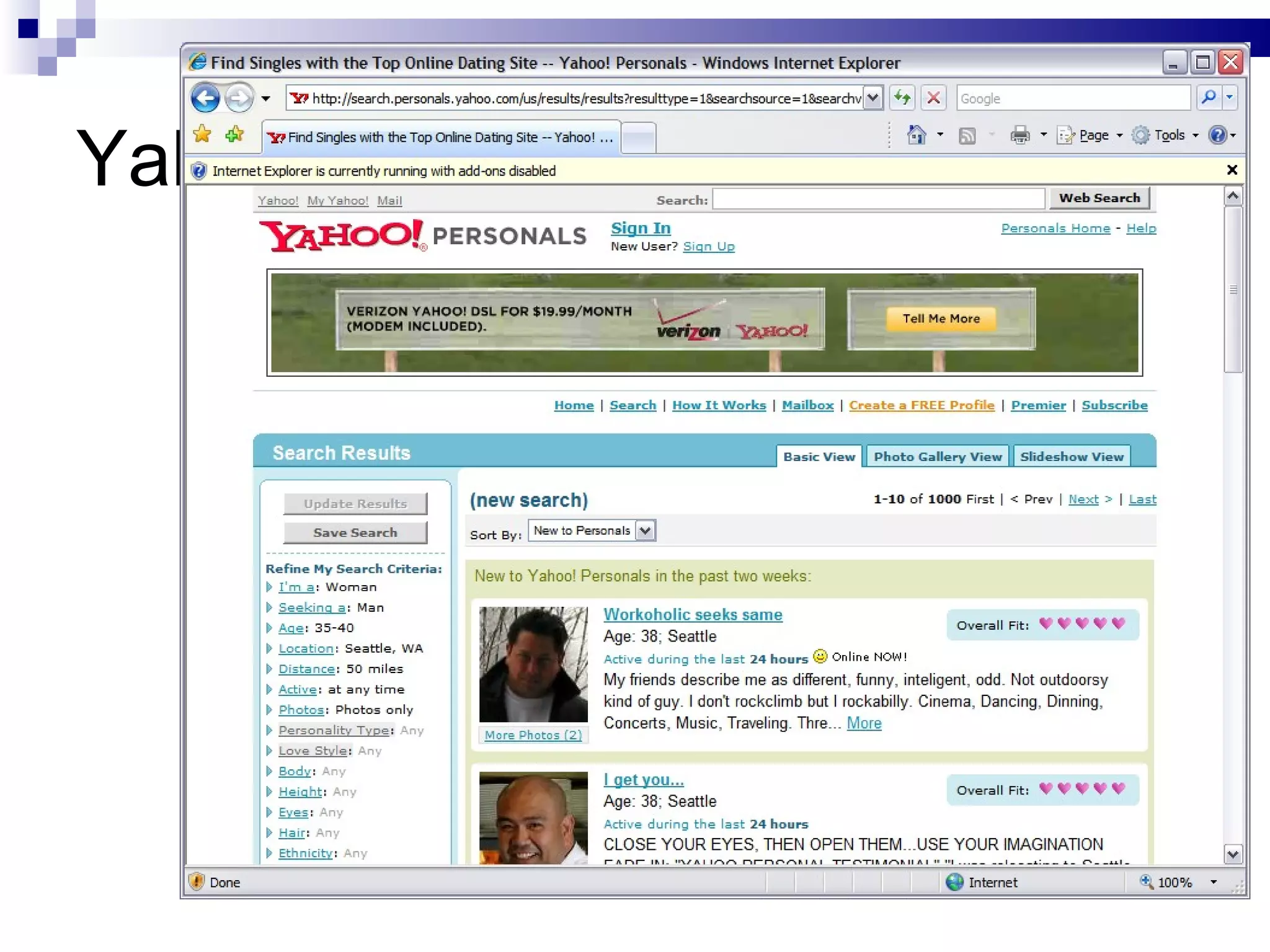
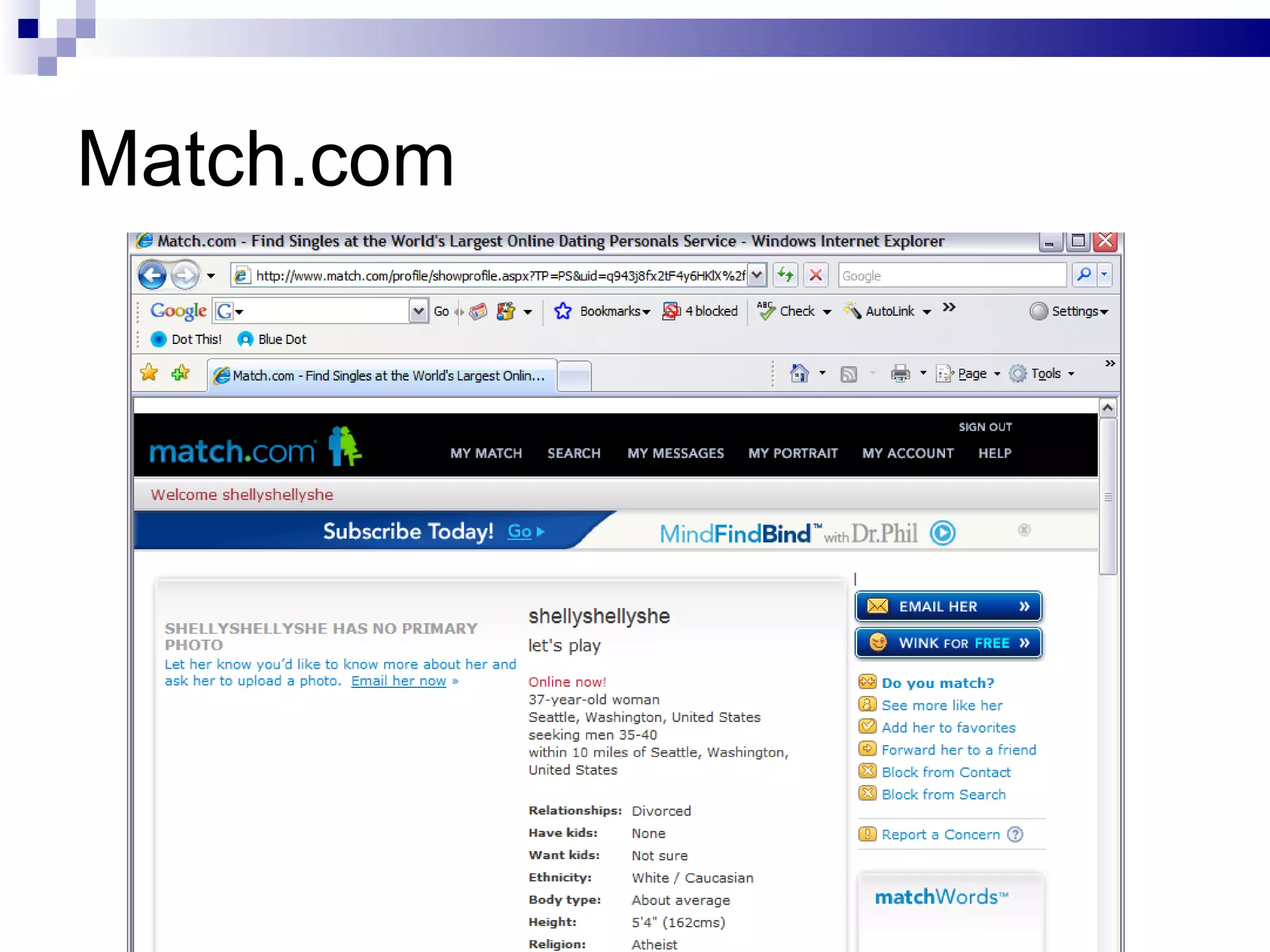
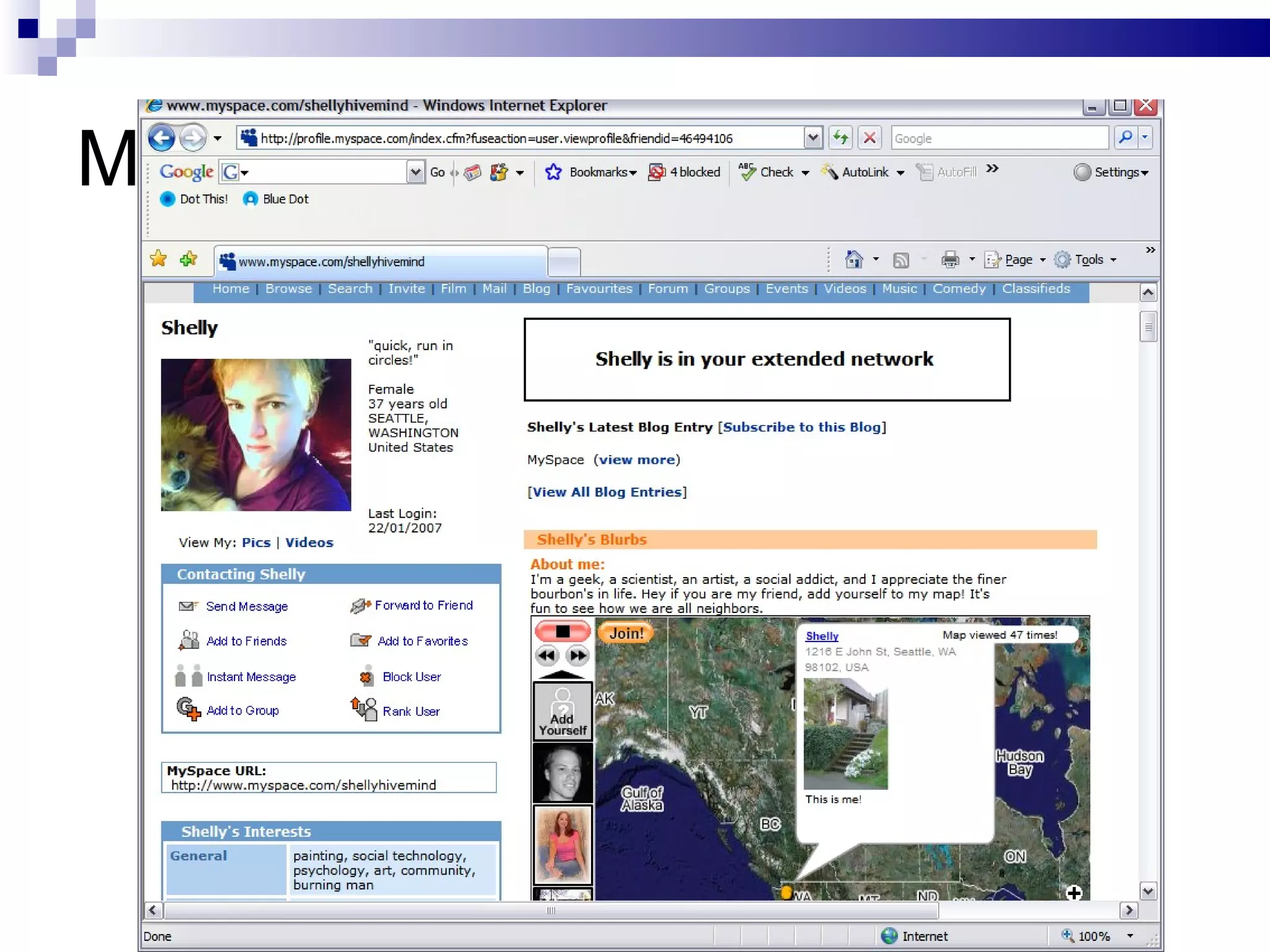
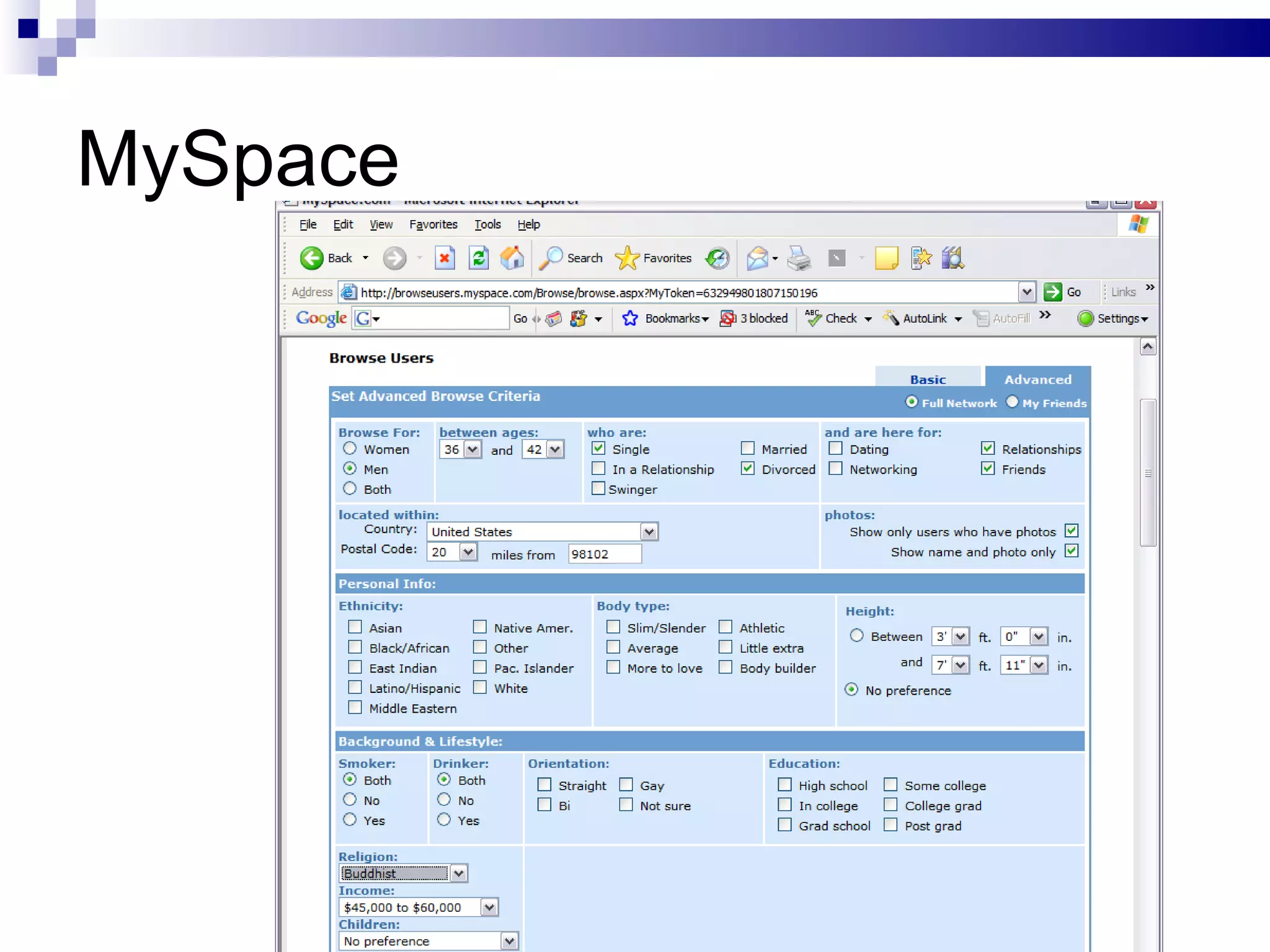
