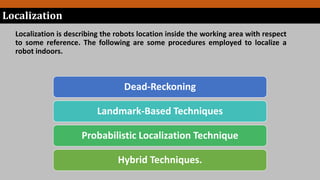
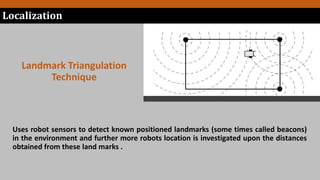
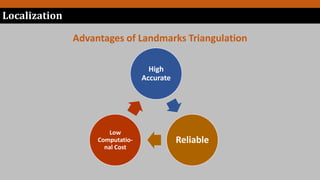
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) allows a robot to build a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of its own location within that environment. This addresses the "chicken-and-egg" problem of a robot needing to know its location to map an environment but also needing a map to determine its location. The document discusses SLAM, localization techniques including landmark triangulation and fingerprinting, and mapping techniques including topological and metric mapping.