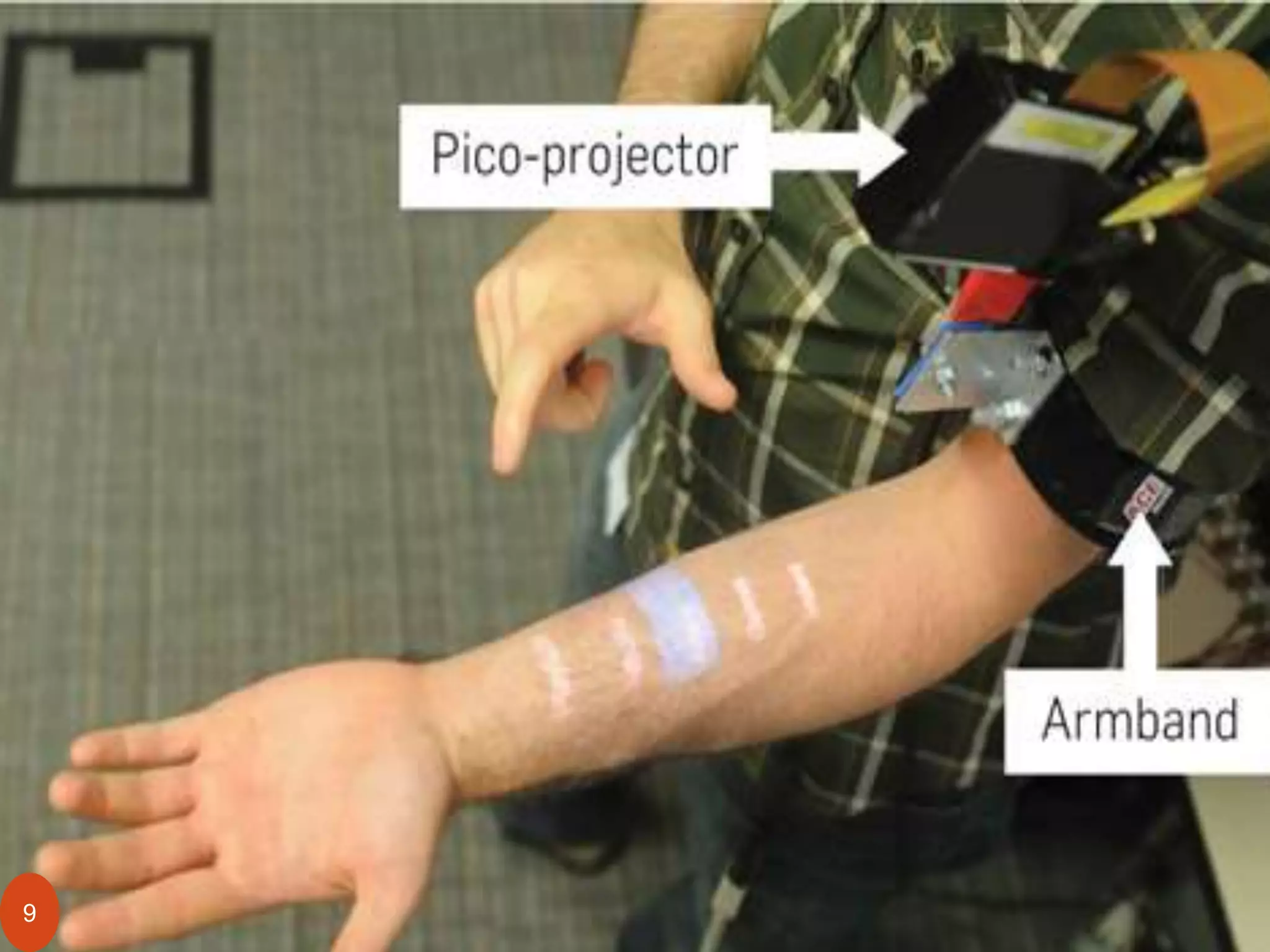
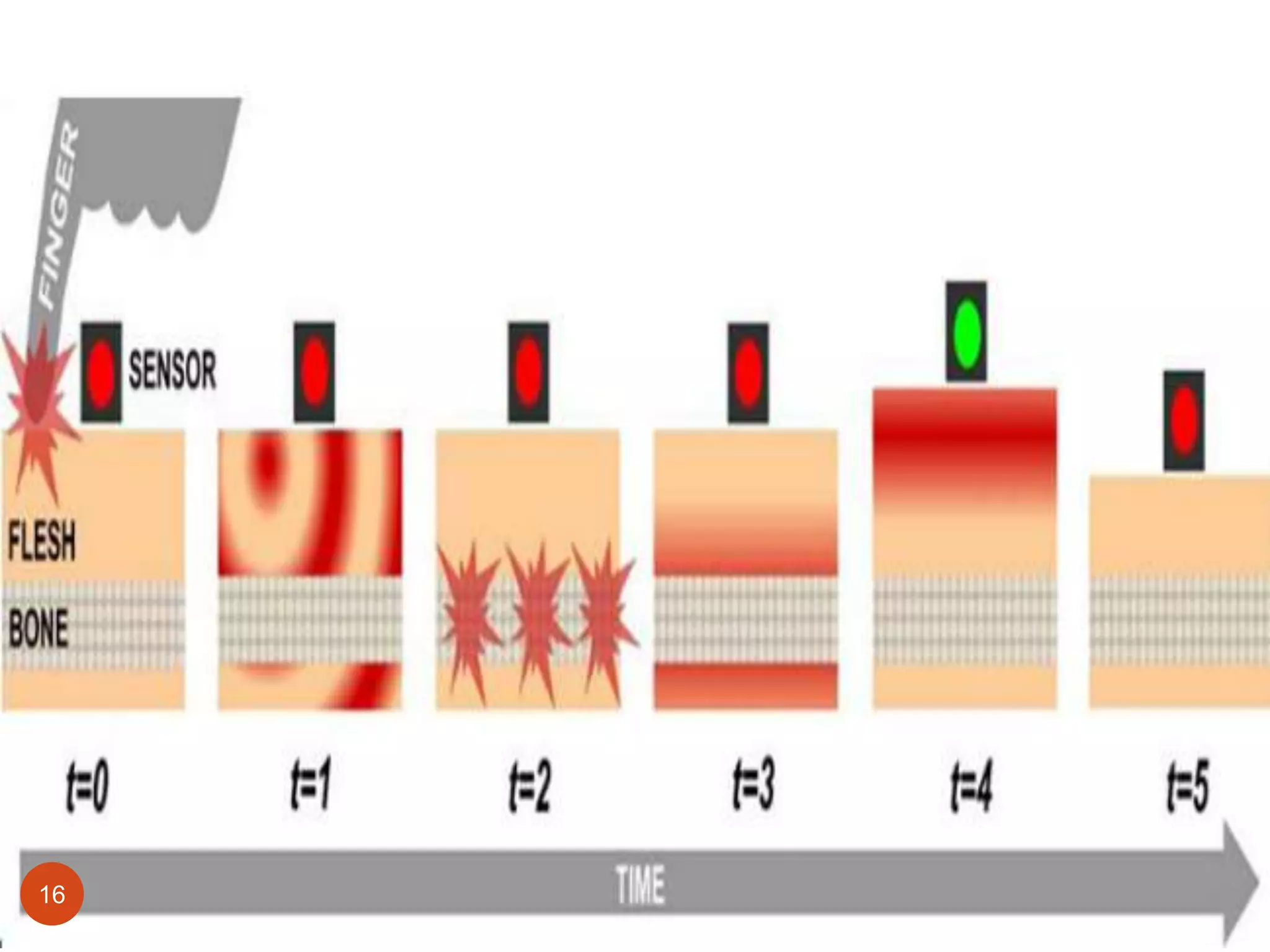
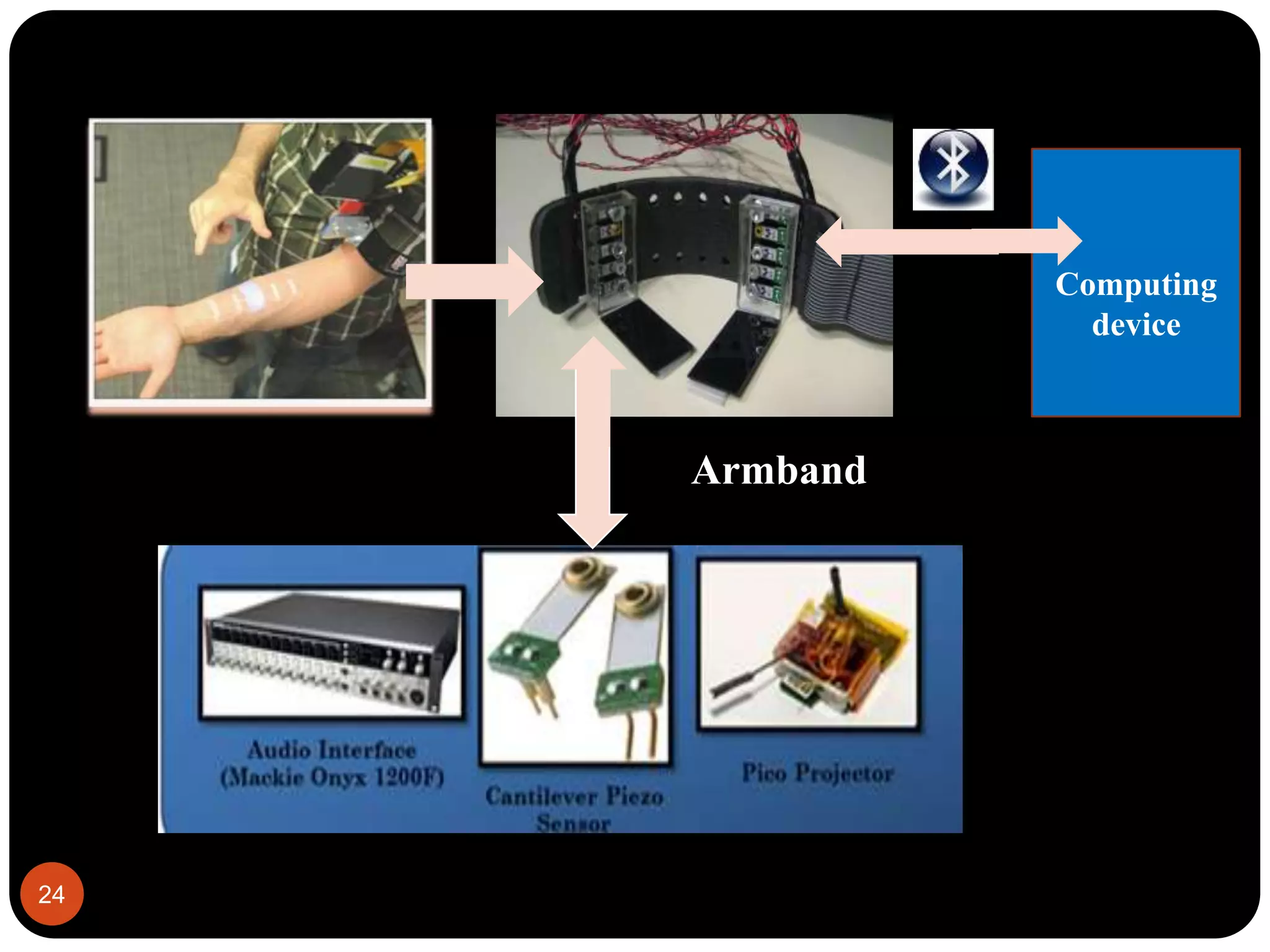
Skinput is a new input technology developed by Microsoft that uses the human body as an input surface. It involves wearing an armband that detects vibrations on the skin from finger taps. This allows a user to control devices by tapping on their arm to browse menus, make calls, or control music players. The armband contains sensors that detect transverse and longitudinal acoustic waves generated by taps. It is a non-invasive way to interact with devices using the body's large interaction area. Skinput has applications for mobile devices, gaming, and assisting disabled individuals. While innovative, it faces challenges related to size, cost, and potential health effects that need further research.