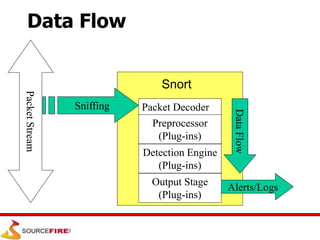
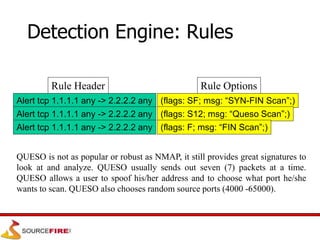
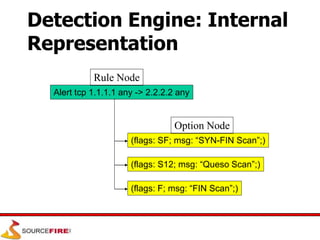
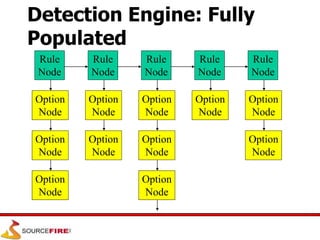
Snort is an open source network intrusion prevention system capable of real-time traffic analysis and packet logging. It uses a rules-based detection engine to examine packets against defined signatures. Snort has three main operational modes: sniffer, packet logger, and network intrusion detection system. It utilizes a modular architecture with plug-ins for preprocessing, detection, and output. Rules provide flexible and configurable detection signatures.