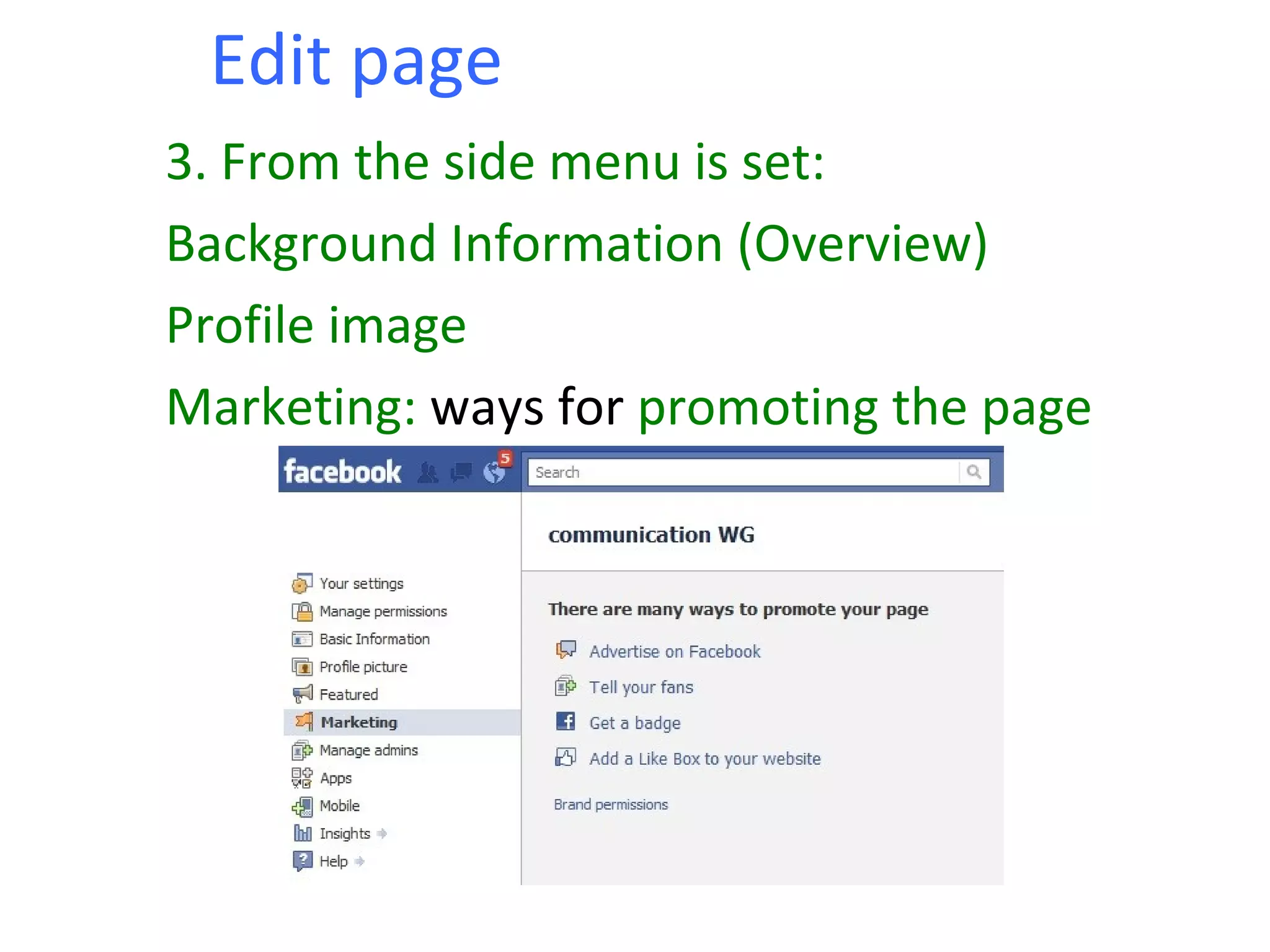
The document provides an extensive overview of social media, its definitions, and the implications of web 2.0 technologies in fostering social interaction. It discusses various social networking platforms such as Facebook and LinkedIn, detailing their uses, advantages, and user demographics. Additionally, it contrasts social media with mass media, emphasizing the accessibility, immediacy, and interactive nature of social media content creation and consumption.
















































![Thanks to:
Virginia Espinosa, for the translation [http://www.virginiaespin29.blogspot.com]
René Rodriguez (@_renerodriguez)
Ana López ,
Juan Quaglia (@juanquaglia),
Miguel Carrillo (@miguel_k ),
Rosario Ortega [http://www.auladigitalactiva.com/]
Isra García (http://isragarcia.es/)
Pablo Garaizar Sagarminaga y
Lorena Fernández (http://www.loretahur.net/)
To keep in touch, for any question that arise later at:
miguel.barreralyx@gmail.com
miguel.barrera@oapee.es
@mbarreralyx (on twitter)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socialmedia9demayosinlogos-110512173109-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Social-Media-54-2048.jpg)