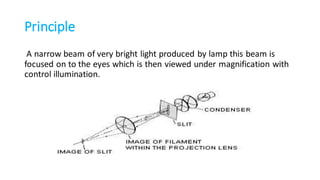
The document discusses the slit lamp biomicroscope, which is an important tool used to examine the anterior segment of the eye. It works on the same principle as a compound microscope, with an objective lens facing the patient and an eyepiece facing the examiner. There are different types of slit lamps produced by Zeiss and Haag Streit. Examination involves properly positioning the patient and adjusting the instrument, then using various illumination methods like diffuse, direct, and retro illumination to view the different structures of the anterior eye segment. The slit lamp is used for both diagnostic evaluation of ocular diseases and performing procedures.





![Parts of slit lamp
INSTRUMENTATION
1- observation system [ microscope ]
2- illumination system [ Slit lamp ]
3- mechanical system [ Engineering support ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slitlamp-220122112740/85/Slit-lamp-7-320.jpg)











