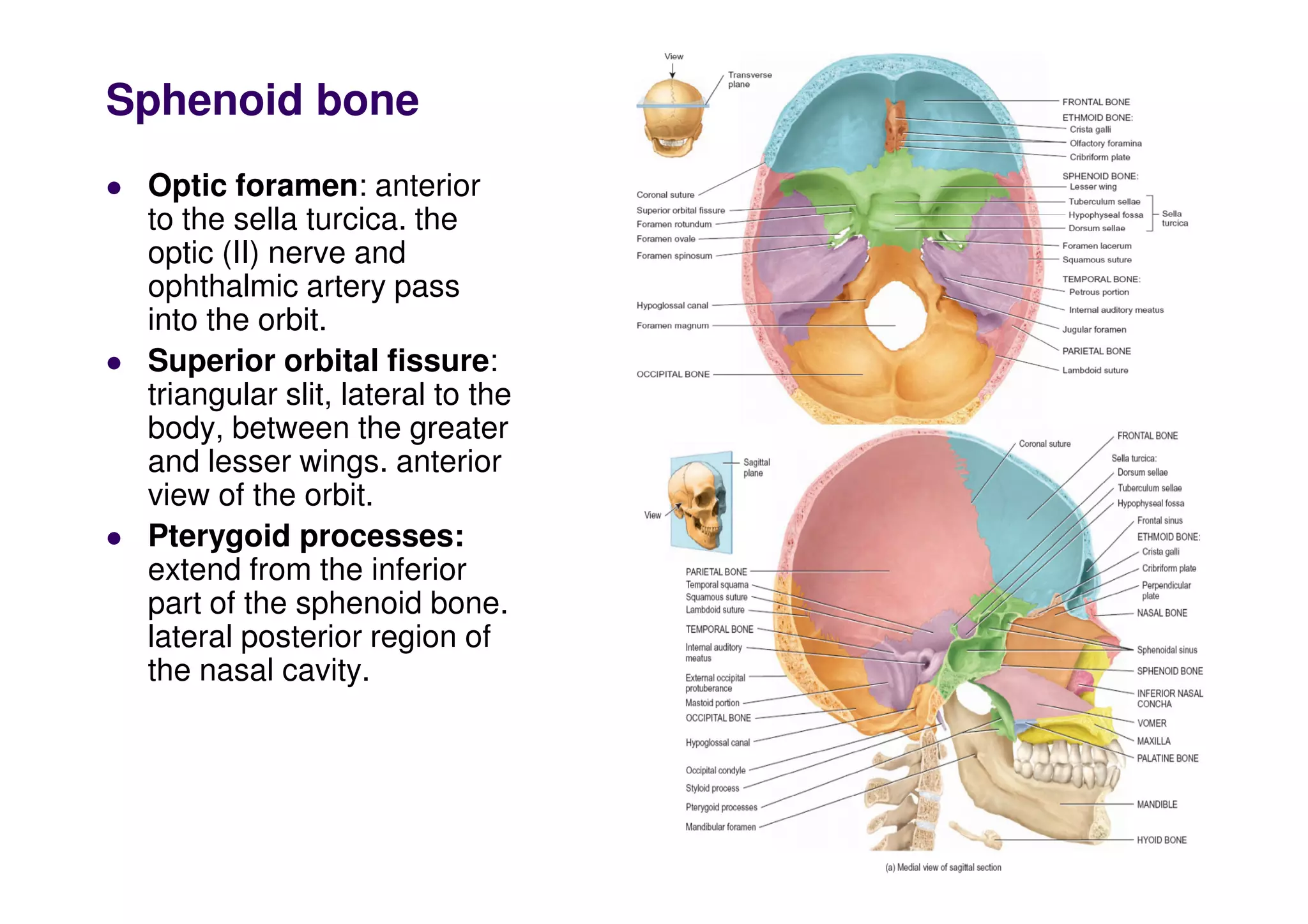
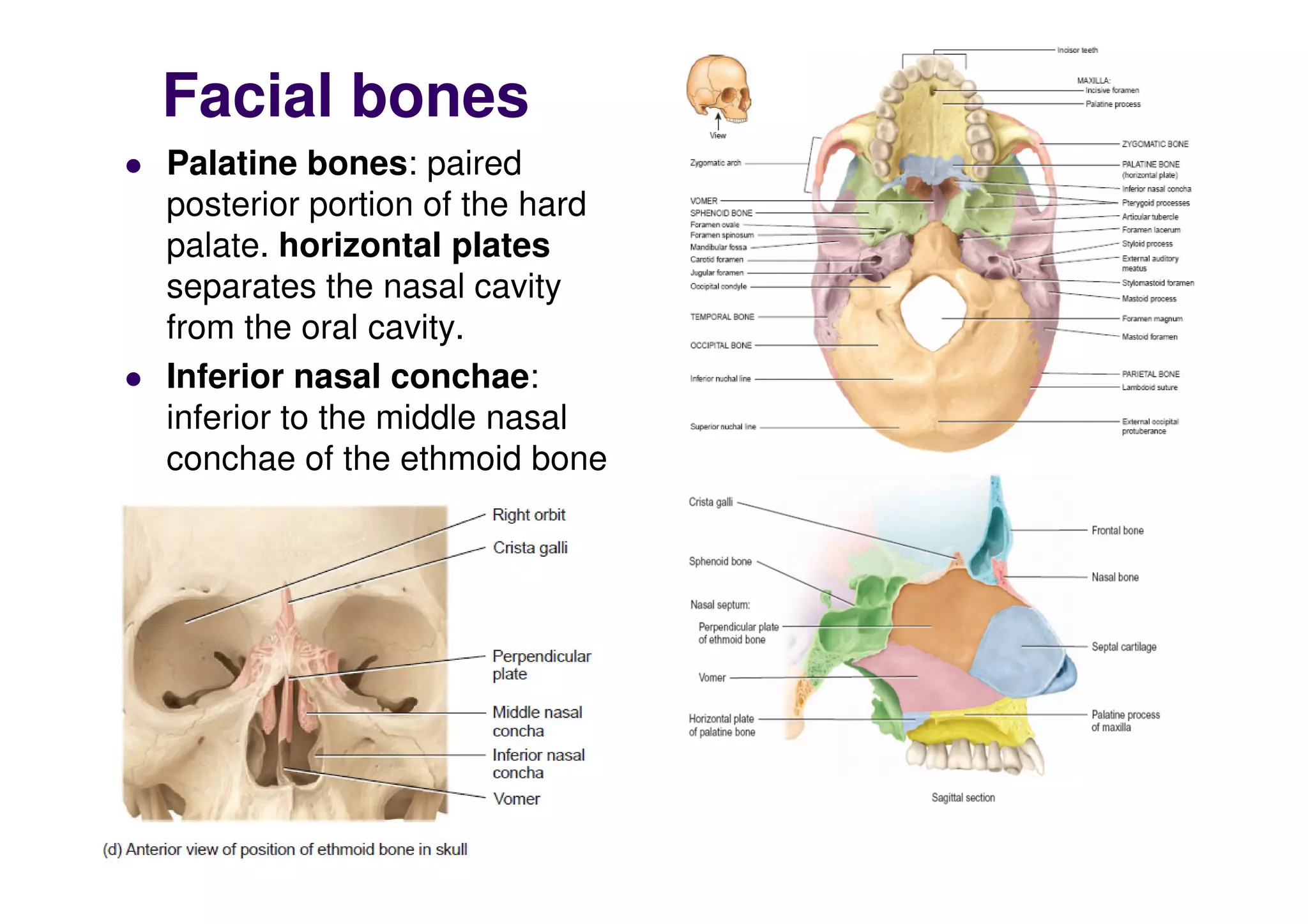
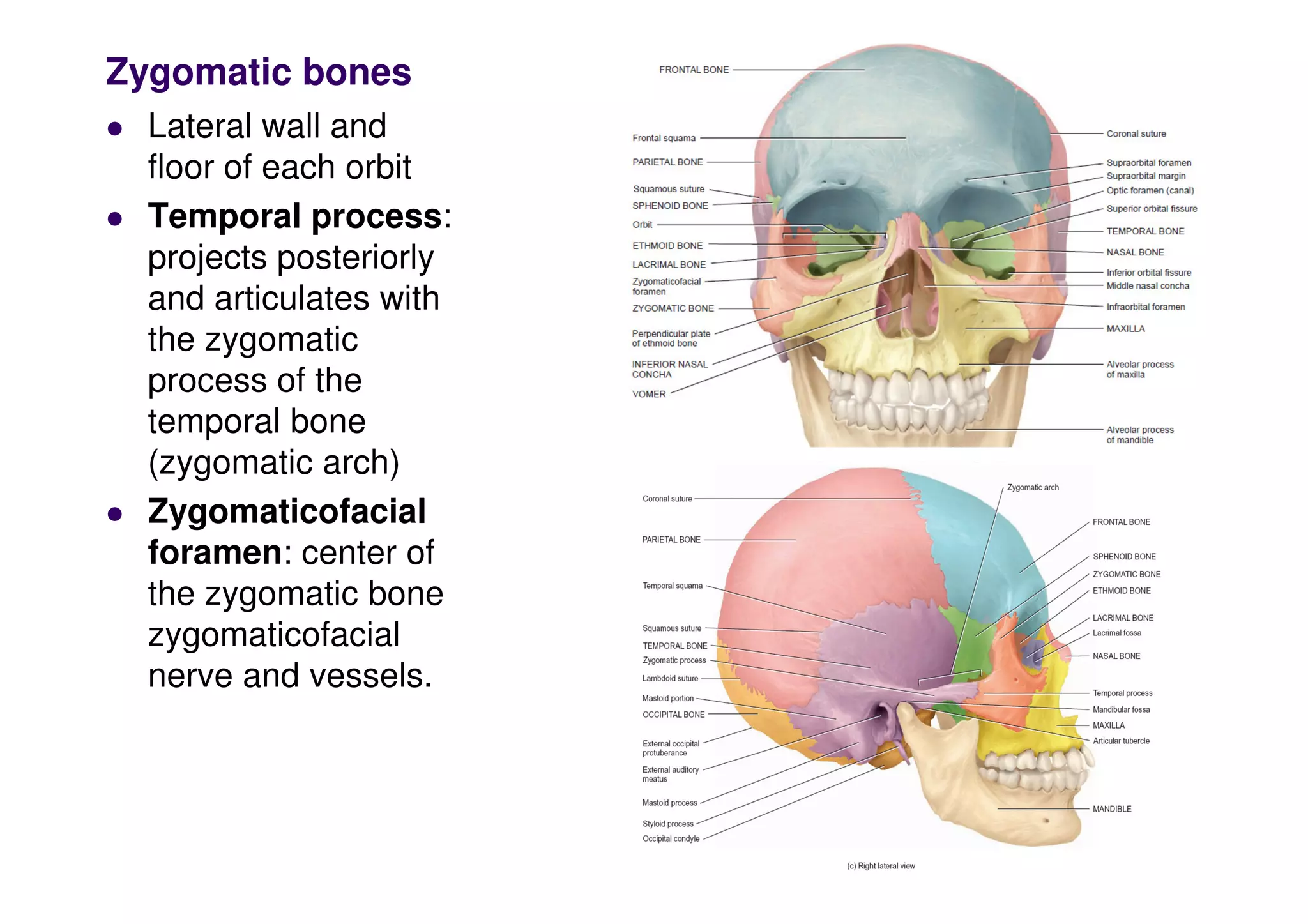
The sphenoid bone contains several important foramina and processes including the optic foramen, superior orbital fissure, pterygoid processes, foramen rotundum, foramen ovale, foramen spinosum and foramen lacerum. The ethmoid bone forms parts of the cranial floor, orbits and nasal septum including the lateral masses, perpendicular and cribriform plates. The facial bones include the nasal, lacrimal, palatine, vomer, maxillae, zygomatic and mandible bones which form parts of the face, orbits, nasal cavity and palate.