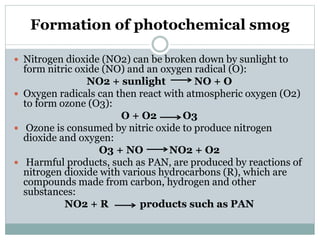
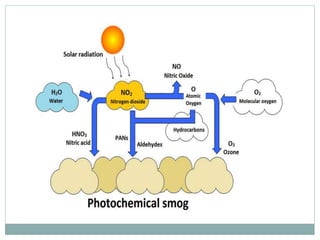
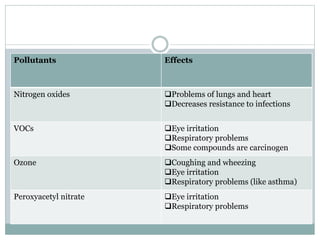
Photochemical smog is formed when nitrogen oxides and VOCs in the atmosphere react with sunlight to form secondary pollutants such as ozone and PAN. It causes respiratory and plant health issues. The main sources are fossil fuel combustion from vehicles and power stations, as well as solvent evaporation and biomass burning. Control methods include catalytic converters to reduce nitrogen oxides from vehicles and using alternative fuels to decrease VOC emissions.