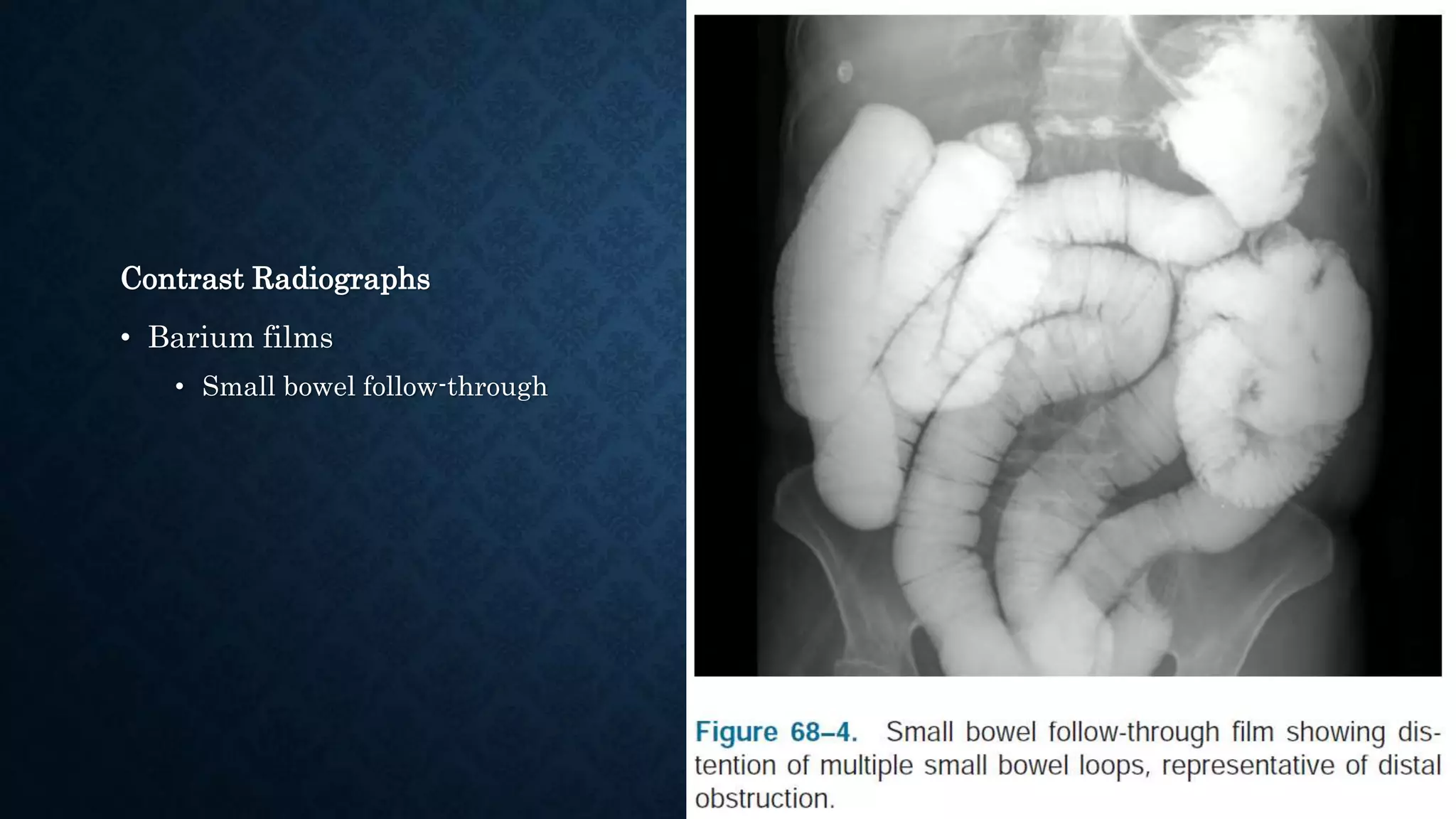
This document provides an overview of small bowel obstruction (SBO), including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. It notes that SBO accounts for 12-16% of acute abdominal surgical admissions. Causes include adhesions (75% of cases), hernias (25% of cases), and other factors like inflammation, ischemia, and masses. Symptoms range from mild discomfort to shock. Diagnosis involves physical exam, lab tests, and imaging like CT scan or contrast radiographs. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the obstruction, but generally involves resuscitation, monitoring, and surgery if signs of strangulation or ischemia are present or if conservative measures fail.