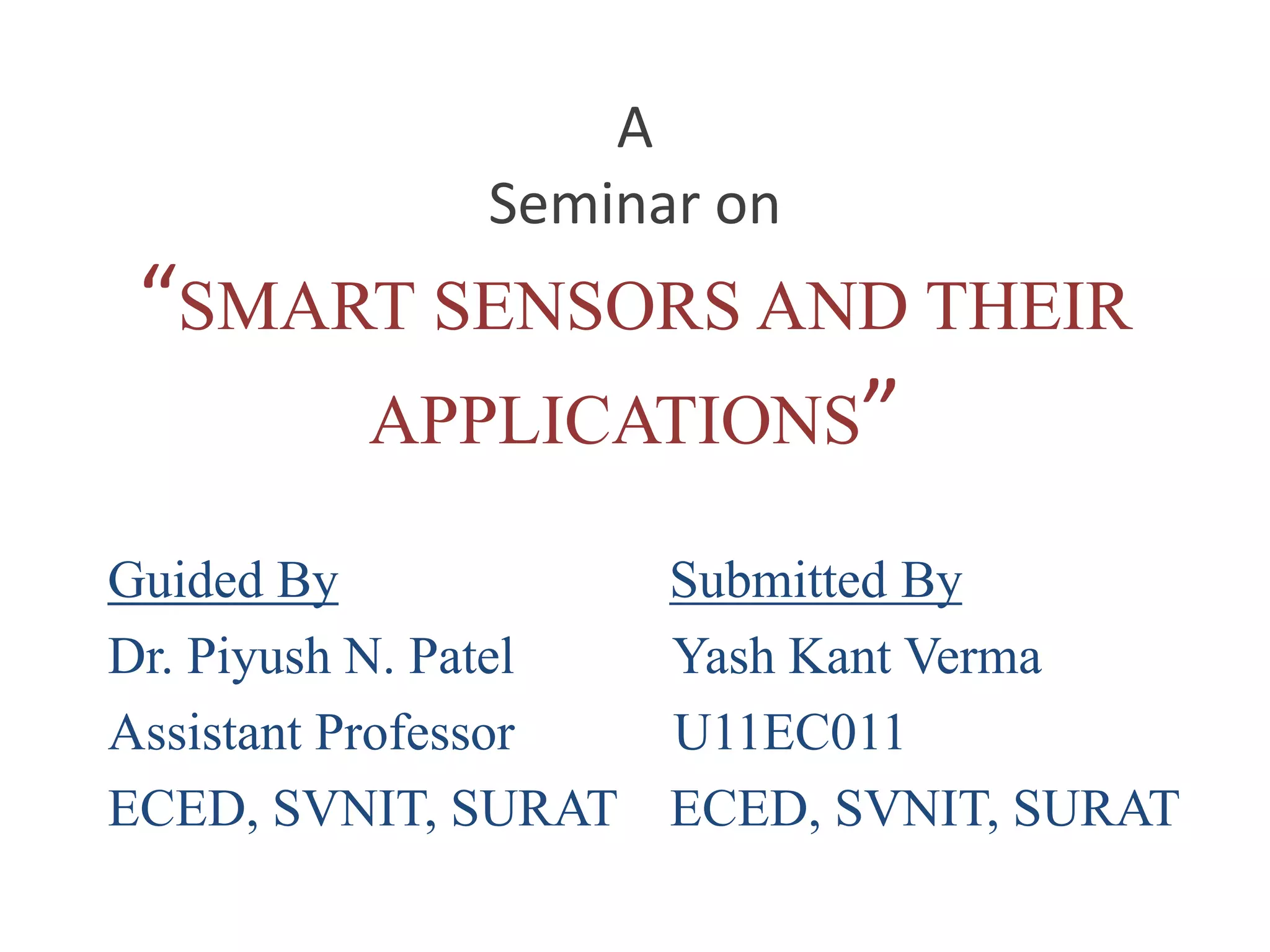
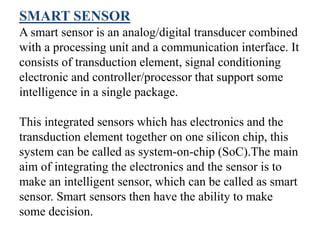
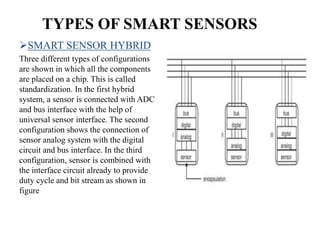
This document provides an overview of smart sensors, including their architecture, fabrication, applications, and advantages. It defines smart sensors as sensors integrated with processing and communication capabilities. The key components of a smart sensor's architecture are a sensing element, analog/digital conversion circuitry, memory, and a communication interface. Smart sensors can be fabricated using techniques like micro-machining and wafer bonding. Their applications span industries, automotive, biomedicine, defense, and more. Advantages include reduced processing load and faster operation compared to conventional sensors.


