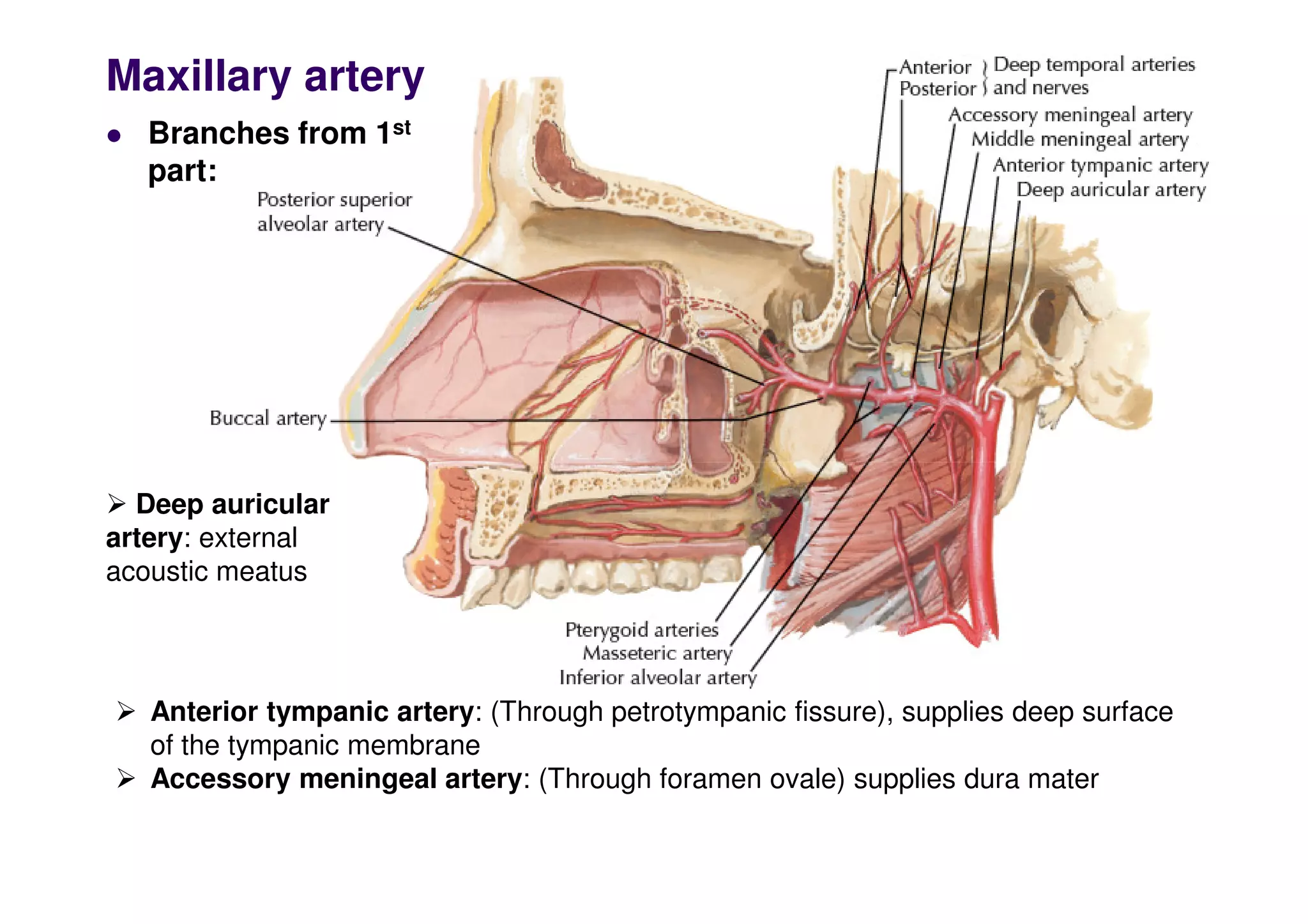
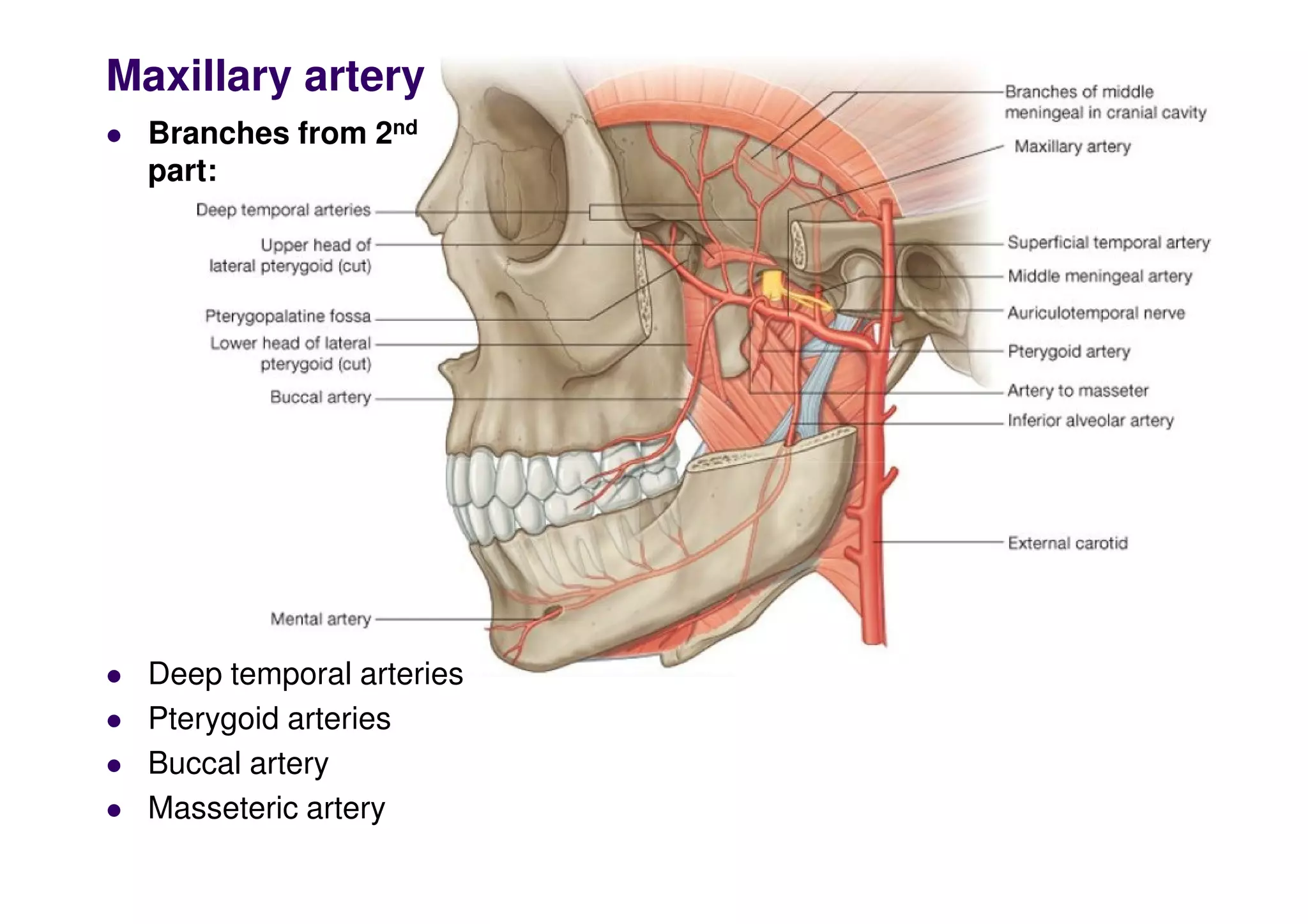
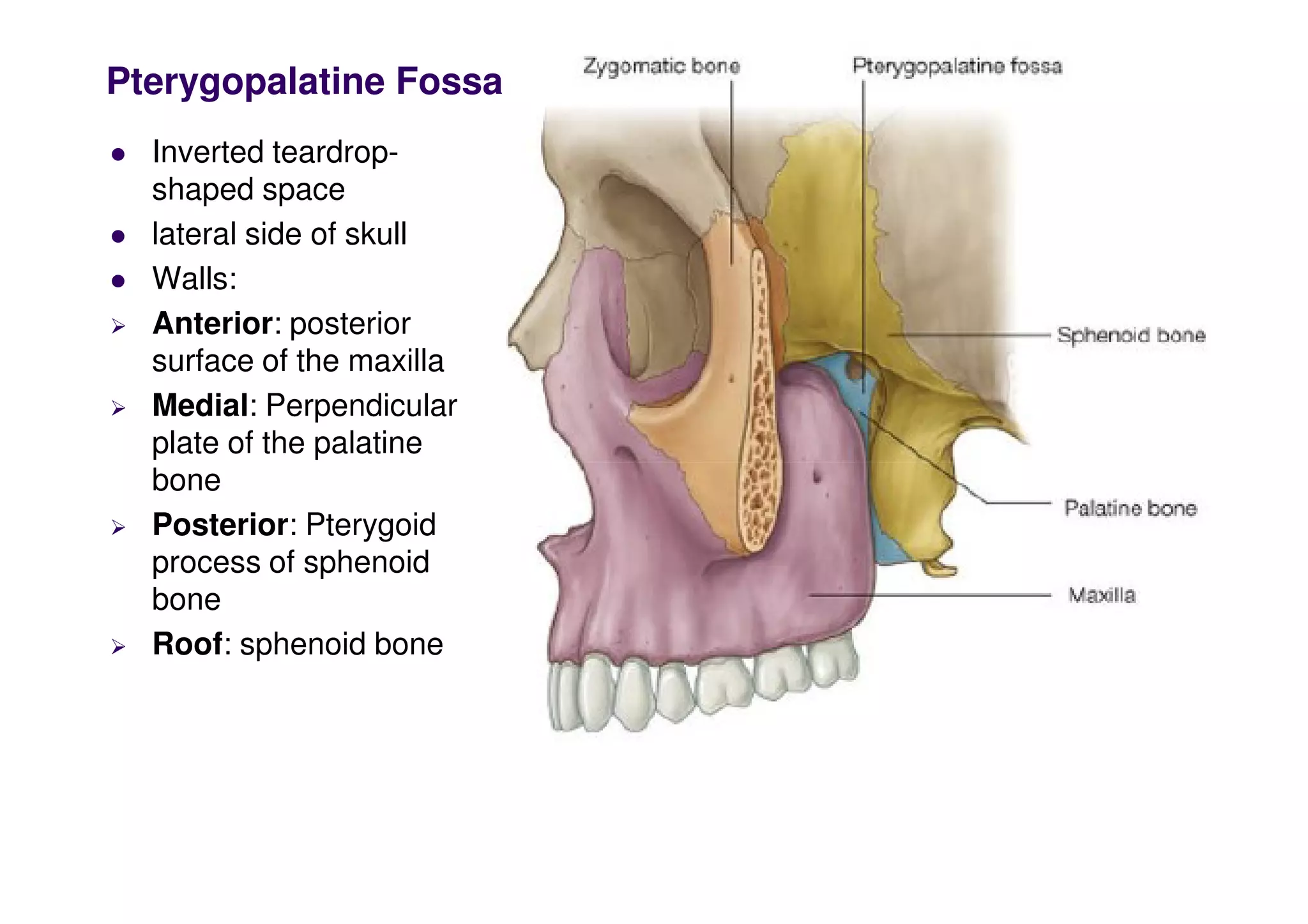
