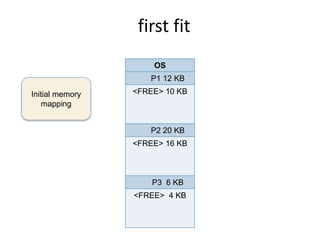
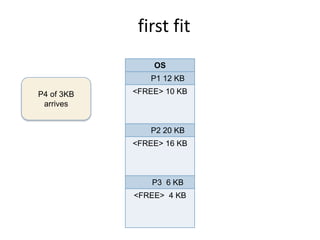
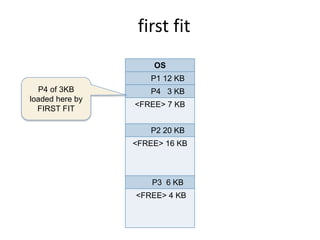
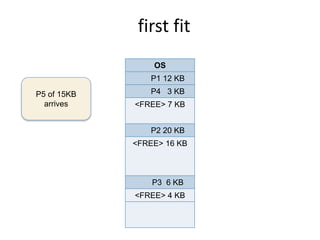
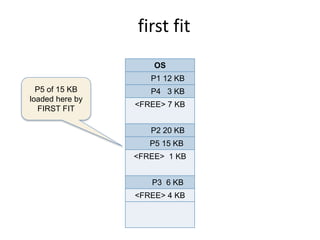
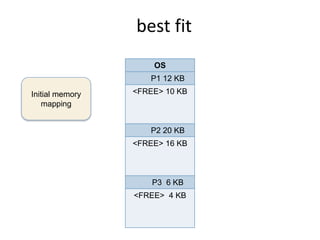
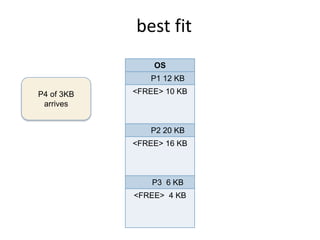
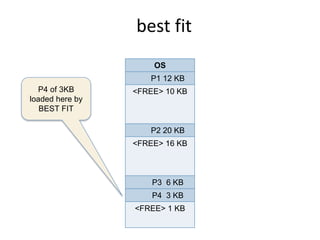
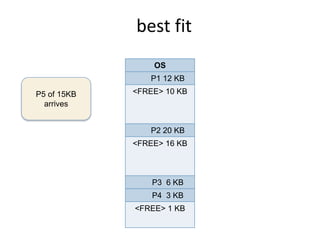
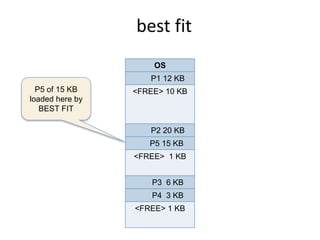
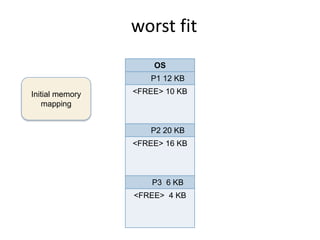
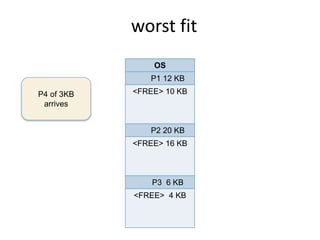
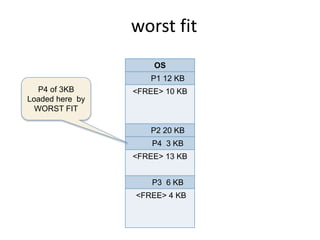
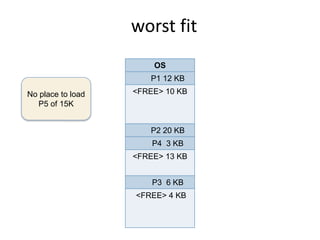
This document discusses three algorithms for allocating memory to processes: first fit, best fit, and worst fit. First fit allocates the first block of memory large enough for the process. Best fit allocates the smallest block large enough. Worst fit allocates the largest block large enough. The document provides examples of how each algorithm would allocate memory to processes of different sizes and evaluates which algorithm makes the most efficient use of memory.