![Smart sensors / Intelligent sensor
are sensors with integrated
electronics that can perform one
or more of the following
function:[1]
1. Data Conversion
2. Bidirectional communication
3. Take decisions
4. Perform logical operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![INTEGRATED SMART SENSORS
If we integrate all functions from sensor to bus interface in one chip, we get an
integrated smart sensor as shown in figure below.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-8-320.jpg)
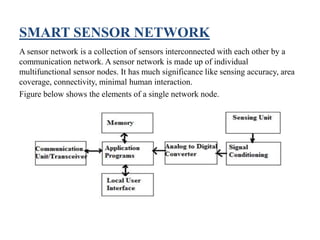
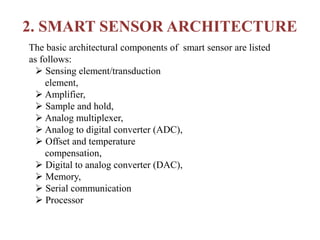
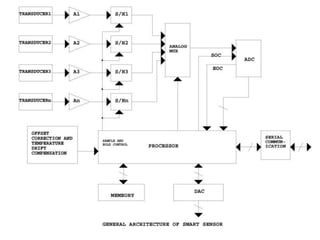
![Five main parts of sensor node are:
The central unit: It is in the
form of microprocessor which
manages the tasks.
Battery: Is the source of
energy
A Transceiver: Interacts with
the environment and collects
data.
Memory: Used as storage
media for storing data or
processing data.
Communication module: It
includes transceivers and
forwards queries and data to
and from central module. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-12-320.jpg)


![Communication and Bus Interaction
• A smart sensor should be capable of interacting with a
higher level controller that manages the overall system.
• Efforts are currently underway to develop such a standard
bus for sensor applications that is uniquely designed to
optimize functionality, speed and overall cost.
• A variety of information can be exchanged between the
sensor and the controller over the bus, including calibration
and compensation data, addresses and personality
information, measured data, and programming data initiated
by the controller, the communication interface should have
the ability to receive and transmit information over the bus
at a fairly high speed it should be noted that many sensor
signals have limited bandwidth and even in the case of a
multi-sensor system, the bus data rate may be sufficient to
accommodate all sensors [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-15-320.jpg)

![• Solid- State integrated
sensors are basically
composed of four elements
namely, custom films for
transduction,
microstructures, integrated
interface circuitry and
microcomputer based signal
processing algorithms.
Mainly, three techniques
bulk micro-machining,
surface micromachining and
wafer bonding process are
used for fabrication of smart
sensors
• Fig showing the fabrication
of a pressure sensor[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-17-320.jpg)
![4. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES[4]
The smart sensor takes over the conditioning and control of the
sensor signal, reducing the load on the central control system,
allowing faster system operation.
Direct digital control provides high accuracy, not achievable
with analog control systems and central processing.
The cost of smart sensor systems is presently higher than that
of conventional systems, but when the cost of maintenance,
ease of programming, ease of adding new sensors is taken into
account, the long- term cost of smart sensor systems is less.
Individual controllers can monitor and control more than one
process variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-18-320.jpg)


![PATTERN RECOGNISITION
The sensor uses incident light or backlight to detect
the contours of an object and compares them with the
contours of one or several models in a reference
image.
TELECOMMUNICATION
A smart card known as a Wireless Identity Module, is
similar to the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) used
on existing GSM cellular phones. The card
guarantees 100-percent security for e-commerce
transactions by providing authentication of the parties
involved, by means of encryption and digital
signatures.[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-21-320.jpg)
![SMART TOYS
These days the trend in toys is to make them as life-like as
possible which move or change directions after sensing objects
around them.
SMART DUST:
Smart dust is a hypothetical wireless network of tiny micro-
electro-mechanical (MEMS) sensors, robots, or devices, which
can detect (for example) light, temperature, or vibration. The
devices will eventually be the size of a grain of sand, or even a
dust particle, with each mote having self-contained sensing,
computation, communication and power.[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-22-320.jpg)


![REFERENCES
1. Frank. R; “Understanding the Smart Sensors”; Artech House;
Second edition; Page 1-5; 2000
2. Nitaigour P. Mahalik: Sensor Networks and Configuration.
Fundamentals, Standards, Platforms and Applications. Springer
Verlag Berlin, english, 1st ed. November 2006, ISBN 3-540-
37364-0, ISBN 978-3-540-37364-3
3. Borky J M and Wise K D 1979 Integrated signal conditioning for
silicon pressure sensors IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices ED-26
1906-10
4. M. Bowen, G. Smith, “Considerations for the design of smart
sensors,” Sensors and Actuators, A 46- 47(1995) 516-520.
5. S. Middelhoer and A.C. Hoogerwerf, “Smart sensors when and
where,” Sensors and Actuators, 8(1985) 39-48.
6. http://www.smartsensortechnologies.com/fs-system.html
[Retrieved on 11-11-2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-221125070110-85fd28eb/85/smartsensorsandapplication-141127040002-conversion-gate02-pdf-26-320.jpg)