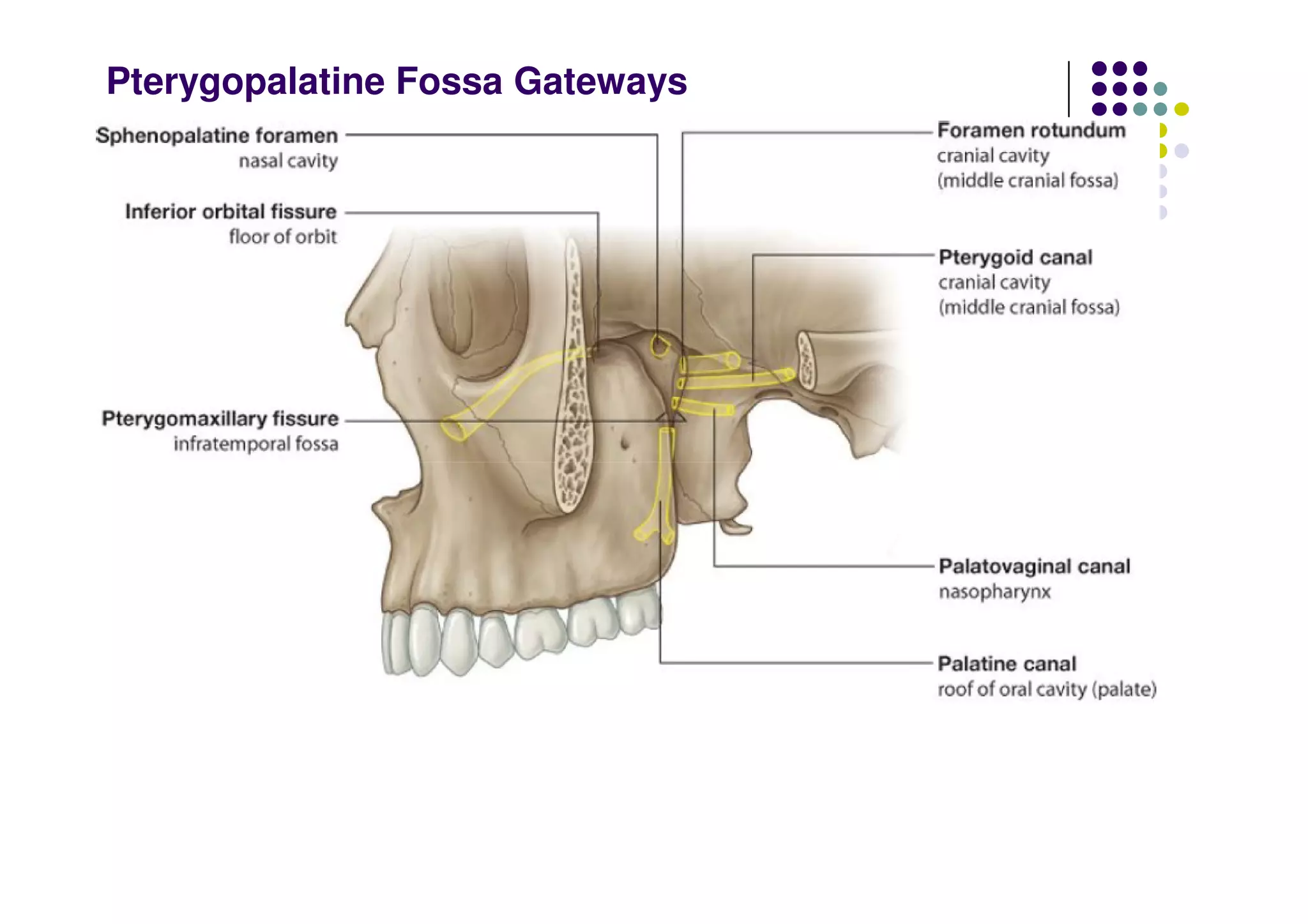
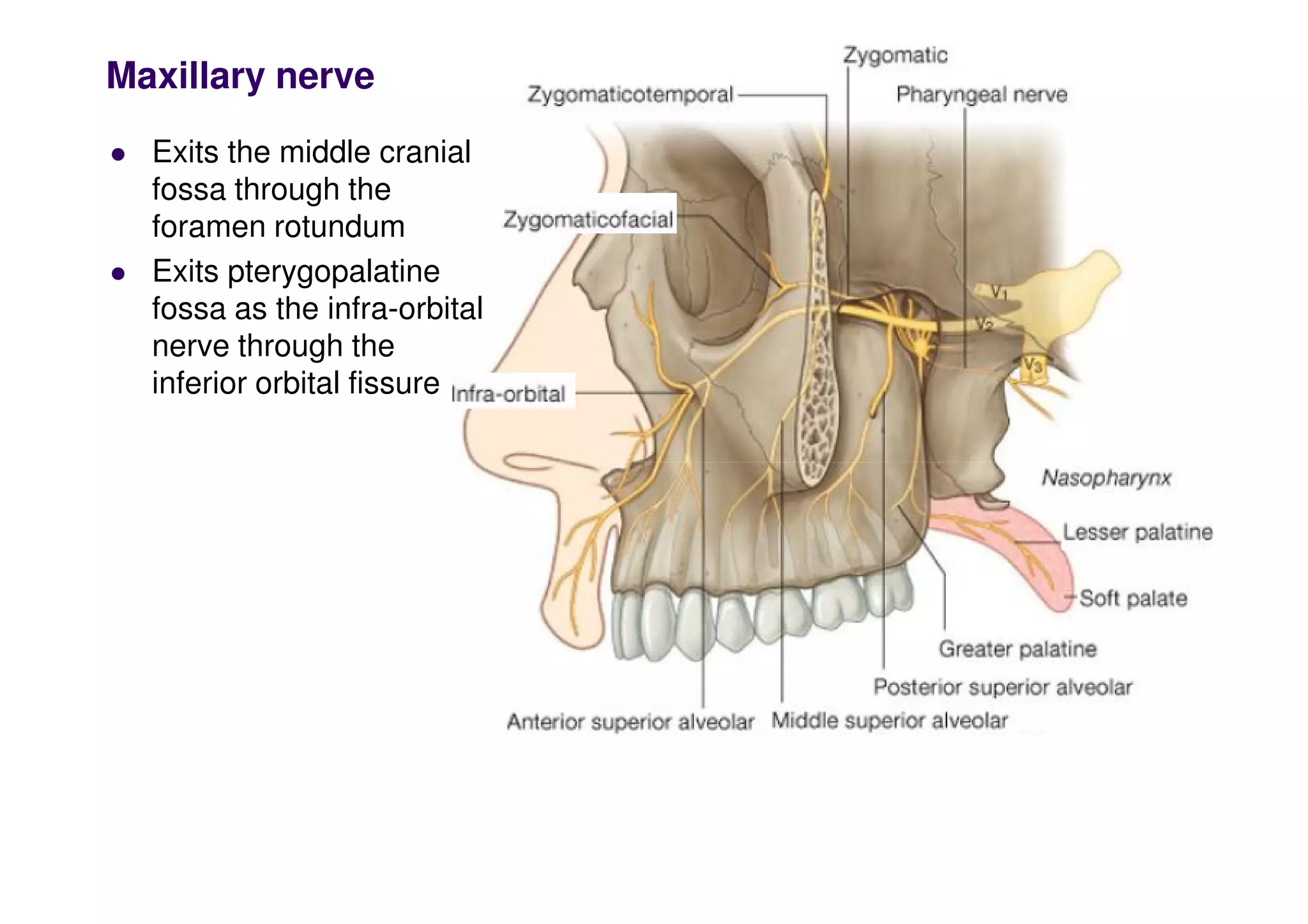
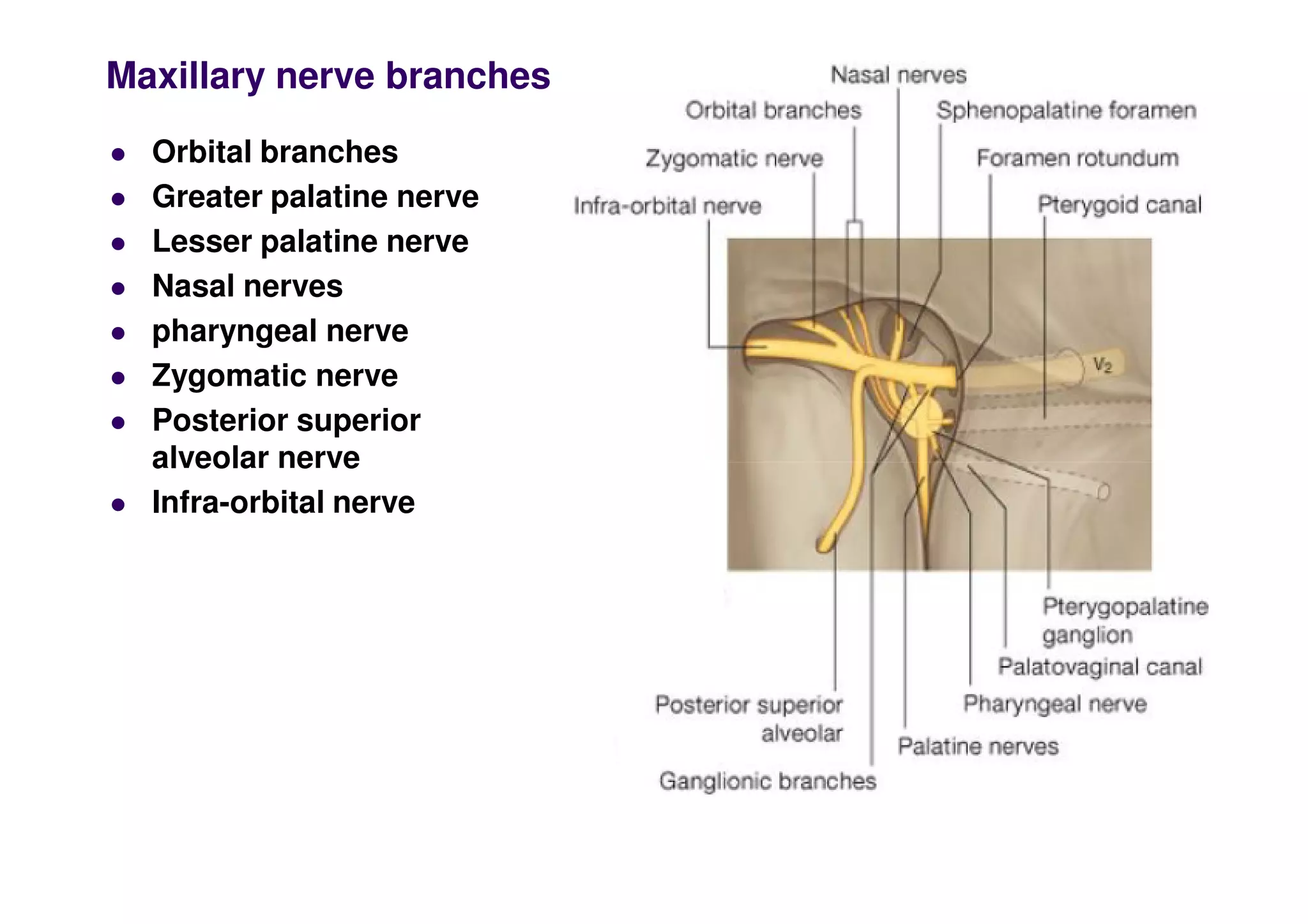
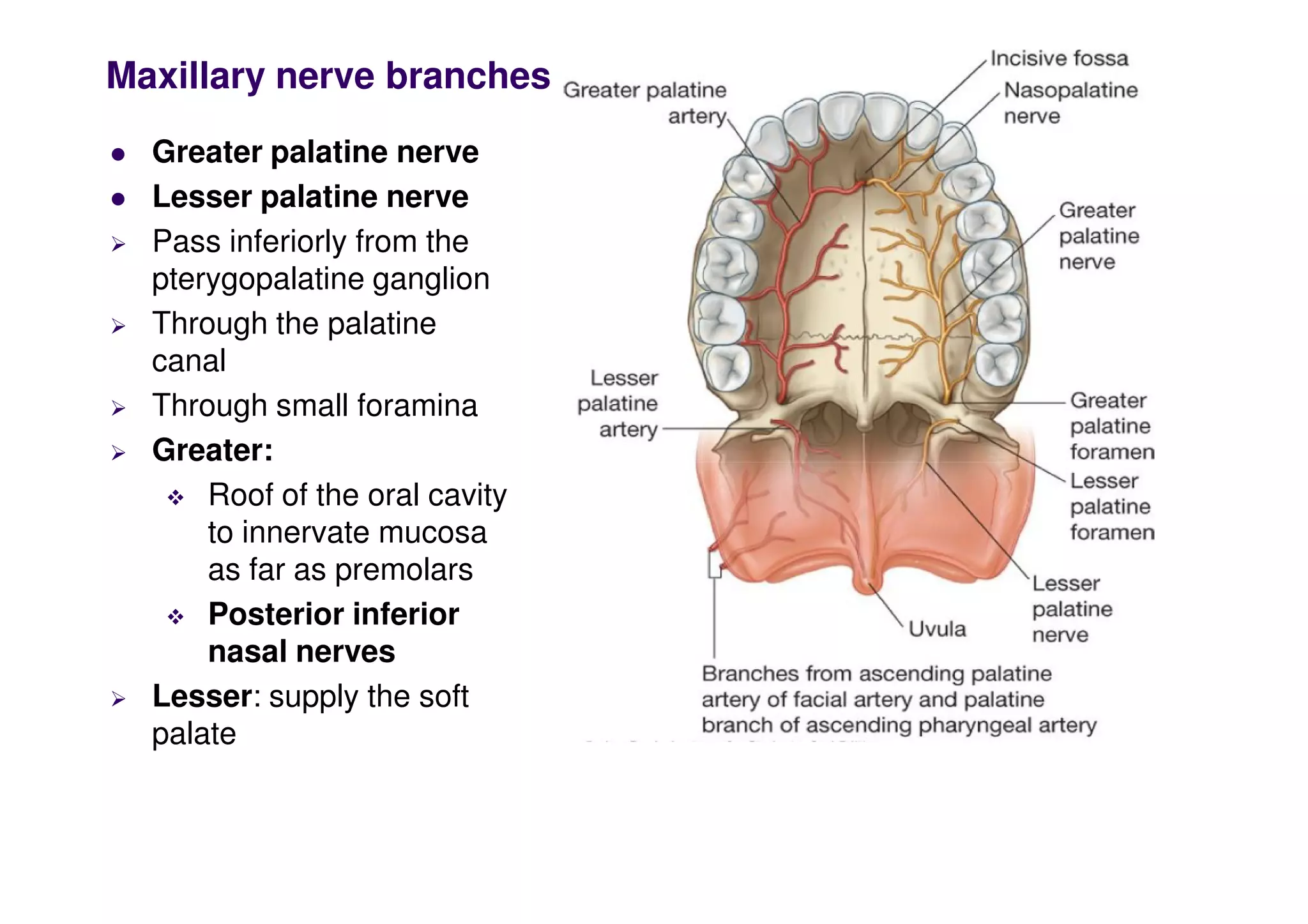
