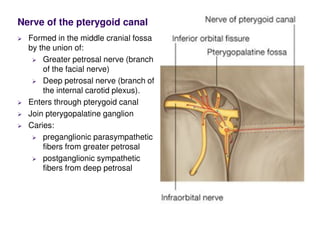
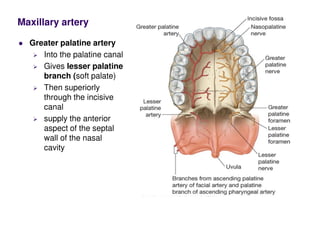
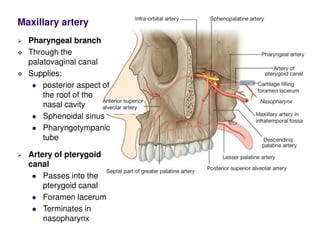
The nerve of the pterygoid canal is formed by the union of the greater petrosal nerve, a branch of the facial nerve, and the deep petrosal nerve, a branch of the internal carotid plexus. These nerves enter the pterygoid canal and join the pterygopalatine ganglion. The ganglion provides parasympathetic fibers from the greater petrosal nerve and sympathetic fibers from the deep petrosal nerve. Branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion join the maxillary nerve and are distributed to structures like the lacrimal gland.