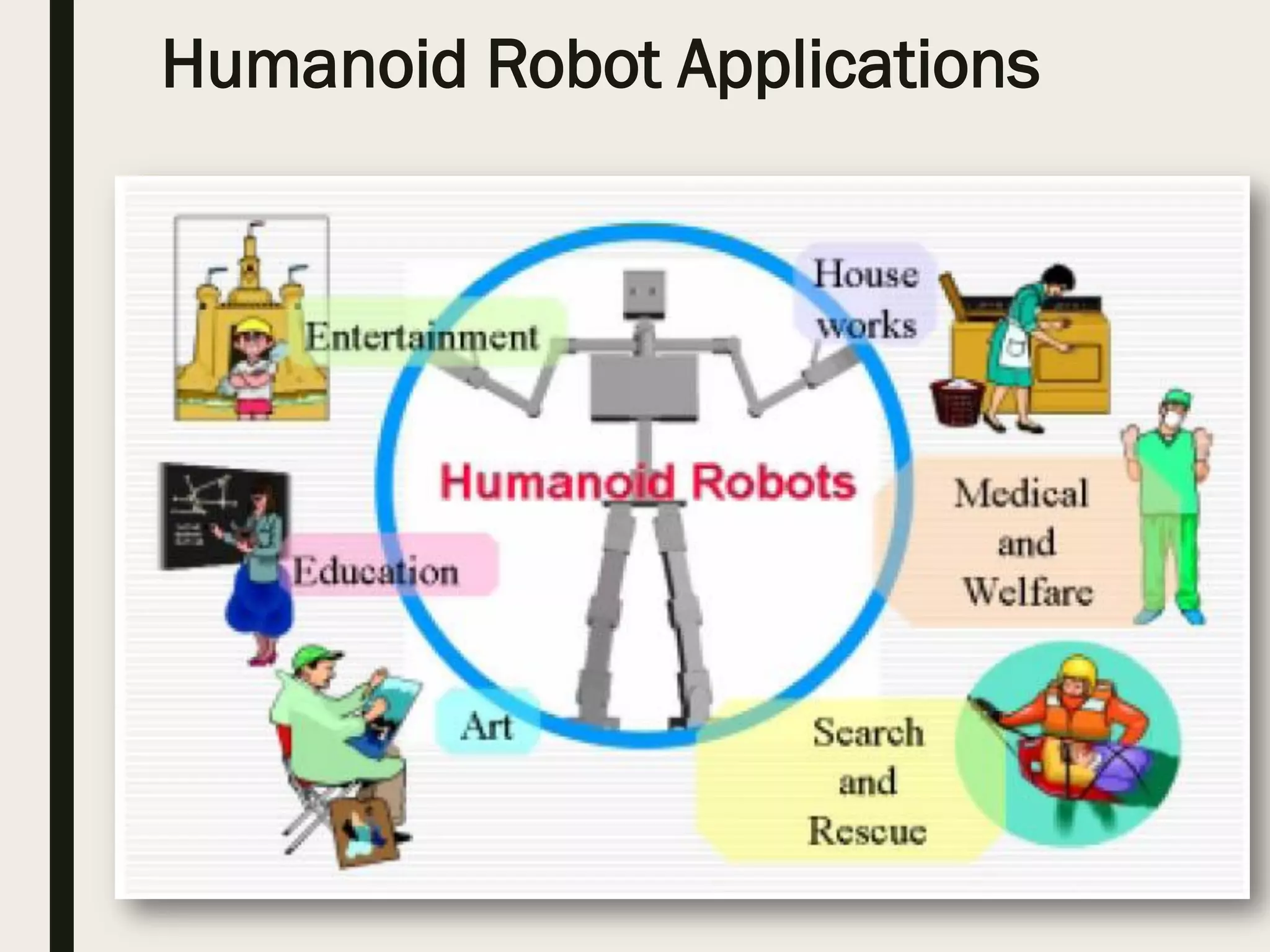
This document discusses humanoid robots, including their history, composition, types, and applications. It focuses on simulating a humanoid robot in a 3D environment and forming a control system using PID and fuzzy control. PID control aims to minimize error using proportional, integral, and derivative gains. Fuzzy control maps sensor inputs, processes results, and outputs conversions. Together, PID and fuzzy control allow the robot to maintain error/speed and position itself parallel to objects. Potential applications of humanoid robots include safe load carrying and cooperative object movement.