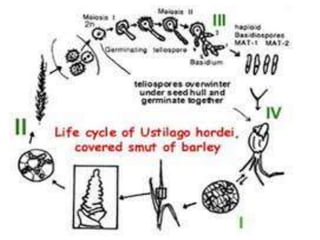
- The smut of barley is caused by the fungus Ustilago hordei. It is a seed-borne disease where the fungus systemically infects the plant.
- Symptoms appear at heading, with infected kernels replaced by dark brown masses of spores. Infected heads are hard and compact.
- The disease cycle involves the fungus spreading from contaminated seeds. The mycelium grows inside the plant with emerging ears and produces spores in floral parts. Spores are released during threshing to contaminate new seeds.
- Control measures include rogueing infected plants, using disease-free seed, seed treatment with fungicides, and growing resistant varieties.