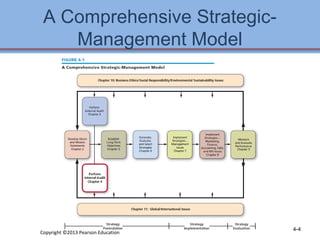
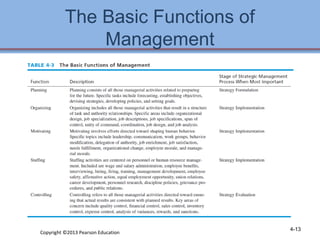
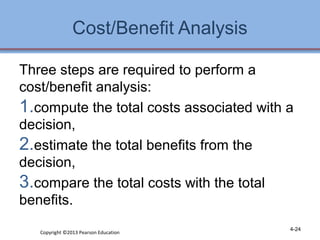
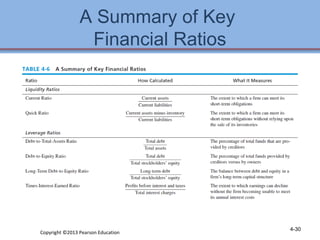
1. The chapter discusses performing an internal assessment of a company, including analyzing the company's resources, management, marketing, finance, production, and management information systems.
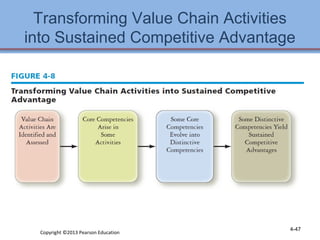
2. It describes the Resource-Based View theory that a company's internal resources are more important for competitive advantage than external factors.
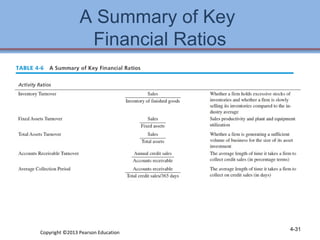
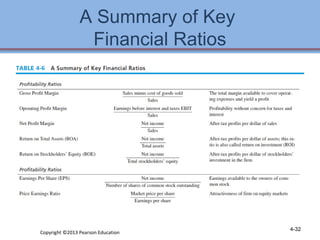
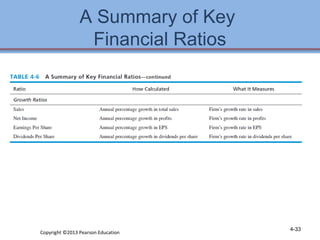
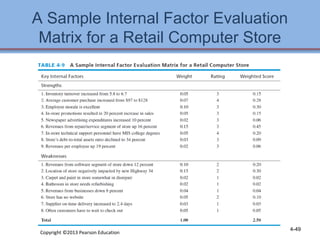
3. Checklists are provided to help evaluate the strengths and weaknesses within each functional area as part of developing an internal strategic assessment.