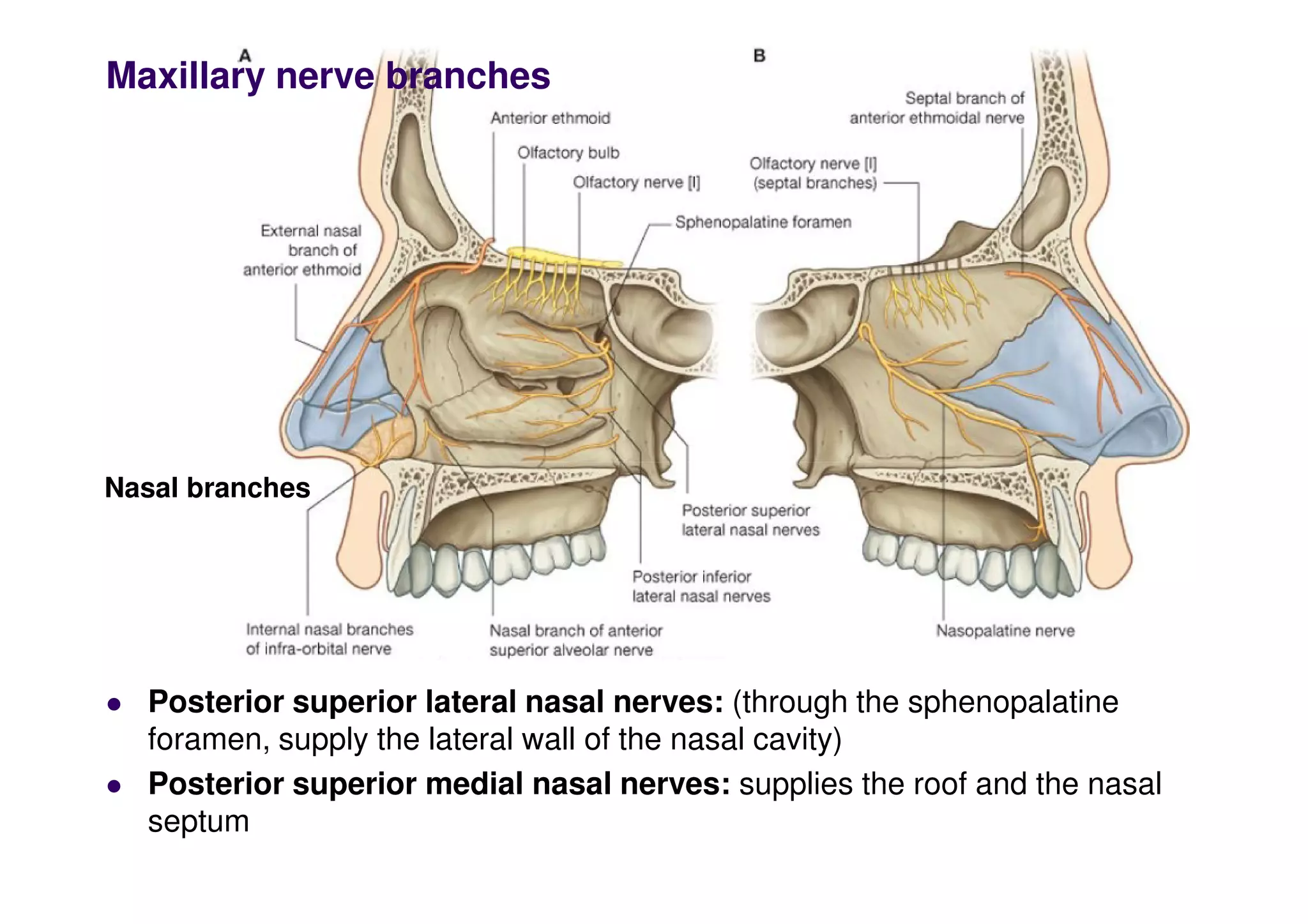
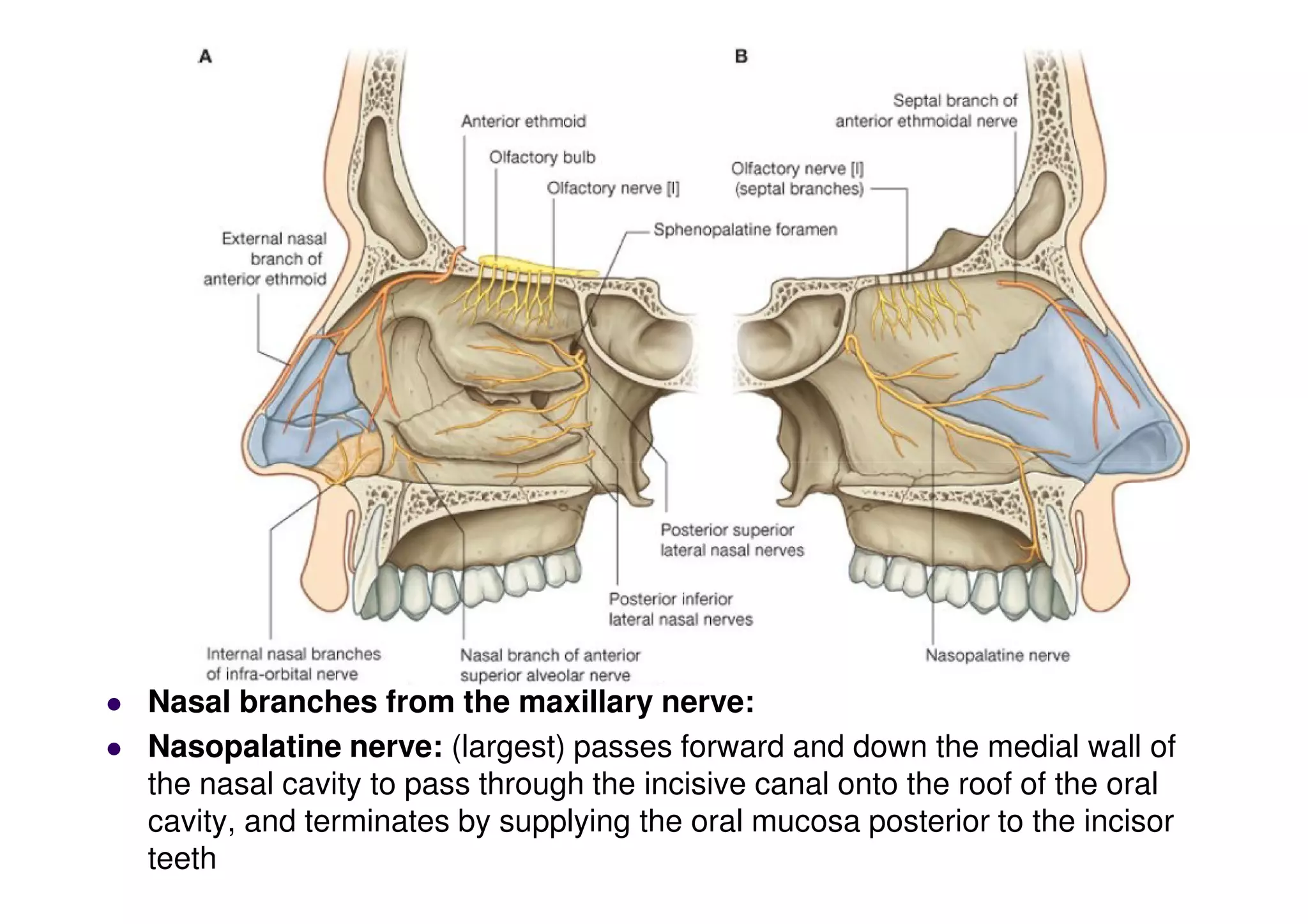
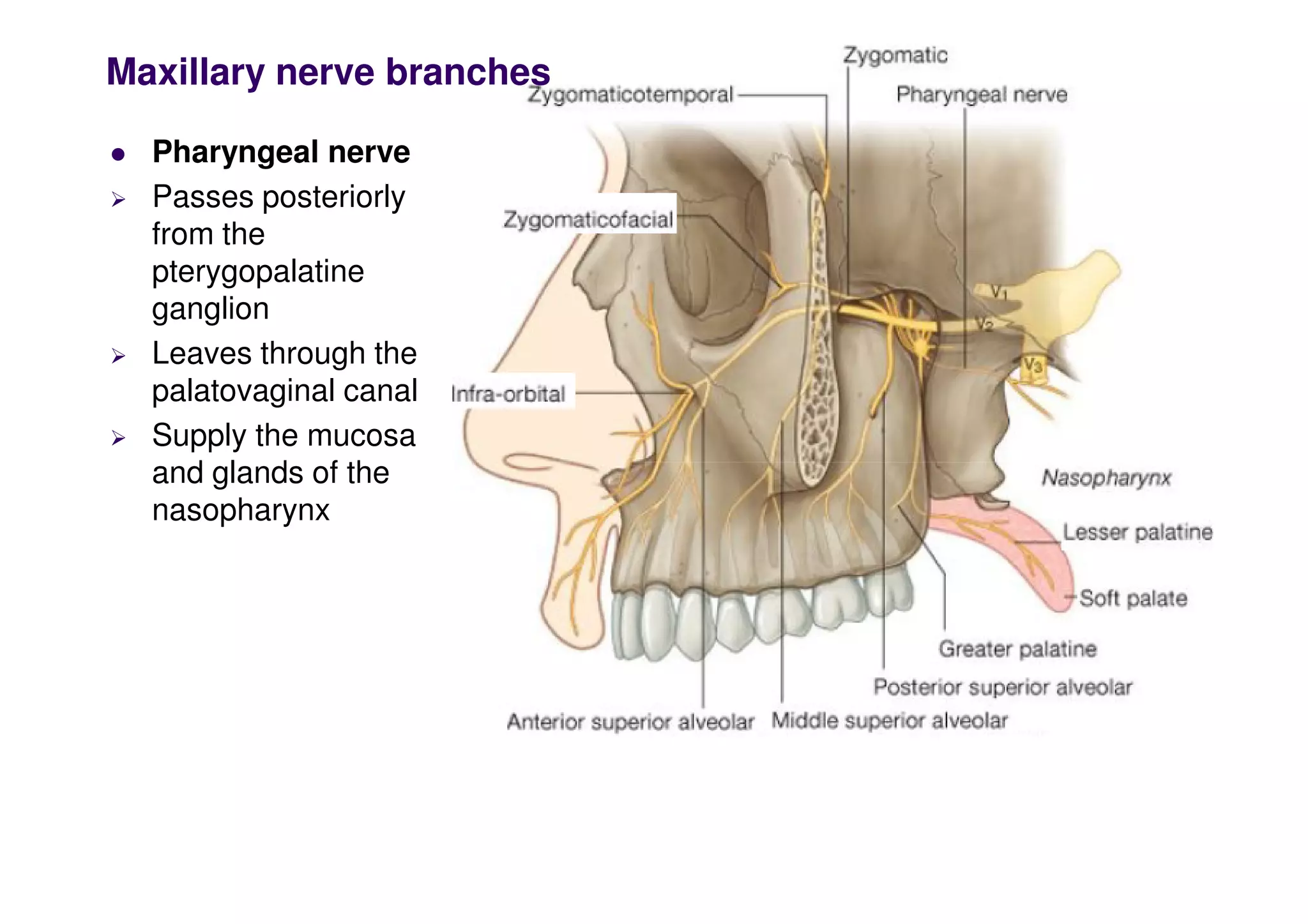
