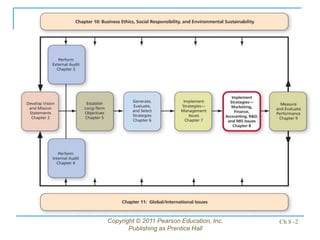
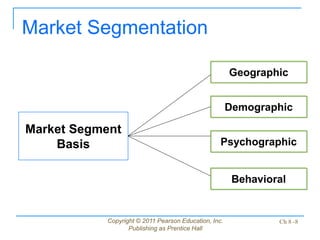
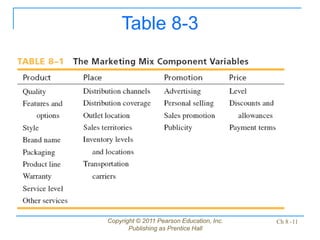
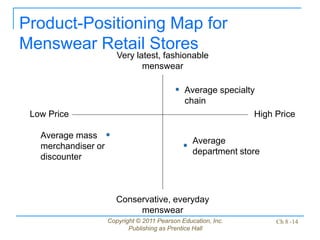
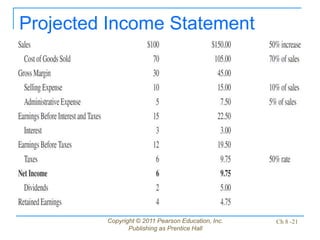
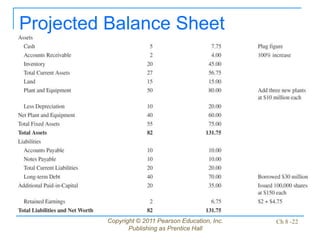
This document discusses issues related to implementing business strategies. It covers marketing, finance/accounting, research and development (R&D), and management information systems (MIS) issues. Some key points include that less than 10% of strategies are successfully implemented due to factors like improper market segmentation. It also discusses the importance of market segmentation, product positioning, acquiring capital, developing financial projections, and having an effective MIS system to differentiate successful firms.