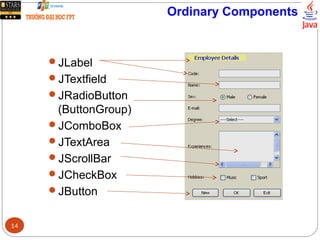
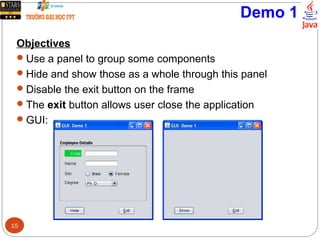
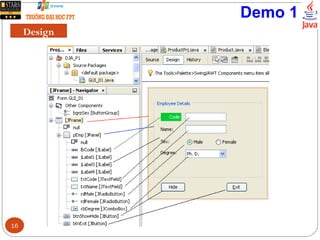
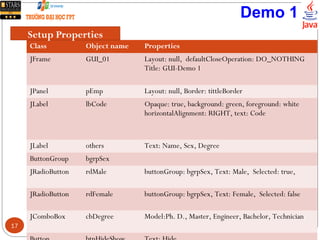
This document discusses creating graphical user interfaces in Java. It covers two types of applications, event-based and console applications. It describes Java's model for event management using listeners and handlers. It also discusses the Java Foundation Classes for building GUIs, including Swing components, internationalization support, and look and feel customization. The document provides a strategy for designing GUIs and examples of using common Swing components like JLabel, JButton, and JComboBox.




![1- Two Kinds of Apps
Console App.
Compute-centric Apps
Event-based App.
User-centric Apps(GUI)
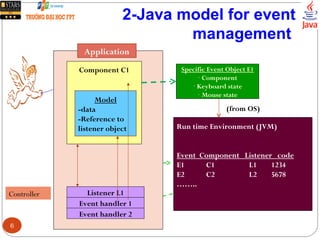
Model-View Controller Architecture for GUI component.
Model: Object contains data.
View: Object users can see it on the screen
Controller: Object manages events
[www.songho.ca]5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slot04-creatinggui-180617070854/85/Slot04-creating-gui-5-320.jpg)