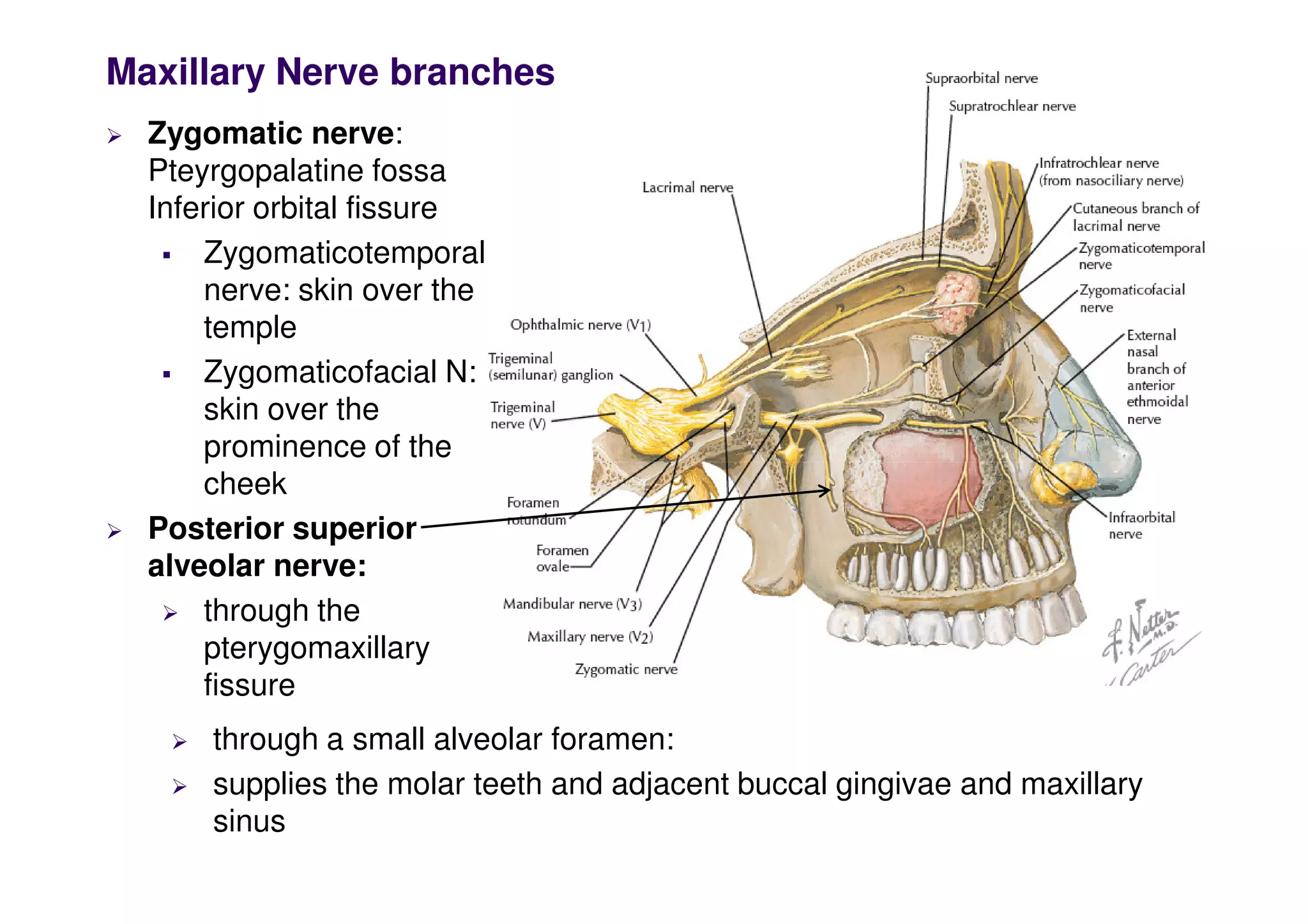
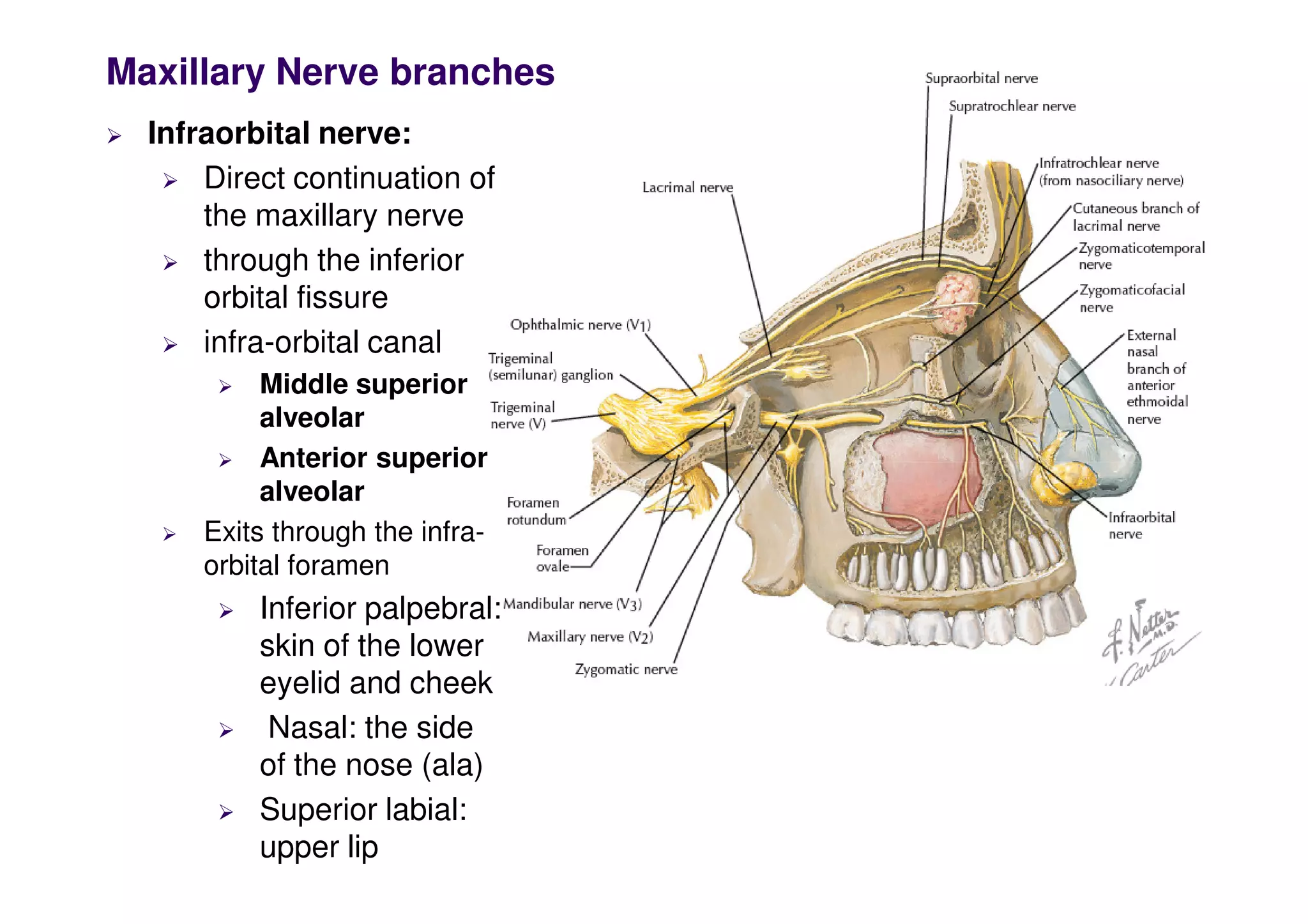
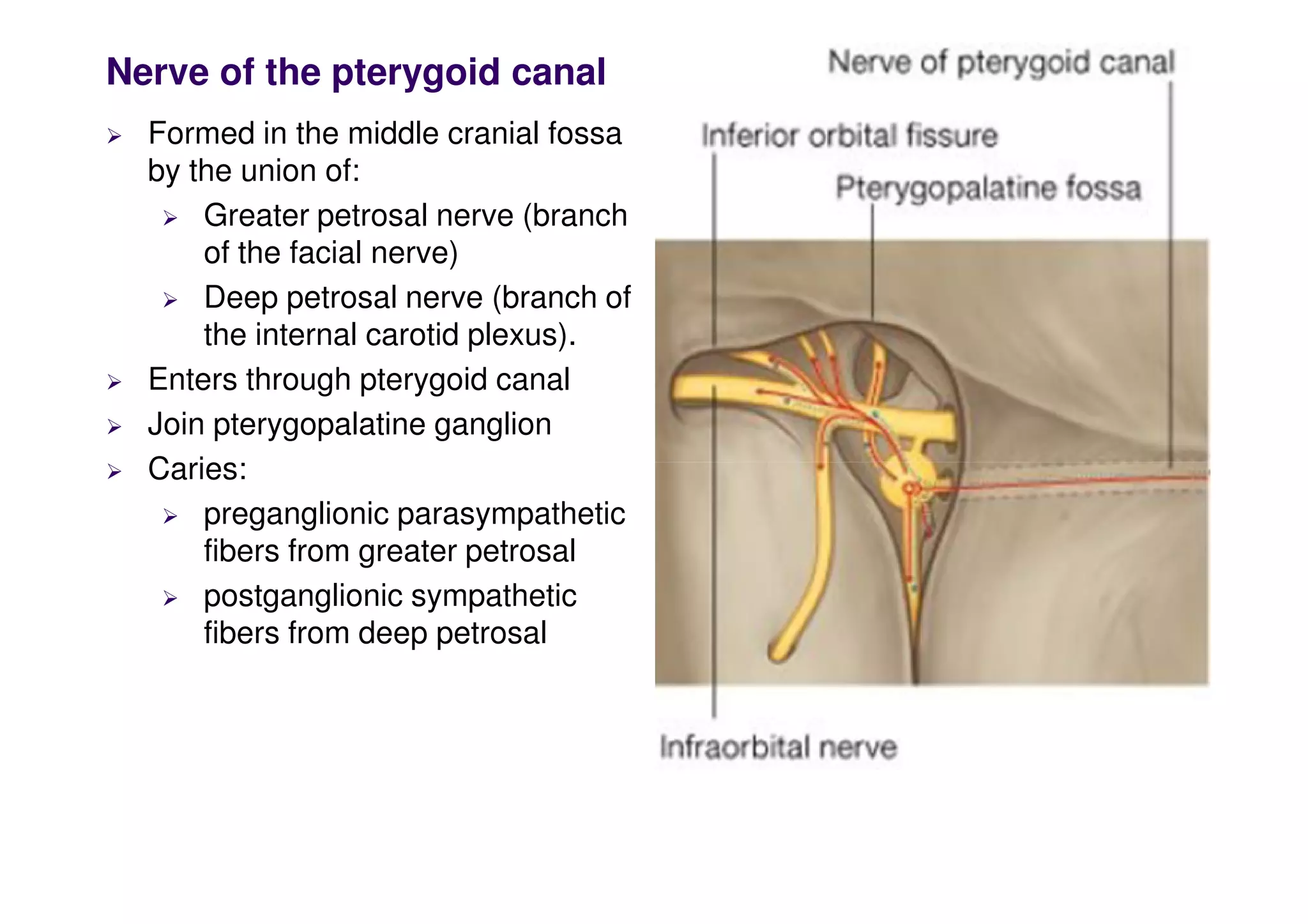
The maxillary artery branches within the pterygopalatine fossa, a teardrop-shaped space within the skull. It gives off the deep temporal, pterygoid, buccal, and masseteric arteries. The maxillary nerve exits the pterygopalatine fossa through the inferior orbital fissure, branching to innervate structures like the nasal cavity, palate, pharynx and upper lip. Its branches include the infraorbital nerve, which exits the face through the infraorbital foramen, supplying surrounding structures. The nerve of the pterygoid canal forms in the skull and enters the pterygopalatine ganglion, carrying pregangl