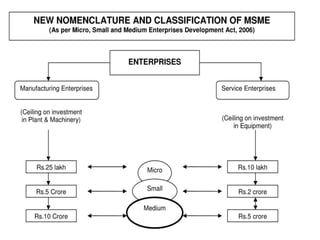
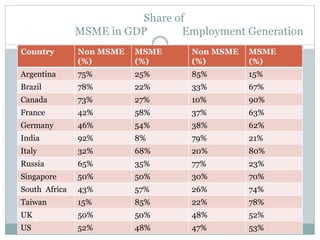
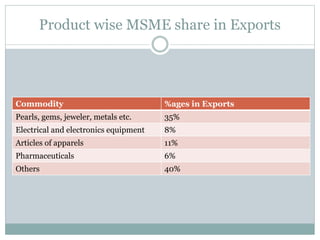
MSMEs play an important role in the Indian economy, contributing approximately 8% to GDP, 40% to manufacturing output, and 45% to exports. They emerged based on Gandhian principles and were encouraged by the MSME Act of 2006. Common challenges faced by MSMEs include lack of access to financing, raw materials, skilled labor, and effective marketing strategies. The government has implemented various schemes and programs to support MSME growth and address these challenges.