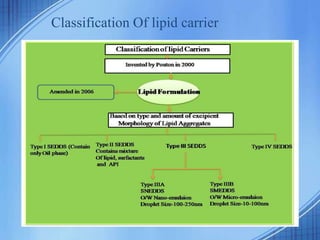
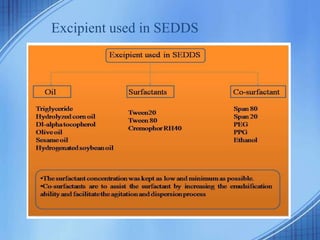
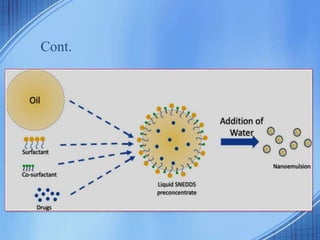
The document discusses Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) with a focus on their formulation, advantages, and applications, particularly for the poorly soluble drug glibenclamide. SNEDDS enhances the bioavailability of drugs by utilizing a mixture of oils, surfactants, and other excipients to create stable emulsions that improve gastrointestinal absorption. The conclusion emphasizes SNEDDS as a promising method to address the challenges of low water solubility in drug delivery.