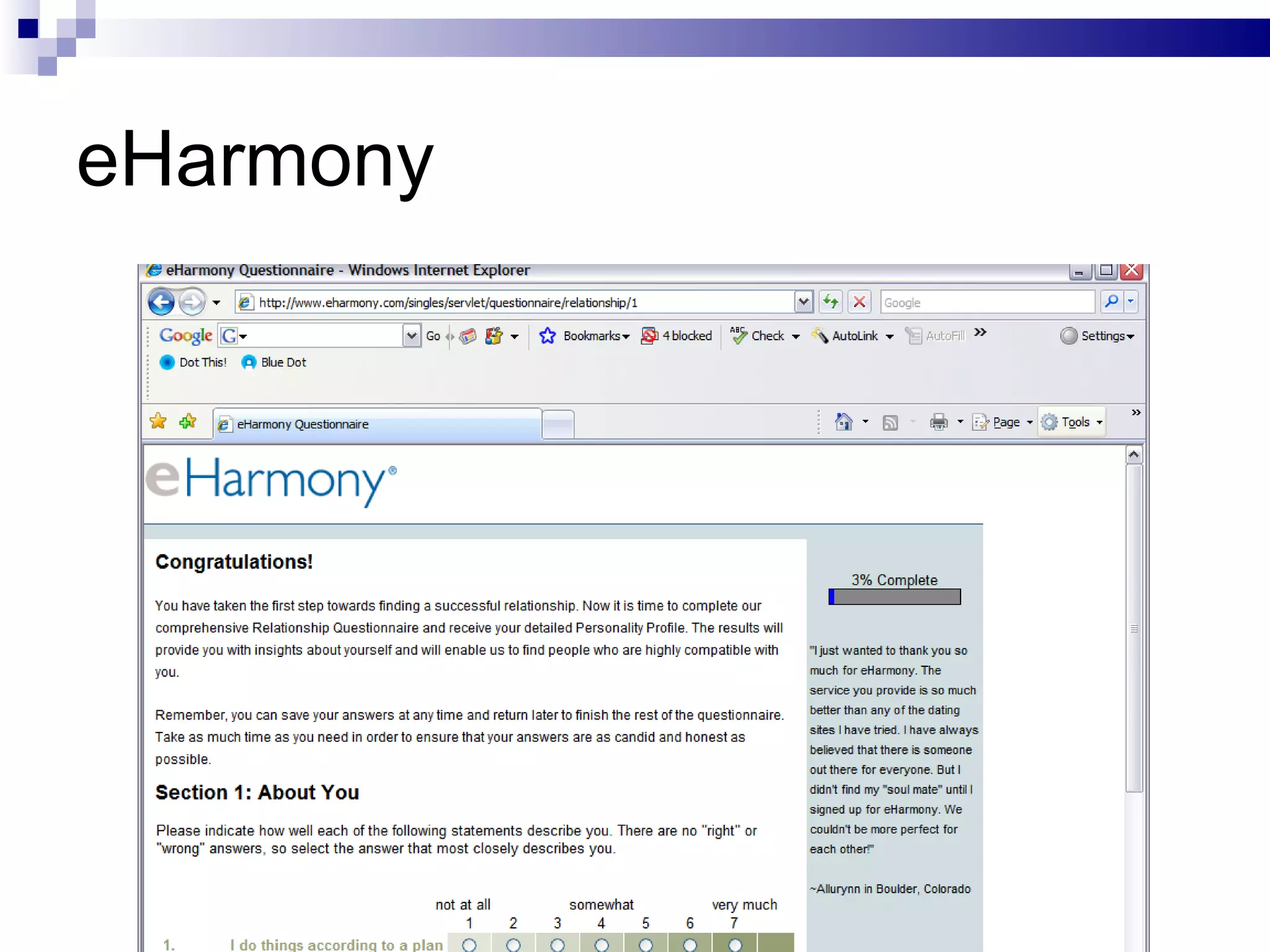
The document discusses the implications of social technologies on digital media, focusing on identity management and online matchmaking through various social contexts. It explores the advantages and disadvantages of online identity, self-presentation, and the complexities of maintaining multiple roles in digital environments. Additionally, it highlights the relationship between user profiles and online dating systems, along with practical applications for enhancing user experiences with social technologies.