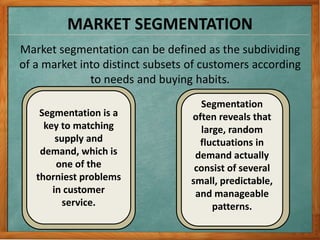
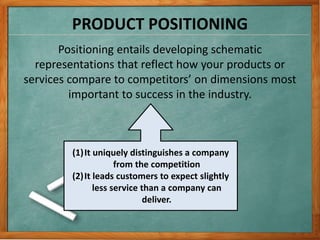
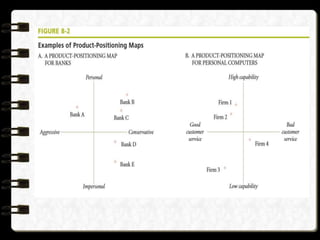
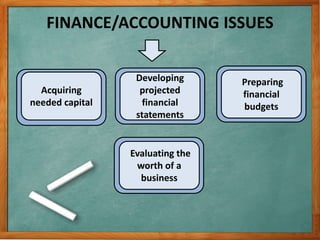
1) The document discusses various issues related to implementing strategies, including marketing, finance/accounting, R&D, and MIS.
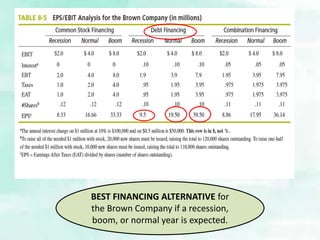
2) It provides examples of relevant decisions in each area, such as using exclusive or multiple distribution channels in marketing, and raising capital through debt or equity in finance.
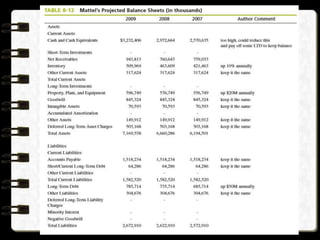
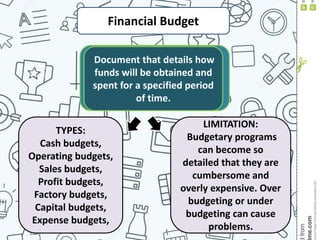
3) Projected financial statements and budgets are described as key tools for examining the expected results of implementation decisions and obtaining necessary funds.