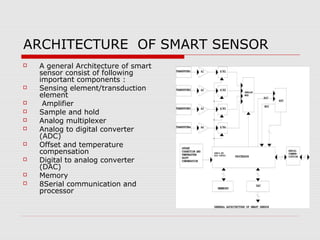
This document discusses a seminar presentation on smart sensors. It provides an introduction to smart sensors, defining them as sensors with integrated electronics that can perform logic functions, two-way communication, and make decisions. It discusses the usefulness of silicon technology in smart sensors and their general architecture. The architecture typically includes elements like a sensing element, amplifier, analog-to-digital converter, memory, and processor. In conclusions, smart sensors provide benefits like reduced costs, remote diagnostics, enhanced applications, improved reliability, and better signal-to-noise ratios compared to traditional sensors.