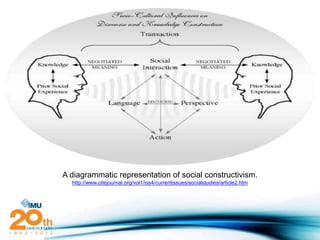
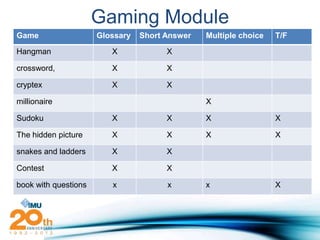
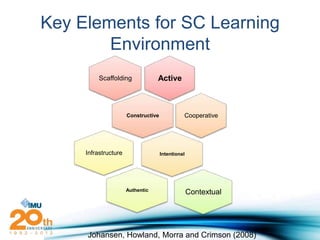
Social constructivism is a theory of learning that says knowledge is constructed through social interaction and collaboration. It emphasizes active learning where students work together to solve problems. According to this theory, knowledge arises through discourse, negotiation, and shared understanding between learners interacting within a community. The document then provides examples of how social constructivist principles can be implemented through tools like gaming modules, social media, and simulations to create collaborative learning environments.













![References
• Basu A. et al. (2011) Integrating Medical Education with Medical Practice: Role of Web 2.0 Tools, www.igi-
global.com/chapter/integrating-medical-education-medicalpractice/49268
• Doolottle, P.E. (2001). The need to leverage theory in the development of guidelines for using technology in social studies
teacher preparation: A reply to Crocco and Mason et al. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education
[Online serial] , 1 (4) . Available: http://www.citejournal.org/vol1/iss4/currentissues/socialstudies/article2.htm
• Doolottle, P.E. (2001). The need to leverage theory in the development of guidelines for using technology in social studies
teacher preparation: A reply to Crocco and Mason et al. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education
[Online serial] , 1 (4) . Available: http://www.citejournal.org/vol1/iss4/currentissues/socialstudies/article2.htm
• Fosnot, C. T. (1996). Constructivism: Theory, perspective, and practice. New York: Teachers College Press.
• Laurillard, D. (1994) Multimedia and the changing experience of the learner, In Ryan, M. (ed.) Proceedings of Asia Pacific
Information Technology in Training and Education Conference and Exhibition: APITITE 94. Brisbane. Australia. Vol. 1. pp.
19-24
• Knolwes, M.S. Holton, E.F. and Swanson, R.A. (1998) The Adult Learner: The Definitive Classic in Adult Education and
Human Resource Development. 5th Edition. MA. Butterwirth-Heinemann.
• University of Warwick’s Medical School , http://education.icnetwork.co.uk/midlands-education-
news/2012/03/15/birmingham-student-designs-world-leading-3d-anatomy-model-65233-30537638/
• Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University ,
http://ezramagazine.cornell.edu/update/April11/EU.WCMC.anatomy.donors.html
• http://www.perdanauniversity.edu.my/pugsom/
• Ice Storm is a healthcare simulation training program. Demonstrated at the MT3 Conference in Orlando, Florida.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KPJz_evaQwk
• http://www.uthsc.edu/allied/
• http://www.rgbstock.com/download/melodi2/mjYxU8O.jpg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socialconstructivismsc24v1-120525042529-phpapp02/85/Social-constructivism-sc-24v1-18-320.jpg)