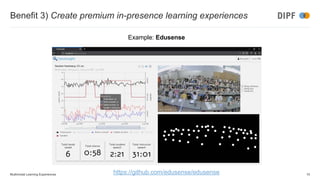
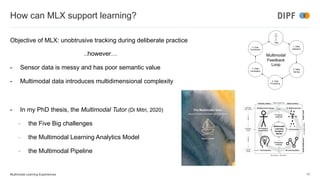
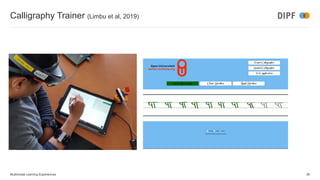
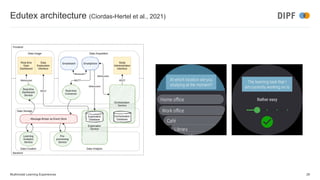
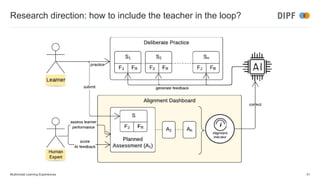
The keynote discusses the integration of artificial intelligence and multimodal learning experiences in online education, emphasizing the need for authentic practice and the role of context in learning. It presents the benefits of multimodal learning, including richer online experiences and enhanced psychomotor skill acquisition but also highlights potential risks such as privacy concerns and social inequalities. The speaker concludes that while multimodal learning can significantly improve educational outcomes, further research is required to address associated challenges.